Contents
- 1 Characteristics and properties of lecithin or phospholipids
- 1.1 What is lecithin or phospholipids?
- 1.2 What does lecithin (phospholipid) contain?
- 1.3 Nutritional composition of lecithin or phospholipids
- 1.4 Chemical structure of lecithin
- 1.5 What is lecithin called chemically?
- 1.6 What are the types of lecithins or phospholipids?
- 1.7 Types of phospholipids found in lecithins
- 1.8 What type of fat is lecithin?
- 1.9 Lecithin functions
- 1.10 Properties of lecithin
- 1.11 Advantages of soy lecithin compared to others
Characteristics and properties of lecithin or phospholipids
What is lecithin or phospholipids?
What is known as lecithin is a nutritional supplement extracted from soybean oil (soybean lecithin), egg yolk (egg lecithin) or sunflower oil (sunflower lecithin).
Technically, the term lecithin is synonymous with phospholipid. This page explains where this supplement comes from, what is its composition, its structure, its functions and its benefits in the body.
What does lecithin (phospholipid) contain?

Lecithin is an extract of the oil (fat) of a food. As it is a purified substance (extract), it does not contain proteins, carbohydrates, isoflavones, antinutrients or fiber, components that can be found in soy or food, but not in the fatty extract.
More specifically, lecithin is a type of special fat called phospholipid. Unlike other fats, it has more components besides triglycerides (glycerol and fatty acids).
Nutritional composition of lecithin or phospholipids
Below is the table of nutritional composition of a lecithin supplement. The most remarkable thing about reading it is that it contains 100% fat, therefore it does not provide other remarkable nutrients:
| Nutritional composition of soy lecithin per 100 g. | |
| Calories | 763 kcal. |
| Fat | 100 g. |
| Vitamin E | 9,21 mg. |
Chemical structure of lecithin
Lecithin or phospholipid is a large molecule of fat formed by different parts, all of them beneficial. According to the chemical definition of lecithin, its composition consists mainly of four parts:
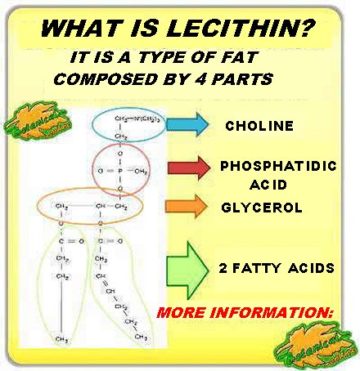
- A glycerol molecule
- Two (2) fatty acids bound to a glycerol
- A phosphatidic acid bound to glycerol on the one hand, and in turn linked to other substances, such as amines or amino acids
What is lecithin called chemically?
Chemically, the union of glycerol, fatty acids and phosphatidic acid is called phosphoglyceride. When phosphatidic acid is bound to another substance it is called phospholipid.
Therefore, when talking about lecithin, it actually refers to a type of fat called phospholipids. More specifically, it is popularly called phosphatidylcholine , which is a phospholipid that contains choline, and the most abundant type of fat in soybean lecithin.
What are the types of lecithins or phospholipids?
Depending on the type of substance to which phosphatidic acid binds, different types of phospholipids (types of lecithin) result: the most common is phosphatidylcholine, but there is also phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine (cephalin), etc.
Types of phospholipids found in lecithins

Normally lecithins (extracts of oils sold as supplements) contain different types of lecithins (phospholipids):
- Phosphatidylcholine (phospholipid formed by choline). Popularly it is called lecithin and is the most abundant component in soy lecithin. Choline is part of acetylcholine, a substance that acts as a neurotransmitter of the nervous system. For this reason, soy lecithin helps prevent Alzheimer’s disease, increase memory, improve concentration and other nervous disorders such as hyperactivity.
- Phosphatidylinositol (phospholipid formed by inositol). Inositol is involved in many metabolic functions, in the proper functioning of the nervous system (essential for neurotransmitters to act properly), fertility, and is necessary for healthy skin, nails and hair.
- Phosphatidylethanolamine (phospholipid formed by ethanolamine) around 20.8-23% of total phospholipids. It is commonly known as cephalin and is one of the most abundant phospholipids in the human body.
- Phosphatidylserine (phospholipid formed by serine)
In the body, these substances can be “cut” from each other and therefore it is possible to obtain the different components that make them up.
What type of fat is lecithin?
Phospholipids are a type of special fat, which in biology is classified into lipids or saponifiable fats, because in their composition they have fatty acids.
Lecithin functions
The function of phospholipids is to be part of cell membranes throughout the body and produce bile. When they decompose, certain components, such as choline or inositol, are used to form structures of neuronal bodies, in the form of neurotransmitters.
Properties of lecithin
The main property of these molecules is to emulsify. An emulsifier is an amphipathic molecule, which is a chemical property used to describe that it can bind water with oil, or what is the same, hydrophilic substances with hydrophobic.
Soy lecithin in supplementation
Normally, lecithin is known to be part of a food supplement very rich in phospholipids, inositol, choline and vitamin E. These components are found in high concentration in the nervous system (brain and nerves) and are part of good cholesterol or HDL.
Advantages of soy lecithin compared to others
The advantage that soy lecithin has over lecithin that is extracted from eggs is that soybean has a higher percentage of phosphatidyl inositol.
![]() More information on lecithin
More information on lecithin