Contents
What is borage?
Borage (Borago officinalis) is a vegetable.
Its looks very similar to spinach but with a light green uniform color both in the stem or in the leaves.
Its flavor is salty with a smooth and pleasant texture, like spinach.
What are the main nutrients of borage? Borage composition
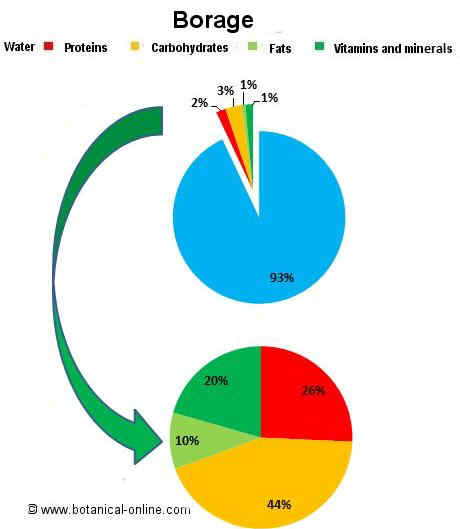
As an energy source, 100 grams of borage we provide 21 kcal.
Its proportion of nutrients is divided into:
- More than 93% is water.
- 0.7% fat.
- 1.8% proteins.
- 3.06% carbohydrates.
Minerals and vitamins of borage
- Borage is rich in potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron, but it also contain an interesting amount of phosphorus, sodium, selenium, and small amounts of zinc, manganese and copper.
- Borage is rich in vitamin A. It also contains significant amounts of vitamin C and vitamin B9, among other B vitamins.
Nutritional characteristics of borage

Borage plant
- It has a very high water content.
- It provides little energy.
- It contains very little fat although a high quality one and with many health benefits.
- It has a significant content in protein.
- It is low in carbohydrates, especially starches.
- It helps to remove toxins from our body, because it contains potassium.
- Because of its calcium content, it maintains the balance of the formation of strong bones.
- Because of its magnesium content, it helps the contraction and relaxation of muscles.
- It helps to prevent anemia because of its iron content.
- For its vitamin B9, it helps us to grow properly.
- It protects the skin and helps keep it healthy, because it contains vitamin A.
- It protects us from colds and helps heal wounds, because it contains vitamin C.
- It protects us from the toxins and aging, because it contains vitamin A, C, zinc and selenium.
Borage in the kitchen:
![]() More information about other foods and nutrition
More information about other foods and nutrition
This article was endorsed by Elisenda Carballido - Dietitian nutritionist. Postgraduate in Phytotherapy and master in Nutrition and Metabolism.