Antioxidant properties of acai
The acai fruit is the fleshy fruit of the Acai palm (Euterpe oleracea), common in the Amazon jungle vegetation. This fruit is the size of an olive. It is known for its deep purple and because it forms part of the culinary tradition of people from pre-Columbian times.
Currently, the consumption of Acai extends throughout the Americas due to its popularity as an antioxidant food. These properties are well known to the population of Belem, a leading global producer of Acai Pulp. It is consumed throughout the country and is in many cases the main beverage, even more important than milk.
To demonstrate the antioxidant power of acai, the Department of Agriculture of the United States makes available to consumers a scale that measures the antioxidant power of food. This scale is called ORAC value scale (“ORAC values”), It offers the antioxidant power of foods studied in vitro by measuring the capacity of Oxygen Radical Absorption (in English, stands for ORAC).
| Currently, in Belem people drink more Acai juice than milk: its consumption is estimated at about 200,000 liters of acai juice per day among its 1.3 million population. |
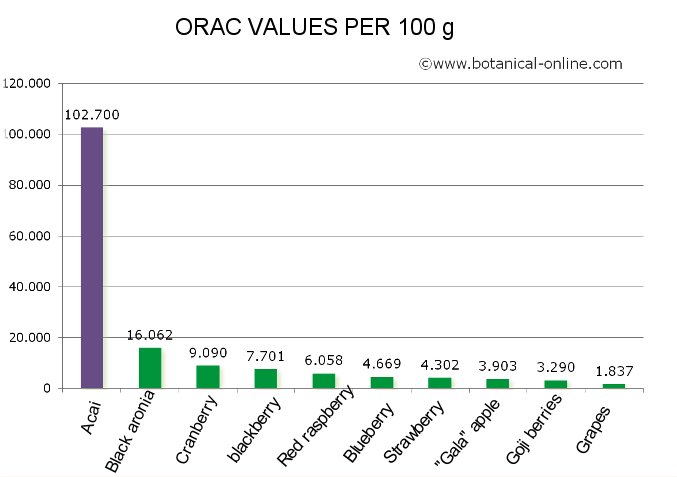
ORAC values for acai
The ORAC scale has emerged from the curiosity and duty of researchers to demonstrate and to inform consumers about the wealth of beneficial substances and antioxidants in vegetables. Also to confirm-or deny-many miracle foods that are advertised through any type of media everyday.
In the case of acai, its antioxidant power (ORAC value) is actually much higher than in other fruits, surpassing blueberries and raspberries.
However, the antioxidant content is measured in the fresh fruit with the whole skin. Acai pulp contains fewer antioxidants and ” vinho de acai or acai juice” even less, because it has gone through a process of pasteurization.
Graph comparing the antioxidant power of different fruits.
The ORAC scale values expressed in micromoles of Trolox eq. per 100g.
The antioxidant power is measured “in vitro”, so that the body “in vivo” may have different effects.
Antioxidant components of acai
- Anthocyanins: Anthocyanins are a group of flavonoids common in many plants with a characteristic cyanotic or purple color, like blueberries or aronia. They are powerful antioxidants, as experiments have discovered their properties in cancer prevention and anti-aging. They also have special qualities to the eye, they help to maintain good eye health.
Anthocyanins are also used as color additives in food.
However, the anthocyanins found in acai are very sensitive to heat and natural degradation of the food at harvest. So acai pulp changes color over time and also varies in anthocyanin content once pasteurized or while under refrigeration.
In the development of products with acai, the process should be quick to avoid the loss of these important nutrients in the fruit. Harvesting, packaging and storing must be a quick process that has to be done in less than 11 hours.
Major anthocyanins from acai pulp are: cyanidin 3-sambubioside, cCianidina 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-rutinoside, peonidin 3-glucoside, peonidin 3-rutinoside, pelargonidin 3-glucoside.
Other antioxidant compounds present in the Acai are: tannins, lutein, quercetin, rutin, orientin, homo-orientin, vitexin, chrysoeriol, ellagic acid and kaempferol.

In the picture: antioxidant supplement made from acai juice enriched with resveratrol, lycopene and other antioxidant compounds.
![]() More information about acai.
More information about acai.