Contents
- 1 Harmful health effects of sugar
- 1.1 What is sugar and in what foods is it found?
- 1.2 Why is sugar unhealthy?
- 1.3 Sugar causes cavities
- 1.4 How to avoid having cavities?
- 1.5 Why is natural sugar not harmful?
- 1.6 Beware of juices and sugar
- 1.7 Sugar, a nutrient thief
- 1.8 Sugar increases the demand for B vitamins
- 1.9 Sugar can lead to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- 1.10 People with obesity should avoid sugar consumption
- 1.11 Sugar creates addiction to refining
- 1.12 Psychological effects of sugar
- 1.13 Consuming a lot of sugar is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular accidents
- 1.14 Consuming sugary products increases the risk of osteoporosis
- 1.15 Sugar gets old!
Harmful health effects of sugar
What is sugar and in what foods is it found?

Sugar is a refined product that is found in its pure form, as a sweetener, or as part of numerous ultra-processed products that are not healthy, such as snacks, breakfast cereals, nectars, sugary yogurts, industrial pastries, etc.
We can also refer to sugar as a nutrient naturally present in foods, such as fruits, sugar cane, sugar beets, fruit juices, and dried fruits.
Why is sugar unhealthy?
Sugar is harmful mainly when used as a sweetener, not when ingested in the form of natural foods. The consumption of sugary products has been linked to:
- Child and adult caries (especially during pregnancy)
- Increases the body’s requirements for B vitamins.
- Craving for sweets
- Increased risk of obesity, which worrisomely affects children.
- Increased cardiovascular risk
- Increased risk of diabetes
- Increased risk of osteoporosis
- Sugar gets old!
Sugar causes cavities
Numerous epidemiological studies link the excessive consumption of simple sugars with the formation of dental caries. This effect occurs because the sugar feeds the bacteria naturally present in the mouth, resulting in the growth of certain types of cariogenic bacteria, which cause tooth decay.
Tooth decay is a growth of a type of microbes, called cariogenic bacteria (Streptococcus mutans), that grows when you eat a lot of sugar. Cariogenic bacteria transform sugar into lactic acid, which lowers the pH of the mouth and attacks tooth enamel.
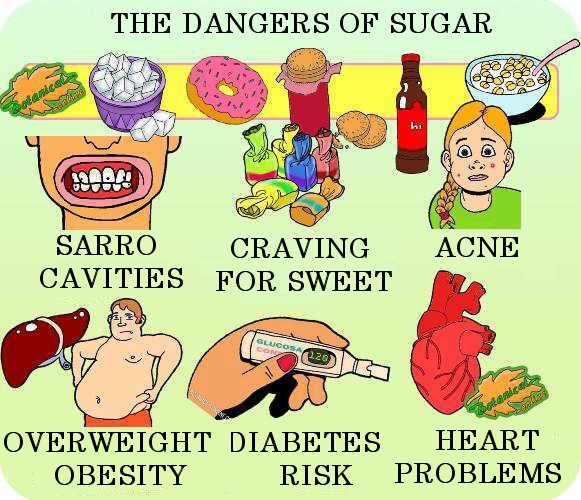
Main harmful negative effects of the consumption of sugary products for health.
How to avoid having cavities?

The best way to avoid these effects of sugar is not to consume sugary products regularly and, if consumed sporadically, brush your teeth afterwards.
As a curiosity, drinking Gunpowder-type green tea daily is very good for oral hygiene due to its high content of fluoride and tannins. Eating cheese has also been observed to have a protective effect on the development of cavities.
Why is natural sugar not harmful?
Foods naturally rich in sugars, among which fruits stand out, do not have the drawbacks of refined sugar for two main reasons:
- First, because normally no fruit has as much sugar as any industrial product. For example, a large banana provides (at most) about 20 grams of sugar, and a bun has more than 30 grams of sugar and fast-absorbing flours (among other ingredients …)
- Second, natural foods have beneficial components, such as those found in bananas: fiber, potassium, magnesium and antioxidants, being nutritious and healthy foods. On the other hand, sugary products are also harmful for other components, such as bad fats, a lot of salt (even if they are sweet) and harmful additives that make us eat more than necessary.
For all these reasons, refined sugar cannot be equated sugar naturally present in food.
Beware of juices and sugar
Fruit juices have more sugar than whole fruits and are not routinely recommended because, although they have certain good components from fruits (such as citroflavonoids in citrus fruits), they are also rich in sugar.
This is especially important in children, to avoid tooth decay in the youngest members, normally caused by fruit purees or industrial fruit nectars.
Likewise, it is important to note that other factors such as oral hygiene, the availability of fluoride, the quality of saliva, genetic and hormonal factors are also important in the formation of cavities.
Sugar, a nutrient thief

Nature provides us with foods rich in sugar, along with the necessary nutrients to absorb them (fruit, milk, vegetables, cereals, etc.).
For example, to digest carbohydrates, the presence of vitamin B1, vitamin B2 and vitamin B5 is necessary, vitamins that are found in these natural foods. Biochemistry explains that B vitamins and lipoic acid are cofactors in glucose transformation reactions. (They are cofactors in the reactions of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA and during the transformation of alpha-ketoglutarate into succinyl CoA, in the Krebs cycle).
Sugar increases the demand for B vitamins
In the case of refined sugar, as its name indicates, it is refined, pure: it only contains sucrose. In its composition it has no vitamins, minerals, or any other nutrient; not even water. For the metabolization of sugar, the presence of group B vitamins is necessary. If these nutrients are not provided by the food itself –as happens in natural foods, such as fruits–, the body has to provide them from its own reserve.
In other words, consuming foods with a lot of sugar increases the requirement for B vitamins.
Sugar can lead to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
Insulin is a hormone secreted in the pancreas responsible for lowering blood sugar levels when it is increased or in cases of hyperglycemia. When the pancreas releases insulin into the blood, it communicates with the cells through receptors that each cell has on its membrane. When cells take up insulin, they work by converting sugar into fat, thereby lowering glucose levels in the blood.
It has been observed that the excessive and continuous consumption of refined sugars produces insulin resistance, that is, that insulin is less and less efficient, due to the cellular receptors responsible for capturing the message of insulin (reducing sugar). In other words, they do not work as effectively.
This causes high blood glucose levels, which if not controlled, can trigger disorders such as anxiety to eat sweets or metabolic diseases in the future.
Imbalances of blood sugar levels, can cause long-term hyperglycemia, adult diabetes ( type 2 diabetes), poor circulation, cataracts, healing problems, tingling in the legs, poorly controlled diabetes and its complications.
People with obesity should avoid sugar consumption

People with obesity and diabetes do not tolerate sugar and therefore should avoid consuming it.
When a disease has been established, it is not a question of evaluating the toxicity of sugar, or how much sugar a food contains and how much can be eaten: it must be clear that the person with diabetes does not tolerate sugar, given their metabolic condition. Therefore it does not matter what type of sugar or how much. Sugar should be avoided.
In obesity and diabetes, insulin does not work well (insulin resistance) and high blood sugar levels are produced, which are very harmful because they damage the walls of the blood vessels and the heart, the eyes (retinopathy), in addition of the walls of the nerves (neuropathy).
Sugar creates addiction to refining
Children especially, although in general the entire population, are quickly hooked on the non-nutritive sweetness of refined sugar.
Refined sugar is much sweeter than the natural sugar found in foods, so the taste buds get used to this intense sweet taste and lose the pleasure of the natural sweetness of other natural foods.
As a consequence, it is possible that the consumption of sugar (chocolates, industrial juices, etc.) displaces other healthier products from the diet (fruit, dried fruit, nuts, bread, sweet potatoes, etc.).
In fact, if we ask a child to name us “naturally sweet” foods, It is a success that he gives us a vegetable as an answer, beyond fruits, like for example pumpkin, carrot, onion, parsnip or cinnamon. We propose sweet recipes compatible with your day to day.
Psychological effects of sugar
The carbohydrates provided by food are transformed into glucose, the sugar that circulates in the blood. Taking into account that glucose is almost the only substrate of neurons, it is indisputable that the quantity and quality of this nutrient in the diet can directly affect the nervous system and mood.
Consuming a lot of sugar is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular accidents

Studies show that populations with high sugar intake are more likely to suffer from risk factors for heart disease, such as obesity, cholesterol, or poor circulation.
In a study published in 2014, this relationship was confirmed in the US population: High sugar consumption was associated with higher mortality from cardiovascular accidents. In addition, the study highlights the high consumption of sugar among the US population, its intake being much higher than the limit allowed by health organizations.
Consuming sugary products increases the risk of osteoporosis
Several important studies have confirmed the relationship between the consumption of sugary products and the increased risk of bone problems, such as osteoporosis. Very especially, sugary drinks are related to these problems, which contain, in addition to sugar, carbonic acid that increases the elimination of calcium.
Sugar gets old!
Regular consumption of sugary products ages the skin. High blood sugar levels promote protein glycation, such as glycated hemoglobin (a marker used to assess diabetes), but also other body proteins, such as collagen.
The proteins that give elasticity and smoothness to the skin can also be glycosylated, so that the sugar binds to its structures and these lose their properties. Poorly controlled diabetes and high sugar levels help the skin to age earlier.
* Related information:
– Why do we crave for something sweet?
– Differences between refined sugar and natural sugar
![]() More information on sugar
More information on sugar








