Contents
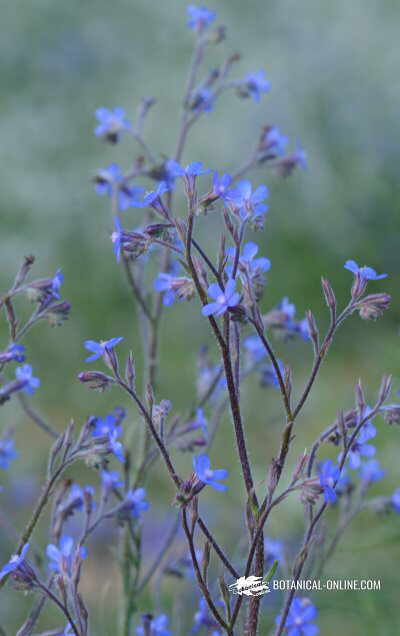
CHARACTERISTICS OF TRAVELER’S JOY

Scientific name: Clematis flammula L.
Common name: Traveler’s joy, fragrant virgin’s bower
Family: Buttercup family – Ranunculaceae
Habitat: field edges and sparse Mediterranean calcareous woods.
Poisons: Anemonin, protoanemonin, saponin and the alkaloid clematine.
Active parts: The whole plant
PROPERTIES OF TRAVELER’S JOY
Medicinal uses of Clematis flammula: It has been traditionally used as a rubefacient and vesicant, which produces a violent irritation in the skin, sometimes with blisters.
Also, horses eat the dry stems as fodder.
Because it is very dangerous, it is not advised to use this plant in home medicine.
Toxicity of traveler’s joy
The toxicity of this plant is extreme.
Symptoms of poisoning with traveler’s joy
- In internal use, it produces a violent irritation of the digestive tract by inflammation of mucous membranes, that appears like:
vomiting,
diarrhea,
respiratory disorders that may lead to a heart failure and death.
- In external use, by means of plasters on the skin, it can develop very painful blisters, so it is better to use another methods.
It has such dangerous toxins up to the point of, being absorbed through the skin, can produce general intoxication.
![]() More information about plants.
More information about plants.








