Contents
Medicinal properties of cowslip (Primula veris L.)
Characteristics of cowslip
Common noun: Cowslip, Common cowslip, Cowslip primose
Scientific noun: Primula veris L., Primula officinalis (L.) Hill
Family: Primrose family – Primulaceae
Habitat: Not very dense woods and wet meadows.

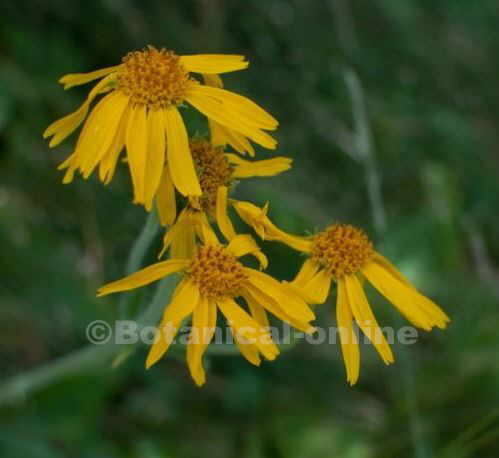
 Description of cowslip
Description of cowslip
Perennial herbaceous plant of the Primrose Family – Primulaceae – up to 30 cm tall.
Quite wrinkled leaves in basal rosette, pubescent or hairy, oval or oblong, abruptly narrowing at the winged stem.
Yellow flowers, gathered in one-sided umbels, with yellow straps inside. Pubescent calyx.
Picking-up and storing: Spring is the best season to collect the leaves, that must never be eaten dry. Rhizome before the plant is in bloom. Flowers before completely. flowered. They must be stored in a dark dry place.
Medicinal properties of cowslip

Cowslip (Primula veris) Expectorant, antispasmodic and antibronchitic: Ideal for the flu treatment, bronchitis and catarrh, with strong cough and mucus (Decoction of 40 gr. of rhizome per liter of water. Drink 4 cups a day)
- Diuretic, antiarthritic and antirheumatic: Because of its diuretic power it is very suitable in cases of gout, arthritis and rheumatism. (Decoction of a handful of flowers in half a liter of water. Drink several little glasses a day.
- Depurative: Its depurative properties can be used to treat acne.
- Analgesic: To soothe any pain caused by some contusion or blow (Decision of 50 gr. of dry rhizome per liter of water till only a third of liquid remains. Apply soaked compresses of this preparation on the suffering part of the body) (To alleviate headaches you can prepare a 3 minutes decoction of 20 gr. of ground rhizome per cup of water. Drink 4 cups a day)

Cowslip edible properties
Fresh tender leaves in Spring can be eaten in salads, providing all the properties seen above. In the same way, flesh flowers can be added to salads and desserts, giving the dishes an original flavor. By macerating some flowers in wine, they transfer a genuine flavor to the wine.
Toxicology of cowslip
They contain glandulous hairs on the leaves, that may produce skin reactions just by touching them. Reactions in the eyes may be quite severe. The active properties in big quantities are toxic.
![]() More information about medicinal plants.
More information about medicinal plants.

 Description of cowslip
Description of cowslip