Contents
What is a purslane?
Characteristics of purslane (Portulaca oleracea)
Common noun: Purslane, Green purslane, Common purslane, Garden purslane, Little hogweed, Akulikuli-kula, Duckweed, Pursley, Wild portulaca.
Scientific noun: Portulaca oleracea L.
Family: Purslane family – Portulacaceae
Habitat: In cultivated, very rich fertilized soils and waste lands.
Characteristics of Purslane
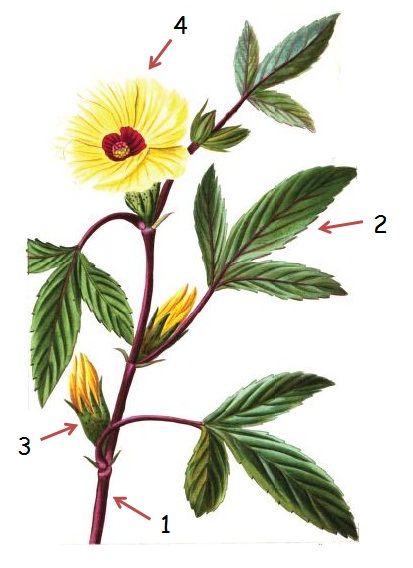
Annual plant of the Purslane family – Portulacaceae- till 30 cm. long. Prostrate, succulent stems, bright dark green. Opposite leaves, till 3 cm. Upper ones verticilate. Flowers till 1,3 cm in diameter, with petals falling very soon, yellow. The fruit is a pixidium. In cultivated, very rich fertilized soils and waste lands.
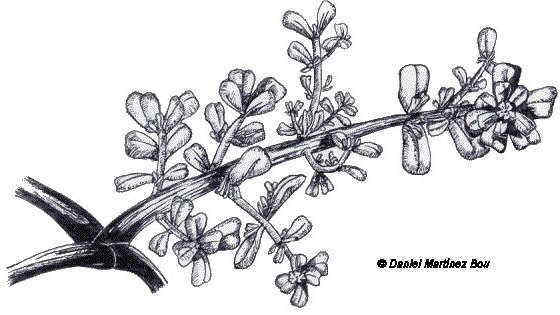
A detail of the plant
Picking-up and storing Purslane
Except the seeds that should be dried once they are gathered, leaves must be eaten fresh. It can be found mainly in summer, but samples can be found from spring to summer.
Composition: Active components of Purslane
The main active components we can find are the following:
- Amino acids: Alanine (it increases the defenses of the immunitary system ); arginine (Very necessary for the muscular growth and the tissues repairing) histidine (vasodilator and stimulative of the gastric juice. It combats the anemia, the arthritis and it is very useful for the ulcers) Isoleucine (Necessary for the appropriate growth) Valine (infantile growth), glutamic acid (antiulcerous, tonic, increases the mental capacity, aspartic acid (Very interesting in the expulsion of the ammonia)
- Acids: Ascorbic (vitamin C); linoleic acid (Vitamin F);; palmitic acid.
- Calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, sulfur…Etc.
- Proteins
- Fiber
- Oxalic acid (Very toxic)
*Related information: Purslane contraindications / Purslane side effects / Purslane toxicity
![]() More information on plants
More information on plants