Contents
What is a water pepper plant?
Characteristics of water pepper (Polygonum hydropiper)
Common English name: water-pepper, water pepper, common smartweed.
– Spanish / Español: pimienta acuática, pimienta de agua, atacaya
Scientific name: Polygonum hydropiper
Taxonomic Synonyms:
– Gray acris Persicaria nom. illeg.
– Persicaria flaccida (Meisn.) H.Gross
– Hydropiper persicaria (L.) Spach
– Hydropiper persicaria (L.) Delarbre
Family: Polygonaceae
Habitat: Native Plant of the European continent, distributed in cold and temperate regions. It is located on the Eurasian continent (Caucasus, Siberia) and North America (Mexico, USA, Canada).
It likes high humidity and high nitrogen soils, growing naturally in swamps, rivers,, etc.. It does not tolerate calcareous soils.
Botanical description of water pepper
The smartweed (Polygonum hydropiper) is an annual herb, 20 to 60 cm tall, usually branched and hairless.
Stems erect, greenish or reddish. Its small petiolated leaves (1) are alternate, lanceolate, acute, entire margins, about 2 cm wide and 12 cm long. They are covered with transparent essence glands.
At the base of each leaf there are the ochreas (2), which are membranous structures departing from the corners of the leaves that surround the stem like a sheath.
In botany, the nodal ocreas typical structures of the Polygonaceae family.
The inflorescences are terminal hanging racemes (3), between 1 and 6 per plant, where the flowers are arranged.
Pepper aquatic blooms in summer and autumn. The flowers are small, about 4 mm long, whitish or greenish, stained with red at maturity. It is a honey plant.
The fruit is an lenticular (compressed) trigonal (triangular) achene or, as if the flower contained two or three styles. It is brown, approximately 3 millimeters.
This fruit has a strong spicy flavor similar to the taste of chilli.
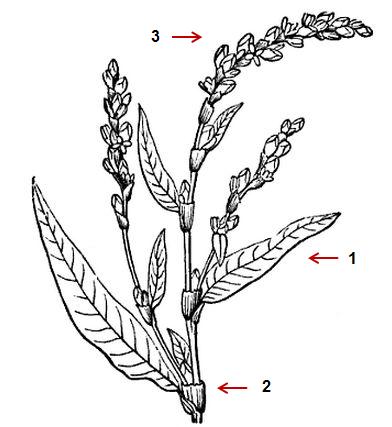
In the picture: botanical illustration of smartweed, showing the stems, leaves and terminal inflorescences of the plant.
Composition of water pepper
– Essential oil: 1,4-cineole, alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, borneol, camphor, carvone, cinnamic acid, cinnamic alcohol, fenchone, P-cymol, phellandrene, poligonone, terpineol.
– Organic acids: formic acid, acetic acid, valeric acid, gallic acid, malic acid, melissic acid, ellagic acid, baldrianic acid, caprionic acid. tannic acid.
– Anthraquinones: oxy methyl anthraquinone (root). Purging compound also present in other Polygonaceae such as rhubarb.
– Tannins
– Phytosterols: beta-sitosterol, sitosterol
– Sesquiterpenes: polygodial (leaves), polygonal (seeds), confertiflorin (seeds), isodrimeninol (seed), isopolygodial (seed), isorhamnetin, isodrimenol, isotadeonal, polygonolide.
– Mucilage
– Flavonoids: rutin, kaempferol, quercetin, quercitrin, rhamnazin, rhamnesin.
– Salts: potassium nitrate, potassium chloride.
| Water piper composition (Polygonum hydropiper) | |
| Chemicals | Contents (en ppm.) |
| Tannins | 35.000 |
| Rutin (leaves) | 25.000 – 30.000 |
| Potassium chloride | 26.000 |
| Rhamnazin | 1.100 |
![]() More information about water pepper and other types of peppers
More information about water pepper and other types of peppers
| Botanical classification | |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta Vascular plants |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta Seed plants |
| Division | Magnoliophyta Flower plants |
| Class | Magnoliopsida Dicotyledons |
| Order | Caryophyllales |
| Family | Polygonaceae |
| Gender | Polygonum |
| Species | P. hydropiper |
![]() More information about water pepper and other types of peppers.
More information about water pepper and other types of peppers.








