Contents
Consequences of taking sarsaparilla
What is sarsaparilla and what applications does it have?
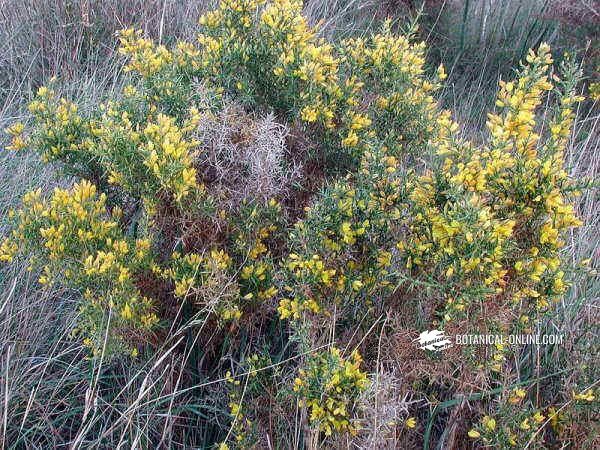
Sarsaparilla (Smilax aspera ) is a climbing vine that is found in the Mediterranean forests.

Used parts and active principles
Its root is traditionally used for medicinal purposes, mainly because of its high content of saponins (2%), essential oil and tannins.
Uses of sarsaparilla
It has diuretic, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, digestive and appetizing properties.
What contraindications does sarsaparilla have?
Many specialists consider that the use of sarsaparilla root, in therapeutic doses, does not present problems.
The main contraindications are:
- Avoid continued administration: The use of this plant regularly or in long treatments is not recommended. In excess, saponins can irritate the gastrointestinal tract and cause diarrhea or vomiting.
- Intestinal diseases: The use of sarsaparilla and its administration as a medicinal plant is not recommended, given that saponins can irritate the digestive system. Sarsaparilla is contraindicated in case of diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, gastritis, heartburn, Crohn’s disease, colitis, etc.
- Hypertension: It is not recommended for people with hypertension or taking medication because increasing diuresis, can lead to an imbalance in blood pressure.
- Medications: Administration of sarsaparilla may interfere with the absorption of certain medications. It should not be taken by people under pharmacological treatment without the consent of their doctor.
- The fruits of sarsaparilla are toxic. Its consumption causes vomiting and diarrhea. It can also cause a high reduction of red blood cells due to the hemolytic properties of saponins.
- Sarsaparilla has to be avoided in pregnancy and lactation
The administration of this plant in case of pregnancy and lactation is not recommended.
![]() More information on sarsaparilla
More information on sarsaparilla
This article was endorsed by Elisenda Carballido - Dietitian nutritionist. Postgraduate in Phytotherapy and master in Nutrition and Metabolism.