Contents
- 1 Health properties of nuts
- 2 MAIN NUTS AND THEIR BENEFITS
- 2.1 Almonds: rich in protein and minerals
- 2.2 Hazelnuts are rich in fiber and omega 9
- 2.3 Walnuts, the richest in omega 3
- 2.4 Coconuts, full of energy and minerals
- 2.5 Brazil nuts, the richest in selenium
- 2.6 What is the richest nut in fat?
- 2.7 Pecans are very rich in flavonoids and other antioxidants
- 2.8 Cashews are high in carbohydrates
- 2.9 Peanuts are rich in protein, folic acid and isoflavones
- 2.10 Chestnuts are rich in carbohydrates but low in fat and protein
- 2.11 Pistachios are rich in protein and phytosterols
Health properties of nuts
WHICH NUT IS BEST?
What is a nut?
From a botanical point of view, strictly speaking, a nut is a indehiscent dry fruit formed by a single seed surrounded by a hard protection. Hazelnuts, chestnuts and acorns are real nuts
For a fruit to be considered a nut it must not self-open when ripe. That is to say, it must be indehiscent.
From an edible point of view, it is considered a nut any type of edible seed, non-cereal, surrounded by a crust or hard layer.
Thus, for example, almonds, pecans, pistachios, walnuts or Brazil nuts are considered nuts, although they are not real nuts, botanically speaking.
Which are real nuts?
Among the most important real nuts, we have the following?

Hazelnuts are real nuts
Which are not real nuts?

Botanically speaking, almonds are not real nuts
Some fruits are dietetically considered nuts, although they are not botanically nuts. Among them, we have the following:
- A Brazil nut is the dry seed of a nutshaped capsul that produces the tree of the same name.
- A coconut is a drupe with fibrous “meat” produced by a palm tree. What we eat the white “meat” actually is the endosperm or the food reserve of the seed.
- A macadamia nut is actually the seed a follicle fruit that produce the trees of the same name. Inside this fruit they are a couple of seeds with a hard shell.
- Almonds are the seeds not the fruits. In fact, they produce a fleshy fruit (drupe), whose fleshy outer parts become dry in time.
- A walnut, like an almond, is the seeds of a drupe.
- A pistachio is the seed of a drupe.
- A pecan or pecan nut is also a drupe
- A peanut is the seed of a legume (Papilionaceae)
- A cashew is the fruit of a false fruit
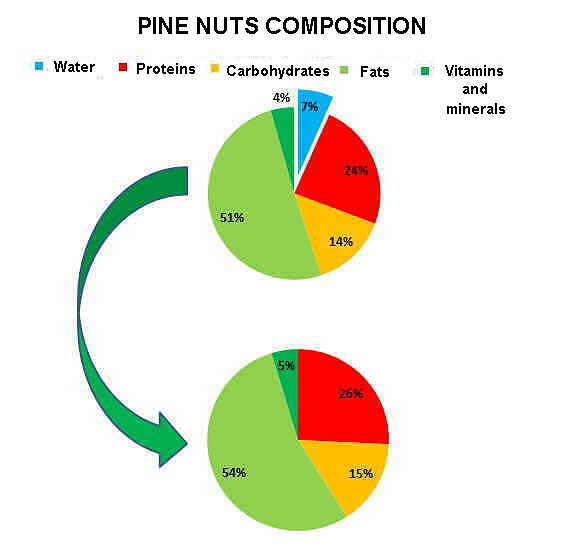
- A pine nut is the seed of a pine tree.
MAIN NUTS AND THEIR BENEFITS
Almonds: rich in protein and minerals
This is one of the richest nuts in protein, high percentage of essential amino acids.. Almonds are an ideal complement for vegetarian diets, diets for athletes, the stages of child development and states of decay and tiredness.
In addition they provide healthy fats, especially omega 9. Scientific studies have shown that consumption of almonds helps reduce cholesterol, prevent stones in the gallbladder and Alzheimer’s.
Hazelnuts are rich in fiber and omega 9
They are especially recommended for people with heart disease and obesity, as they are also rich in insoluble fiber (nearly 10% of its composition), with cholesterol lowering properties and to satisfy hunger.
Hazelnuts are rich in potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, but they also contain calcium and iron.
Walnuts, the richest in omega 3

Walnuts are considered very important nutritive nuts because their content in omega 3
Walnuts have received a very important role in nutrition, because they have an extraordinary content of essential omega-3 fats.
The omega 3 is an essential fat, with properties against cardiovascular disease, cancer and anti-inflammatory properties that can help treat menstrual pain and arthritic or joint pain.
No less important is its content in omega 6. Omega 6 fats are also essential and are found in nuts. They have similar anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3.
In recent years there has been given little importance to these omega 6 fats due to the high consumption of seed oils (sunflower oil, sesame oil, etc.), from whom excessive consumption is done through fried and industrial products.
However, both omega-6 fats and omega-3 fats are necessary for the body and have to be found in food, preferably in the form of nuts, and in moderation, through vegetable oils.
Walnuts are recommended for people people with obesity, because a study showed that daily consumption of one serving of these foods for a year, reduced waist circumference of the people involved.
Walnuts also provide high doses of folic acid, an essential vitamin during pregnancy. Also taking walnuts after delivery can improve postpartum depression because it can be caused by a deficiency of omega 3 fats (DHA type).
Coconuts, full of energy and minerals

Coconut
It contains simple and complex carbohydrates (15g./100g.), The first ones provide energy immediately and long term carbohydrates will provide more prolonged energy. Both of them being very suitable for long workouts and endurance tests.
Coconut pulp is considered the fruit of the athletes. Also suitable for the stomach (gastritis, heartburn, gastric ulcer)
Coconut water is very refreshing, low in sugars, fats and high in minerals. Very good for hypertension, heart diseases and diabetes.
Coconut fatty products should be eaten in moderation, because coconut contains saturated fats, that can cause increased triglycerides.
Brazil nuts, the richest in selenium

Brazil nuts
Brazil nuts have enormous potential as an antioxidant food. They are the dried fruit with more selenium content, much higher than any other food, animal or plant.
Selenium is part of glutathione peroxidase enzyme, an antioxidant system which counteracts the formation of free radicals in the body, improve immune function and prevents premature aging. It has been observed that vegetables grown in soils rich in selenium provide people with lower incidence of cancer.
Eating foods rich in selenium stimulates the antioxidant activity of glutathione peroxidase. This antioxidant function of Brazil nuts is enhanced further by vitamin E.
We can benefit from the properties of food nuts introducing them periodically, but in moderate amounts of 2-5 Brazil nuts daily.
Brazil nuts are recommended in those cases where one has to increase dietary antioxidants: smokers, cleansing diets, chemical poisoning; and those affectations in which increased vitamin E and antioxidants is recommended: arthritis, fibromyalgia, diet for Parkinson’s disease, psoriasis, lupus, Alzheimer’s, etc.
What is the richest nut in fat?

Macadamia nuts
Macadamia nuts are the richest nut in fat, exceeding 75% of its content. Mainly it contains omega 9 (oleic acid and palmitoleic acid).
Macadamia nuts come from a slow-growing tree that can take up to 10 years to be productive, so they are much more expensive than other nuts. We must emphasize its refined taste, reminiscent of coconut and creamy texture.
It is a high-energizing food, ideal for people who has a lot of activity and for sports. In moderation, they can help lower cholesterol because of its oleic acid content. In one study, it was found that moderate consumption of macadamia may lower triglycerides.
Pecans are very rich in flavonoids and other antioxidants

Pecan nuts
Pecan nuts are rich in catechins, pro-vitamin E, selenium and zinc; all of them, antioxidant components.
They are very rich in fat (70% of its composition), mainly contains oleic acid (Omega 9) and, to a lesser extent linoleic acid (Omega 6). However, this high fat content is balanced with healthy fiber content.
Because of its very low sodium content, its contribution in potassium and trace elements, they are recommended for people with high cholesterol, hypertension, diabetes, fluid retention, edema, low-sodium diets or problems of blood circulation.
Cashews are high in carbohydrates

Cashews
Cashews are high in protein and carbohydrates, so, they can be taken in diets that require an input of energy and important amino acids, as in states of stress or students.
Compared to other nuts, cashews are low in fat (40%).
Cashew nuts are very nutritious because they provide a good dose of magnesium, iron and vitamin E. In contrast, they are poor in calcium.
Peanuts are rich in protein, folic acid and isoflavones

Peanuts
Peanuts are very rich vegetable fat, because peanuts come from a leguminous plant.
Like other legumes, peanuts are rich in protein, omega 6 and fiber.
Peanuts are the richest nuts in folic acid and isoflavones. Folic acid prevents heart disease because it regulates blood homocysteine levels. Isoflavones (genistein and daidzein) are plant components that help treat hot flashes and menopause, as well as help reduce cholesterol.
Chestnuts are rich in carbohydrates but low in fat and protein

Chestnuts
Chestnuts are very rich in carbohydrates (40% of its composition), but low in fat (2%) and protein (2%). Unlike other nuts, they do not contain minerals as magnesium or calcium, which are in low doses in this food.
It is a nutritious fruit, rich in easily digestible carbohydrates and demulcent properties, which protects irritated stomach (gastritis) and provides lasting energy throughout the day.
Chestnuts are recommended on any balanced diet, and especially for gastritis cases, either for breakfast or snack for children and students.
Pistachios are rich in protein and phytosterols

Pistachios
Pistachios are rich in protein, fiber, potassium, and they are the nut with the highest content of phytosterols.
Compared with other oleaginous nuts, its composition is low in fat (containing 40% fat, compared to 60-70% of other nuts).
Pistachios are recommended to lower cholesterol because they contain lots of fiber (10%) and phytosterols, especially beta-sitosterol.
Phytosterols are plant components, much like the animal cholesterol, that, once in the intestine, prevents the dietary cholesterol to be absorbed.
![]() More information on nuts.
More information on nuts.