Contents
How is vanilla ingredient?
Vanilla is an aromatic spice, a thin pod of blackish color, the fruit of a climbing vine plant of the orchid family.
Vanilla pods characteristics
It is a greenish fruit when it grows, and becomes brown-black or dark as it matures during 8 months.
Its size ranges from 8 to 30 centimeters long and 1.5 centimeters wide when fresh.
Of all the many species of orchids, vanilla is the only one that is used for human consumption.

Origin of vanilla
Vanilla is native to the American rainforest and specifically from Mexico. The ancient Aztecs knew it as Txilotxitl or Tlilxochitl, meaning “black flower”.
Spanish colonists imported the aromatic spice to Europe. Numerous spice trade routes for centuries have made this spice to be cultivated in many other places, such as Africa and tropical Asia.
Currently, vanilla has become one of the most commercial scents, being applied in cosmetics (perfumes, creams, shampoos, gels,…) and especially in the food industry, forming one of the favorite flavors for chocolate, sugary drinks, cakes, pastries, etc.
What is vanilla flavor?
The scent of vanilla is sweet and intensely aromatic, typically used as a spice for sweet preparations. Its aroma is due to a phenol it contains, called vanillin.
There are varieties of African and Mexican vanillas. Although the plant is native to Mexico, the African variety is now more appreciated because it has a more intense flavor, with bitter aftertaste, as well as being more economical.
Paradoxically, in the “gourmet” Mexican shops, people is shopping Bourbon vanilla (the African variety), instead of commercializing the local vanilla which grows in this country, that would be greener and authentic
Whatever variety it may be, the good vanilla has crystals on the outside of the pod, which correspond to vanillin when crystallized.
Chemistry of vanilla
Of all the components of vanilla, vanillin is the substance responsible for the characteristic aroma of vanilla ingredient.
Chemically, vanillin is a vanillic aldehyde, which can be classified within phenols, such as eugenol (present in large quantities in clove), isoeugenol (nutmeg), anethole (anise) or thymol (thyme).
This aldehyde is a crystalline organic white substance, which can be observed as crystals on the surface of the mature and dry fruits (vanilla pods).
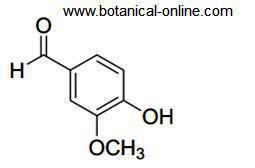
Chemical name: 3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
Molecular formula: C8H8O3
Chemical structural formula: (CH 3) (OH) C6H3CHO
Currently, the chemical industry has managed to make this molecule artificially, making the addition of this food in drugs or cosmetics to provide the “same” aroma.
Recipes with vanilla
Vanilla is used mainly in sweet recipes: ice cream, cookies, chocolates, confectionery, etc.
Also we can find it mixed with black tea, or Rooibos or aromatic tea blends.
* See vanilla-recipes
Where to get vanilla?
Vanilla pod (the dried fruit) is not found in all food stores, although it is increasingly common in some large areas.
We can find it in shops specialized in nutrition, some specialty stores teas, or in some large supermarkets.
![]() More information on vanilla.
More information on vanilla.