Contents
- 1 Scientific studies on the anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric
- 1.1 Why is turmeric anti-inflammatory?
- 1.2 What were the conclusions of this study?
- 1.3 What does it mean that a substance, like turmeric, is anti-inflammatory?
- 1.4 Why is turmeric anti-inflammatory?
- 1.5 Why is it recommended to take turmeric as an anti-inflammatory?
- 1.6 How should turmeric be taken to obtain its anti-inflammatory properties?
- 1.7 What should be the treatments with turmeric?
Scientific studies on the anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric
Why is turmeric anti-inflammatory?
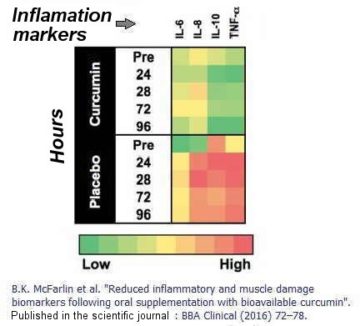
To explain why turmeric has anti-inflammatory action, it is very illustrative a study on the anti-inflammatory effect of turmeric after the exercise called “Reduced inflammatory and muscle damage biomarkers following oral supplementation with bioavailable curcumin”. It was published in the journal BBA Clinical by Brian K. McFarlin and his collaborators in 2016.
What were the conclusions of this study?
Results show that turmeric extract reduced serum inflammation markers after exercise in humans.
This page graph is very illustrative because it shows how the group of people treated with curcumin had lower levels of inflammation than the placebo group.
To simplify: “The curcumin group table is greener because there are fewer inflammation markers”
What does it mean that a substance, like turmeric, is anti-inflammatory?

The study in question evaluated the effect of turmeric extract on muscle pain and inflammation after exercise. To carry out the study, the participants were divided into two groups: 12 people would take a placebo (rice flour) and another 16 would take 400mg of curcumin supplements per day.
This was done 2 days before and 4 days after a session of intense exercise. During that time, previous blood samples were taken (“PRE”, in the image) and after days 1, 2, 3 and 4 after exercise.
After comparing the blood samples, curcumin consumption was shown to reduce all inflammation markers (although not muscle pain of all participants).
The decrease in inflammatory markers translated into a faster recovery after exercise and a better functional capacity during the subsequent exercise sessions.
Why is turmeric anti-inflammatory?
Turmeric is anti-inflammatory because its consumption decreases the inflammation markers of the organism, such as cytokines, CRP or prostaglandins COX2. By reducing these biomarkers, turmeric curcuminoids are able to alleviate many symptoms of these diseases, such as pain, recovery time, or the severity of the affectations.
It has been shown in scientific studies that, in some cases, turmeric is as effective as some anti-inflammatory drugs, with the advantage of not presenting the contraindications or adverse effects of these drugs.
Why is it recommended to take turmeric as an anti-inflammatory?
The previous study is an example of how the use of anti-inflammatory medicinal plants has real effects on the organism and can help to improve many affectations. These anti-inflammatory properties empower it for disorders or diseases where there is inflammation:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Menstrual pain
- Intestinal diseases
- Crohn’s disease
- Colitis
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Arthritis, etc.
In addition, scientific studies have shown that turmeric has other health benefits: for example, in the treatment of cancer, or it is also well known for its properties for the liver.
How should turmeric be taken to obtain its anti-inflammatory properties?
Turmeric is a spice and therefore can always be included in the diet. It is good to know that black pepper greatly increases the absorption of its active ingredients and therefore enhances the properties of turmeric. An example of preparation is the turmeric golden milk.
To obtain the therapeutic effects of this plant, it is more appropriate to take it in the form of extract, in a format very rich in curcuminoids.
* See: how to take turmeric
What should be the treatments with turmeric?
In any case, it is recommended to assess, together with the specialist doctor, the possibility of integrating this plant in conventional treatments (“integrative medicine”), since an improvement can always be expected.
An inadequate diet, with bad fats, excess flours and sugars, insomnia, sedentary lifestyle and stress, are inflammatory and block the beneficial effect of turmeric.
![]() More information on natural anti-inflammatories
More information on natural anti-inflammatories