Contents
What is long pepper?
Characteristics of long pepper (Piper longum)
Common English name: long pepper, common long pepper, pepper from India.
Scientific name: Piper longum L.
Taxonomic synonyms: Chavica roxburghii Miq., Piper longum bauh orientale.; Piper longum Ger. Em.
Family: Piperaceae
Habitat: plant native to India, especially of Malabar and Bengal, which was known in Europe as a spice before than black pepper (Piper nigrum). This spice had a great importance in medieval trade.
Naturalized in Sri Lanka and the Philippines. Grown in tropical Asia Indochina and China.
Botanical description of long pepper
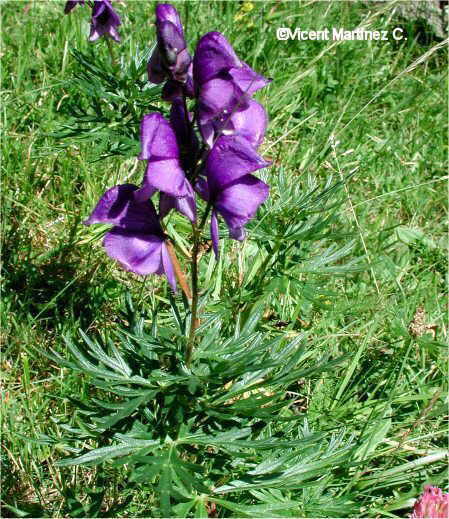
Long pepper (Piper longum) is a climbing plant that grows in tropical climates and has essential oils in leaves and seeds, giving off a strong fragrance.
This perennial low gnarled vine is native to India. Their stems have nodes where the fruitful branches and leaves born. It has adventitious roots.
Leaves numerous, stalked and cordate at the base, with 7 nerves. Upper leaves oblong-cordate with 5 nerves. Growth of the stem leaves alternate, between 6.3 and 9 inches long. Petiole of basal leaves: 5 to 7.5 centimeters. Upper leaves short-stalked or stalkless.
The inflorescence is a pedunculated flower spike that comes from the nodes of the main stems. 2 to 3 cm long, with tiny flowers.
Flowers are greenish yellow and arranged in a spiral along the spine. The flower opening starts from the base of the spike to the apex.
The long pepper fruit is a drupe small, arranged in the flower spike forming a compact fruiting, welded, reminiscent of black catkins and hard, between 2 and 3 (up to 5) cm long.
These fruits are green in their immaturity, stained pink at maturity and are kept dry, when they become dark black. They whole spikes are collected and ground. Used to prepare curry or as a substitute for black pepper (Piper nigrum).
Composition of long pepper
Long pepper has a spicy and aromatic flavor due to its content of alkaloids and essential oils:
– Piperine: main alkaloid responsible for the intense spiciness of the pepper. It also contains the alkaloid piperidine.
– Essential oils: monoterpenes: levo-phellandrene, pinene, limonene, sabinene, myrcene, and sesquiterpenes: beta-caryophyllene, humulene, beta-bisabolone, caryophyllene.
– Scented resin.
Medicinal properties of long pepper
The fruits of long pepper, dried and crushed, are suitable for cooking. It is added to curry mixes or used as a substitute for black pepper. Congener of black pepper.
It has been attributed with the following medicinal properties:
– Diuretic
– Indigestion
– Headache
– Toothache
– Ashma
– Cough
– Fever
– Tuberculosis
– Bronchitis
– Psoriasis
– Insomnia
– Etc
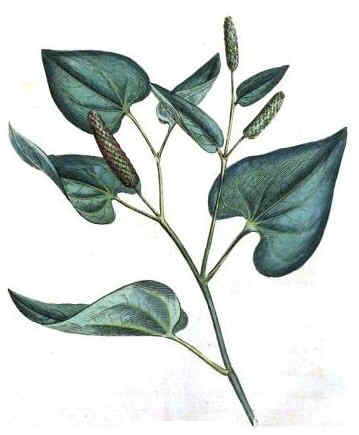
Drawing of long pepper

Photo of long pepper (Piper longum)
![]() More information about black pepper and other types of peppers
More information about black pepper and other types of peppers
| Botanical classification | |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta Vascular plants |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta Seed plants |
| Division | Magnoliophyta Flower plants |
| Class | Magnoliopsida Dicotyledons |
| Order | Piperales |
| Family | Piperaceae |
| Gender | Piper |
| Species | P. longum L. |
![]() More information about black pepper and other types of peppers.
More information about black pepper and other types of peppers.