Contents
- 1 CHARACTERISTICS OF SOLANUM DULCAMARA
- 2 Description of Solanum dulcamara
- 3 Active components of Solanum dulcamara
- 4 PROPERTIES OF SOLANUM DULCAMARA
- 5 Medicinal uses of bittersweet
- 6 External use preparations with Solanum dulcamara
- 7 Cosmetics with Solanum dulcamara
- 8 Toxicity of Solanum dulcamara
- 9 Consequences of eating Solanum dulcamara
- 10 Side effects of Solanum dulcamara
- 11 Is dulcamara toxic to animals?
CHARACTERISTICS OF SOLANUM DULCAMARA
Scientific noun : Solanum dulcamara L.
Common noun: Bittersweet, poisonberry, poisonflower, bittersweet nightshade, woody nightshade, violet bloom
Habitat: In humid shady places, river woods, by the side of streams and near the coast.
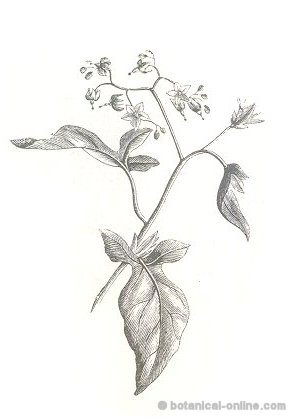
Description of Solanum dulcamara

Perennial shrub of the potato family – Solanaceae – till 2 me long.
Creeping or climbing stems, somewhat white hairy.
Alternate leaves, ovate with long stems till 8 cm. The upper ones entire; those below, lobed.
Violet flowers till 2 cm wide. Stamens with yellow anthers. Flowers gathered in sparse cymes, generally hanging at one side.
The fruits are berries, red in maturity, ovoid, till 1 cm in diameter.
Active components of Solanum dulcamara
- Alkaloids: Solanine, dulcamarin and solamin (stems and bark), solaceine, soladulcamarine, solamargenine (plant), solasodine (root) solanidine, soladulcidine and tomatidine (fruits) Atropine (seeds)
- Saponins: diosgenin, tigogenin and yamogenin (plant)
- Tannins:
- Pectin
Active parts The whole plant.
PROPERTIES OF SOLANUM DULCAMARA
Medicinal uses of bittersweet
Internal use remedies with dulcamara:
– It has been used as sedative by its narcotic properties, just as it happens in other members of the same family among those nightshade, thorn-apple, or mandrake. With regard to those mentioned, its narcotic properties are not so potent.

Although the leaves and the bark of the plant can be used, the most habitual thing is to use the depurative and diuretic properties of the stems that don’t have any branches to purify the organism in those affections where it is necessary the elimination of liquids of the organism and the purification of the blood:
– In rheumatic affections (A habitual form has been the use of flowing extracts that can be found in drugstores. The dose can oscillate between 1 g and 3 g daily)
– The same treatment has been used as depurative to treat water retention in edemas in the legs or to treat gout (A decoction from the stems of this plant to 10% during 5 minutes can be used. Drink a couple of cups a day. Increase the dose progressively until ending up with a decoction in a proportion of 20% of herb contents.)
– In obesity related with accumulation of liquids in the organism caused by an insufficient micturition. (oliguria) A stem decoction would increase the need to urinate (diuretic properties)so that a decrease of the corporal volume would take place. (Decoction previously mentioned)
– In blood circulation problems due to hypertension or cholesterol which imply a faulty fluid of the blood, this herb has been used as antiplethoric, reducing the volume of blood in the organism and facilitating the circulation. (Decoction previously mentioned)
– Equally it has been used for kidney stones treatment. By increasing micturition it will be possible to reduce the risk of formation of kidney stones or it will facilitate their expulsion via urethra.
– The sedative power of this plant has been used more sporadically to palliate asthmatic cough attacks, especially when it is cold. (Drink from one to six daily spoonfuls of prepared syrup that it can be bought in pharmacies.)
– Because of its depurative effect impurities of blood can be eliminated, something which is reflected in the health of the skin. Therefore, to clean the skin”, besides the treatment mentioned below in the external use of this plant, stem decoctions can be used.
External use preparations with Solanum dulcamara
– Externally, the resulting liquid of the decoction of the stem is very useful for the treatment of skin illnesses, mainly in what refers to eczema, psoriasis or ulcers (Apply the resulting liquid on the affected area.)
– The juice of the plant has been used to treat stings or bites from insects.
– Alkaloids from this plant, together with some other ones belonging to other species of the same family, take part in certain preparations that are used in medical investigation to stop the advance of skin cancer.
Cosmetics with Solanum dulcamara
The fruits of the nightshade were very important in as a cosmetic resource during Middle Ages. With them some creams were made for the beauty of the skin. However some references exist stating that the application of the fresh berries on the open wounds or on the skin mucous have produced adverse reactions.
Due to its toxicity it is advised not to take homemade preparations carried out with Solanum dulcamara Although no human cases of poisoning have been registered, except those mentioned in very old writings, its use would be reserved to the preparations carried out by qualified personnel, since the quantities that should be administered are very near to the toxic dose. In any case it should never be administered to pregnant women because it can cause abortion easily. Do not use during nursing or with small children. |
Toxicity of Solanum dulcamara
 Toxicity of this plant is high. Intoxications have generally taken place especially because of some berries ingestion in children, since they find them very attractive. (eating a dozen of fruits can be lethal for a child)
Toxicity of this plant is high. Intoxications have generally taken place especially because of some berries ingestion in children, since they find them very attractive. (eating a dozen of fruits can be lethal for a child)
Because of its sweet stem, it can also attract children who might desire to bite its bark, although they quickly realize their mistake. Saliva immediately transforms its sweetness into a very sour flavor that fortunately invites to spit it.
Equally, references in old texts point out that intoxications in adults have taken place by ingestion of preparations made with stems or bark.
Consequences of eating Solanum dulcamara
The alkaloids contained in the plant are very toxic in high dose producing lesions in the digestive apparatus and lungs. A too high ingestion can produce liver necrosis or water retention in lungs.
As for the fruits, they are much more dangerous before maturing, when they present the highest solanine dose. Once mature, they only contain some saponins that are less toxic than solanine.
Side effects of Solanum dulcamara
In minor doses, poisoning with this plant shows the following symptoms:
- Digestive disorders
- Stomachache
- Salivation
- Diarrhea
- Liver problems.
In high doses:
- Slowing of heart rate
- Convulsions
- Cardiorespiratory failure and death.
Medical treatment: Stomach pumping, artificial respiration and medical care.
Is dulcamara toxic to animals?
Dulcamara plant is toxic to animals. The fruits of nightshade, whe they are mature, can be eaten by the animals without being intoxicated.
![]() More information about plants.
More information about plants.








