Contents
Characteristics of mastic tree or lentisc (Pistacia lentiscus L.)
What is a lentisc plant?
Common noun: Lentisc, Mastic tree, Pistachier Lentisque
Scientific noun: Pistacia lentiscus L.
Family. Cashew family -Anacardiaceae
Habitat: Where does mastic tree grow?
In woods by the side of the holm oak inland or with the carob tree and palmetto at the seaside. It doesn’ t like cold places.
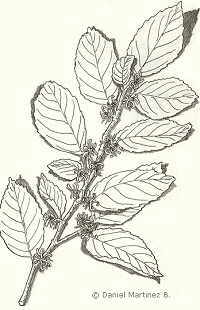
Description of mastic tree
Perennial bush of the till 2 meters tall (It is not generally found so many big samples because of the fires or some other human aggressions)
Leaves are formed with 3 to 6 pairs of elliptical coriaceous leaflets.
Male flowers without petals, female ones darker.
The fruit is a drupe of about 8 mm, which being green at the beginning,changes to red and becomes black in ripening fruits.
Those samples achieving tree dimensions produce in a natural way or when they are tapped a latex,which is called mastic that has several properties, as we’ ll se later.
Picking and storing: It is better to pick the tender stems and the leaves in Spring, but since we are talking about a perennial plant, one can collect its parts when necessary.

Properties of mastic tree
Medicinal properties
- Astringent: The infusion of leaves and tender stems is a good remedy to cure diarrhea.
- Dental cements: Mastic is used by dentists to prepare dental cements. It was previously used as a chewing gum because it gave good scent to our breath and fortified our gums. Very useful for bleeding gums.
Industrial properties
Mastic was used for the varnish industry. The isle of Quio is well- known in this Sense. A place whose economy depends upon that industrial product, the most part of it is obtained by the exploitation of a local variety of mastic tree (Pistacia lentiscus Chia)
![]() More information about medicinal plants.
More information about medicinal plants.