Contents [show]
Benefits of gingerol from ginger
What is gingerol?
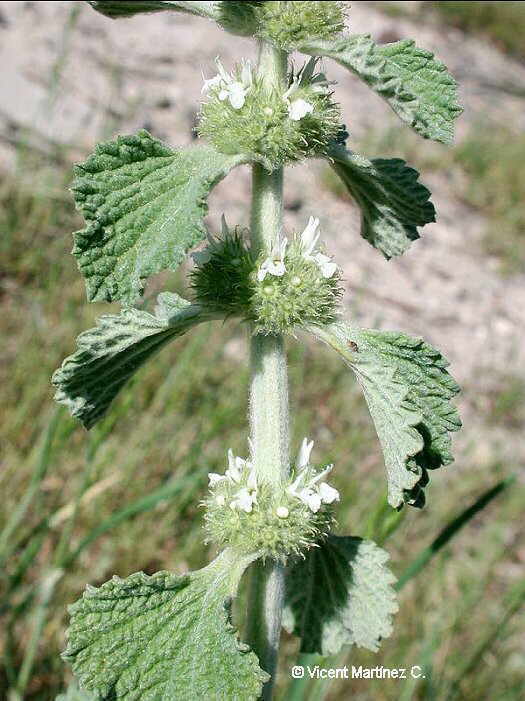
Gingerol is one of the main components of ginger (Zingiber officinale)
Gingerol gives raw ginger its typical pungent flavor, which is not surprising since this compound is related to the same compound that gives hot peppers (piperine) or cayenne pepper their pungent flavor (capsaicin).
Why is ginger hot?
Gingerol is responsible for ginger being a spice, because it mainly gives it the property of flavoring

foods. Gingerol only appears as such when ginger is fresh, as cooking transforms it into zingerone, which has a superior aroma but less pungent taste.
On the other hand, the pungent flavor of ginger is enhanced when dried, since gingerol is transformed into shogaol.
The degree of pungency or heat of a food is measured on the Scoville Scale in what are called Scoville Heat Units (SHU). On a scale from higher to lower degree of pungency, we would have the aforementioned products:
- First capsaicin (15,000,000 SHU)
- Second place the shogaol (160,000 SHU)
- Third Piperine (100,000 SHU) – The
- Finally, gingerol (60,000 SHU)
Medicinal properties of gingerol
In addition to providing the typical flavor, the gingerol in ginger also has a number of very interesting healing properties. The main ones are the following:
- Antioxidant
- Analgesic
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anti-allergic
- Antiemetic
- Fungicide
- Antipyretic
- Antiaggregant
- Hypotensive
Gingerol for cancer
Studies have been conducted on the positive effects of gingerols in the treatment of certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic, ovarian or breast cancer.
Gingerol to improve the conditions of the person with arthritis
Due to their anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, gingerols can help reduce the negative symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
(See: Ginger for arthritis, Ginger remedies)
![]() More information on ginger
More information on ginger








