Contents
- 1 STEVIA, A NATURAL SWEETENER
- 1.1 Stevia, a natural, calorie-free sweetener
- 1.2 Why does stevia taste sweet?
- 1.3 Sweetening value of stevia components
- 1.4 Advantages of stevia over sugar
- 1.5 Stevia for diabetes
- 1.6 Stevia for obesity
- 1.7 Natural and artificial sweeteners for intestinal flora
- 1.8 Where to buy stevia?
- 1.9 Attention! Misleading stevia products
- 1.10 Types of sweeteners with stevia
- 2 STEVIA IN FOOD
STEVIA, A NATURAL SWEETENER
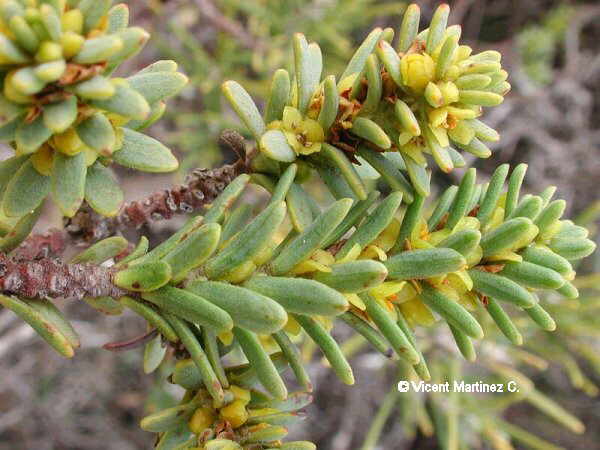
Stevia, a natural, calorie-free sweetener
The discovery of the sweetening properties of stevia has been a real turning point in the world of food.
In some countries such as Japan, 49% of the sweeteners consumed are products made from this plant.

The main advantage of stevia over sugar and other simple carbohydrates is that it has a superior sweetening capacity and is also practically calorie-free.
One gram of sugar provides 4 calories, while stevia has only about 0.2 kcal per gram.
Despite this, it is considered that the leaves of this plant can sweeten 20 to 30 times more than sugar.
Stevia extract, used as a natural sweetener, has a sweetening value greater than that of the leaves.
Stevia does not cause cavities.
Why does stevia taste sweet?
Stevia does not contain sugar. The reason for its sweetening value is due to the fact that its composition includes a series of components that provide it with sweetening properties.
Although stevia contains sucrose, that is, sugar, the proportion of it is very low.
It also contains traces of anethole, but its sweetening power is mainly due to a combination of dulcoside A, different rebaudiosides and steviosides, which are the main natural sweeteners.
Among all of them, rebaudioside A is the component with the greatest sweetening value, being 242 times sweeter than sucrose (sugar), followed by rebaudioside D, which is 221 times sweeter, and stevioside (the main sweetening component), which sweetens 210 times more than sugar.
Sweetening value of stevia components
Stevia has different components that affect its sweetening power.
The table below shows what sweetening components stevia contains and its sweetening value, compared to sucrose (sugar).
| Sweetening components of stevia leaves (Stevia reubadiana) in ppm (parts per million) | |
| Sweeteners | Sweetening power |
| Sucrose (sugar) (negligible amounts) | 100 |
| Stevioside (22.000 – 185.000 ppm) | 210 times higher |
| Rebaudioside A (14.000 – 40.000 ppm) | 242 times higher than sugar |
| Rebaudioside C (4.000 – 20.000 ppm) | 30 times higher |
| Dulcoside-A (2.000 – 7.000 ppm) | 30 times higher than sugar |
| Rebaudioside B (4.400 ppm) | 150 times higher than sugar |
| Rebaudioside D (300 ppm) | 221 times higher |
| Rebaudioside E (300 ppm) | 174 times higher |
| Rebaudioside F (negligible amounts) | ——- |
| Anethole (negligible amounts) | 13 times higher than sugar |
Advantages of stevia over sugar
There are several advantages that stevia sweeteners have over sugar or other simple carbohydrates:
Stevia for diabetes
Stevia is a sweetener suitable for diabetics: There are studies that suggest, although there is no conclusive evidence about this, that this type of sweetener is very suitable for diabetes mellitus, since it makes diabetics more tolerant to glucose, and that glucose levels remain more stable.
In particular, it has been shown that the components of stevia could be very positive for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (adult diabetes), due to its hypoglycemic properties.
People with diabetes can take stevia sweetener because it does not alter blood sugar levels (glycemia), unlike other sweeteners such as fructose.
*More information: Stevia for diabetes
Stevia for obesity

Stevia is a calorie-free sweetener that allows you to reduce the calorie content of sweets without sacrificing flavor. With stevia you can prepare sweets, desserts, shakes or sweeten any preparation, without adding calories to the dish.
This makes it very useful in weight loss diets and in obesity prevention and other related abnormalities, such as hypertension, cholesterol or triglycerides.
Since the calorific value of stevia sugars is practically zero, we can use them to sweeten foods without ingesting additional calories. In addition, stevia does not cause cavities.
A remedy to stop the craving for food: The problem with sugar and other foods rich in simple carbohydrates is the “rebound effect” they produce. Foods with a lot of sugar are responsible for the food cravings that occur shortly after eating them.
The reason is mainly due to the inability of foods rich in simple sugars to maintain stable blood glucose levels, which is why the body asks us to eat more sweets.
Using sweeteners like stevia instead of sugar helps reduce food obsession (See more information on the topic “craving for sweets“).
Natural and artificial sweeteners for intestinal flora
A study was recently published in which the intestinal flora of consumers of the three most commonly used artificial sweeteners was analyzed: saccharin, aspartame and sucralose (Splenda®).
Initial results showed that the use of these sweeteners produced changes in the intestinal flora, so that the body has greater difficulty regulating blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of obesity and diabetes.
In this sense, stevia is presented as an alternative to the use of artificial sweeteners (which are not found in nature).

Where to buy stevia?

Until a few years ago, stevia sweetener was very difficult to obtain in some European countries, until the European Food Commission regulated the use of the plant for food purposes at the end of 2011.
Stevia leaves can be found in herbalists or natural product stores.
It is now possible to buy products containing stevia extract (steviol glycosides) in supermarkets, although the plant is not so popular as to be found in coffee shops as an alternative to saccharin…
Attention! Misleading stevia products
Stevia has become fashionable as a healthier sweetener than others and many stores have started to market misleading products. For example, some sweeteners only contain 2% steviol glycosides.
Therefore, it is always recommended to read the ingredients on the labels of the products we buy.
Types of sweeteners with stevia
Stevia is sold or can be consumed in the following presentations:

Dried stevia leaves In herb form: Like other herbal teas, stevia is packaged in paper sachets with dried stevia leaves inside.
It is used to prepare infusions with water, milk, vegetable drink or other liquid, which can be used to sweeten foods (homemade vegetable milks, fruit salads, ice creams, etc.).
Dried stevia leaves are mixed with other medicinal herbs to sweeten herbal teas. (See possible contraindications of stevia in the list below).

Photo of different products with stevia that can be found in the supermarket Stevia in tablet form: It consists of the plant extract in a single-dose presentation, prepared to sweeten in one dose, like saccharin or other sweeteners.
- Stevia powder: Stevia concentrate for sweetening, with a potency approximately 200 times greater than sugar. Contains 100% of the sweetening principles of the plant. Most are suitable for baking (see label). Some commercial brands incorporate other sweeteners in the composition of these powders, such as sorbitol or xylitol (see label).
- In liquid form: It can take several forms. For example, as a thick extract extracted from the decoction of the leaves with a dark color and strong flavor and with properties similar to the powder, although less concentrated.
It has a power equivalent to about 60 times that of sugar. A couple of drops are enough to sweeten a drink or dish. It is also sold as a clearer liquid depending on the purity of the extract.
STEVIA IN FOOD
Recipes with stevia
The leaves of this plant are edible. They can be prepared raw as a sweetener in recipes, or cooked like other vegetables. (when boiled they lose much of their sweetness).
Stevia is traditionally used to sweeten mate tea, and can be combined with other infusions for the same purpose (green tea, dandelion, chicory, etc.).
- Easy homemade vegetable drink recipe
- Wild herb salad
- Stevia leaves can be added to fruit salads
- Ice creams
- Recipes for diabetics, replacing sugar, fructose, or other sweeteners
- Fresh chia water with stevia
In some places, dried stevia leaves are chewed for a while to suppress the craving for sweet foods.
![]() More information on toxicity and properties of stevia
More information on toxicity and properties of stevia