Contents
- 1 Characteristics of xylitol or sweetener E 967
- 1.1 What is xylitol?
- 1.2 Where is xylitol extracted or in what foods is it found?
- 1.3 Sweetening power of xylitol
- 1.4 Xylitol benefits
- 1.5 Chemical properties of xylitol
- 1.6 Food uses of xylitol
- 1.7 Xylitol toxicity
- 1.8 Adverse effects or reactions from consuming xylitol
- 1.9 Can you consume xylitol in pregnancy?
Characteristics of xylitol or sweetener E 967
What is xylitol?
Xylitol is a food additive classified within caloric sweetener group. It has sweetening power and has a certain energy contribution, although insignificant in the doses used (specifically, it has half the calories of sugar).
Where is xylitol extracted or in what foods is it found?

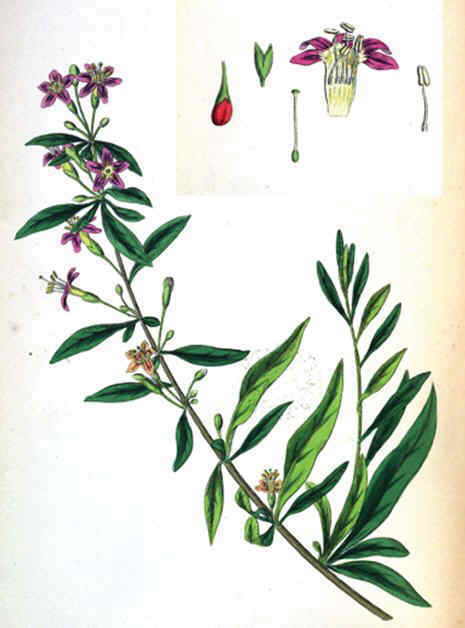
Xylitol is a natural sweetener that is found in nature as part of wood, many fruits and especially plants such as birch, although it is found in many others, such as garlic, etc.
It can also be obtained artificially from xylose or glucose and can be synthesized biotechnologically.
Sweetening power of xylitol
The sweetening power of xylitol is the same as that of sugar (sucrose or table sugar). That is, the sweetening power of 1 g of xylitol is the same as 1 g of sugar.
It provides almost half the calories of sugar. While sugar contributes 4 kcal per gram, it is estimated that xylitol only contributes 2.4 kcal per gram.
The advantage of using xylitol as a sweetener, for example birch sugar (100% xylitol), is that it is as sweet as sugar, thus sweetening with half the calories, and also does not cause cavities.
*Related information: What is better, stevia or agave syrup?
Xylitol benefits
The main benefits of xylitol are:
- Does not produce cavities (not cariogenic)
- In addition to not producing cavities, many studies indicate that xylitol may have an anticaries effect, because it prevents the formation of plaque and stimulates salivary flow, helping to maintain the pH of the blood. It has been seen that it can prevent or reduce existing cavities, which is why it is a common sweetener in dental hygiene pastes.
- It does not need insulin to be metabolized
- It does not contain sugar and therefore has a very low glycemic index: the glycemic index of xylitol is 7. This makes it a suitable sweetener in diets to lose weight, diets for the heart, diets for diabetes, diets without sugar, etc.
Chemical properties of xylitol
Chemically it is classified as a polyol, which is a different molecule from sugars, such as fructose or glucose. It is a water-soluble substance, stable to heat and acids.
- It dissolves in liquids
- It can be cooked to make cakes, pies, cookies, etc.
Food uses of xylitol
- Natural pure sweetener: on the market there is a sweetener called birch sugar that consists of an extract of birch 100% xylitol. As it is not metabolized with insulin, it is marketed as a healthy option for diabetics.
- Foods with xylitol: Low-calorie desserts, industrial ice cream, sweets, chewing gum, mustard sauce. Also medications.
Xylitol toxicity

Xylitol does not have a certain ADI, which indicates that it is considered a non-toxic sweetener for health. ADI stands for Acceptable Daily Intake, a maximum authorized figure for all toxic sweeteners, such as aspartame or acesulfame-K. For example, sweeteners that can be carcinogenic have to have a safe maximum dose in order to regulate their use in industry.
Xylitol does not have toxic or dangerous effects and for this reason it does not have a determined ADI.
As a note, it should be mentioned that xylitol is toxic to pets (dogs, cats…) and therefore should be kept out of their reach.
Adverse effects or reactions from consuming xylitol
The main contraindication to xylitol is that in excess it can be a laxative. In large quantities (more than 30-50 mg daily) it can cause flatulence, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Can you consume xylitol in pregnancy?
This sweetener can be consumed during pregnancy and lactation, with the caution that these stages require.
Therefore, birch sugar can be used if you are pregnant, albeit in low doses, due to its possible laxative effects.
Other caloric sweeteners that are commonly used in food:
![]() More information on food additives
More information on food additives