Contents
- 1 PROPERTIES OF SPIRULINA
- 2 USES OF SPIRULINA
- 2.1 Traditional use of Spirulina
- 2.2 Spirulina is one source of non-animal protein
- 2.3 A source of vitamins and minerals
- 2.4 Spirulina, a remedy to sleep well:
- 2.5 Spirulina for weight loss
- 2.6 MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF SPIRULINA
- 2.7 Sources of espirulina:
- 2.8 Contraindications and side effects of espirulina
PROPERTIES OF SPIRULINA
SPIRULINA MAXIMA/SPIRULINA PRATENSIS
Common name: Spirulina
Scientific name: There are over 1500 species of blue green algae. The most used are Spirulina maxima and Spirulina pratensis.
Other well-known species are Spirulina corakiana, Spirulina crispum, Spirulina labyrinthiformis, Spirulina laxa, Spirulina laxissima, Spirulina major, Spirulina meneghiniana, Spirulina nordstedtii, Spirulina princeps, Spirulina subsalsa, Spirulina subtilissima, Spirulina platensis, Spirulina tenerrima or Spirulina weissii
Characteristics / description of Spirulina
Spirulina are organisms belonging to the group of cyanobacteria. This is a type of microscopic organisms living in freshwater lakes or artificial containers, manufactured specifically for them to develop.
They are formed by a single cell capable of producing organic matter through photosynthesis and assembled in the form of filaments that makes them look like algae (hence they are also known as blue algae), although they are actually bacteria.
Habitat: They were originally organisms coming from the lakes of Africa and tropical America that have spread to other warm regions of the world using their ability to adapt in places where other organisms can’t. (Very salty or alkaline lakes, volcanic cones, etc)
 Image of spirulina
Image of spirulina
Components of Spirulina:
– Proteins (until a 70%)
– Carbohydrates (50 -70%). Mainly glucose, galactose, mannose and ribose.
– Pigments: Betacarotene (provitamin A), xanthophylls, zeaxanthin, beta-cryptoxanthin, etc.
– Vitamins: (10%) Mainly vitamin D, vitamin C and vitamins of group B (Vitamin B12, folic acid, niacin, riboflavin)
– Fiber (5%), especially mucilage.
– Enzymes
– Fats. Mainly essential fatty acids. (Gamma-linolenic acid – Omega 6)
– Minerals: Especially iron and iodine, along with calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, copper, zinc and selenium.
USES OF SPIRULINA
Traditional use of Spirulina
Traditionally spirulina has been widely used. There are written references to its use in pre-Columbian America by the Aztecs that extracted it from Texcoco lake. Today this lake, exploited by the Sosa-Texcoco company, is the world’s largest production of spirulina.
It was used widely in China, especially with medicinal aims since it was used to increase desire and to prevent hair loss. Spirulina was part of the food many communities of the world regularly consumed because, in addition to having an extremely protein food, they thought it protected them from many diseases, some as deadly as heart attacks or cancer.
Today it is widely consumed in Japan and the United States, places where many people consider it as the best remedy for losing weight.
Spirulina is one source of non-animal protein
Today spirulina is considered a nutritional supplement sold in most health food centers, pharmacies or health food section of department stores. Many people know its richness in proteins that can reach 70% of its gross weight.
Proteins in spirulina contain all the essential amino acids, from which the body builds its architecture. Although the amino acids in spirulina are not as complete as the animal meat – especially in regard to methionine, cysteine and lysine– they are much more complete than plant proteins, including those of legumes.
Spirulina does not have the drawbacks of animal meat proteins in terms of the content of cholesterol. This makes it a to very recognized natural alternative to animal protein. It is along with soy, the main protein source of vegetarian diets. Vegetarian athletes can use it to cover part of their needs.

Spirulin tablets
A source of vitamins and minerals
Spirulina contains vitamins, especially Vitamin A in the form of betacarotene, vitamin C and vitamins of group B. We know of the importance of vitamin B and of vitamin C as antioxidants in the prevention of numerous degenerative diseases. Spirulina is particularly noted for its content in cobalamin or B12 vitamin and folic acid or vitamin B9. Folic acid, among other reasons, it is necessary for cell formation and proper functioning of the heart and nervous system.
Cobalamin is necessary for the absorption of iron. Lacking it, not only can lead to deficiencies of this mineral, but the brain, the nervous system, the heart, and the body defenses will not work correctly. It is important to say that very few plant are sources of cobalamin, which is mainly found in foods of animal origin, so that strict vegetarians must rely on supplements.
We should not forget that spirulina contains much iron; that is why spirulina supplements are well suited to prevent or treat anemia.
Spirulina alone does not cover the needs of all these vitamins and minerals, but it may help prevent deficiencies.
Spirulina, a remedy to sleep well:
Spirulina is rich in melatonin, a hormone that has been used as supplements for the treatment of numerous anomalies such as insomnia, prolongation of youth, the treatment of cancer, etc.
Spirulina for weight loss
Spirulina contains a lot of fiber, especially mucilage that causes a great fullness. Its high slow- release complex sugar content maintains levels of blood glucose constant, which helps decrease the sensation of hunger. All this makes spirulina very useful as a dietary supplement for weight loss diets. It is this sense, spirulina supplements, administered under the terms of the prospectus, can help fight obesity.
The studies on the satiating properties of spirulina are abundant. Some specialists had prescribed supplements of spirulina in the treatment of obesity or for the diets to lose weight because they were based on the fact that spirulina contains an essential amino acid called phenylalanine, which is attributed a high capacity to reduce hunger.
Recent studies suggest that the content of this principle is too low to be effective.
Its iodine content could be useful in people who have problems to reduce fat by presenting hypothyroidism. Only this factor and its wealth fibers can justify its use as a slimming.
MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF SPIRULINA
The role of this organism in modern phytotherapy has become to be considered, given the numerous studies that have shown, mainly by means of animal studies, its potential healing properties in humans
Internal use
– Vision loss: Spirulina has been used to treat deficiencies of vitamin A, responsible for vision loss in people whose diets are deficient in this vitamin. One proved to be effective, the WHO (World Health Organization) took the decision to add 1 g of Spirulina to the diet of children in India.
Statistics compiled from this decision have shown that the rate of blindness has decreased since the adoption of this initiative. Therefore the inclusion of spirulina supplements to people with vision problems, such as macular degeneration or night blindness could be very convenient.

Supplement of espirulina of the company Puritan’s Pride
– Arthritis: Spirulina has a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially linolenic acid, a fatty acid that is part of the so called Omega 6.
The ability of this component to reduce inflammatory processes makes it applicable to diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
– Problems of the circulatory system: Numerous studies in rats have demonstrated that the elevated essential fatty acid levels, especially Omega 6, in Spirulina exerted a beneficial effect on the circulatory system.
The intake of foods rich in omega-6 fatty acids or supplements that contain this principle lowers triglycerides and cholesterol, prevents blood clots in the arteries (by means of preventing platelet aggregation) and slightly decreases blood pressure.
In general spirulina can be considered a blood thinner remedy that protects against heart attacks, strokes, angina pectoris, Raynaud’s disease, etc. Moreover, the cardioprotective role is further enhanced by the ability of these oils to increase the transmission power of the heart muscle to prevent diseases such as arrhythmias.
– Remedy to increase the defenses: Other studies have demonstrated the ability of these bacteria to stimulate immunity, so its use could be useful in preventing certain diseases in which the defenses are involved.
Hence, many investigations are underway to check whether spirulina is beneficial for people with AIDS (HIV), certain forms of cancer, poisonings by heavy metals, etc.
External use
– Bad breath: The chlorophyll content of this bacteria is very appropriate in the treatment of halitosis or bad mouth odor. Chlorophyll refreshes the mouth and provides good breath.
That is why many industrial mouthwashes include it in their composition. (You can buy a mouthwash in pharmacies or shops that contains this principle or to use Spirulina powder – half teaspoon dissolved in 125 ml of water and rinse your mouth – or tablet – chewing a tablet-)
– Mouth sores: Its vitamin content C determines that the rinses realized with a mouth rinse containing spirulina help to disinfect the mouth ulcers and facilitate healing. On the other hand, chlorophyll also possesses anti-ulcer and vulnerary properties. (Perform the previous treatment)
– Cancer of mouth: The above treatment is suitable for treating white patches in the mouth (oral leukoplakia) that may lead to oral cancer. Chlorophyll has cancer preventive properties, not only for oral cancer but also liver cancer and colon cancer.
So, spirulina remedies could be useful not only for external prevention of this disease, but for those cancers that develop inside the body.
Sources of espirulina:
Although this organism forms colonies in coastal marine waters, spirulina collected from the sea should not be used, given the high amount of organic waste containing heavy metals, especially cadmium and mercury.
There is also the possibility of confusion with some very toxic blue green algae that very similar to the colonies of spirulina.
Therefore, one must resort to supplements sold in pharmacies or stores. We must visit a reliable shop which will offer us a product free of toxins and in good condition.
Spirulina can be bought in tablets, powder, tincture, liquid or capsules. The usual dose is 3 to 5 grams per day in adults, although this can vary depending on the type of person or the condition. Therefore, always consult your doctor or specialist about the advisability of taking this supplement as well as how to do it and the recommended doses.
Contraindications and side effects of espirulina
– Do not take preparations from this plant in case of gout or phenylketonuria.
-Although spirulina is not discouraged for pregnant or breastfeeding, it is best to consult with your doctor before taking products containing it.
– In some people it can produce diarrhea, vomits, headache, muscle pain, difficulty in concentrating, increased sweating or reactions in the skin. In this case, you should stop taking it or decrease the dose.
– Its use can interfere with some medicines or supplements, reason why you should consult with a specialist if you are taking any supplement or medication.
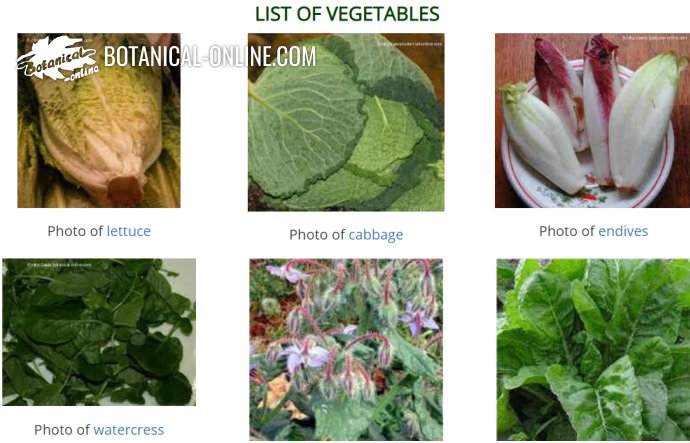
![]() More information on foods.
More information on foods.