Contents
How to obtain plant proteins
VEGETABLE PROTEIN IN THE DIET
How to get vegetable protein?
“Pure” vegetarians have enough plant foods to meet their protein needs. Among the vegetable rich-protein foods, we have legumes, whole grains and nuts.
Ovolactovegetarians, besides using the above groups, can get proteins with the ingestion of milk, dairy products and eggs.
It should be noted that vegetable proteins are of lower quality than animal protein because they have deficiencies in amino acids (limiting amino acids).
However, the combination of different groups of plant foods achieves to provide very healthy proteins.
SPECIAL SOURCES OF VEGETABLE PROTEIN
There are another “alternative foods”, derived from plant foods , containing a great wealth of plant proteins. Among the main sources of vegetable protein,w will include the following:
Plant proteins from soy products
|
– Soybean is a legume that is consumed in the East for centuries. Given its high protein composition, in recent decades this crop has grown exponentially, being highly use in the food industry, both for human consumption and for feed production.
The result of this exploitation is leading to ecosystem disturbances in some places because of intensive soy monocultures.
Soy protein is notable because it is rich in amino acids, especially lysine. It also contains essential fatty acids, lecithin, fiber, magnesium and isoflavones.
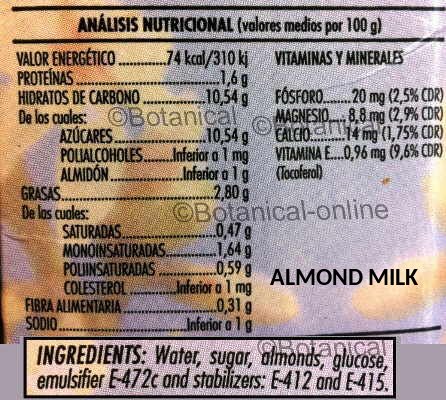
– Soy drink: It is the richest source of plant protein among vegetable drinks, and it also provides more magnesium than cow’s milk. It is recommended to consume it calcium-fortified.
– Yuba: It is is a food derived from soy. It is obtained by boiling soy drink until it creates, such as milk, a thin layer on the outside that is commonly referred to as “soy cream” or ” tofu skin.”
– Tempeh: Tempeh is a food derived from soybeans, which has a high protein content. This is obtained by fermentation of grain legume by a fungus called Rhizopus oligosporus and later baking .
– Tofu: It is made from curdled milk obtained from cooking soybean seeds. It is considered a vegetable substitute for meat because it has a firm texture and high protein content.
– Soy protein: It is made from extruded soybeans. It has a spongy texture and gray or cream color. It is the less nutritious derivative, as it does not contain the other components of the grain (fiber, fatty acids, minerals, vitamins, etc.)
The limiting amino acid of these products is methionine, a sulfur-containing amino acid that can be found in cereals and nuts. For this reason, it is appropriate, in recipes, to combine legumes with cereals (bread, rice, flour, etc.) and / or nuts (especially sunflower seeds and sesame or tahini,).
Plant proteins from cereal products
– Gluten: It is the quintessential protein that can be found in many cereals, such as barley, wheat, oats and rye. Celiac patients can not consume it and should otain proteins from other food sources that do not contain it.
– Brewer’s yeast: It is a food that results from the fermentation of barley, which produces beer. The sediment that is deposited is treated and is often used as food supplement thanks to its nutritional content. It is a food with high protein content, minerals and vitamins. Not suitable for people with celiac disease because it contains gluten.
Photo of wheat germ ready to eat |
– Wheat germ: It is the core of cereals grain, where most nutrients are concentrated, hence it is high in all of them. It has a high caloric content, because it contains mono- and polyunsaturated fats. Especially rich in vitamin E, but it also has significant amounts of protein, B vitamins and minerals. It is also often used as a food supplement like the previous two, in situations of nutritional deficiency. Not suitable for celiac patients since it contains gluten.
– Seitan: Seitan is a food that is derived from wheat. In the central part of the wheat kernel it is contained the so-called wheat germ. It is the part that is commonly used as a dietary supplement because of the large amount of nutrients it contains. It is particularly rich in lipids, proteins and vitamin E. It is not suitable for celiac
The limiting amino in cereals acid is lysine, an amino acid that can be found in legumes. For this reason, it is desirable to combine cereals with legumes (soybeans, peanuts, etc.).
Proteins from bee products
– Pollen: It is a food that bees obtain from flowers. Its protein content is high but lower than yeast, though, in this case, it does not contain gluten and it is suitable and a great choice for celiac patients. Pollen is usually prescribed as reinforcing and by its high content of beta carotene.
Plant proteins from seaweed products
– Algae: They contain interesting protein levels, but they are not considered substitutes for other protein foods themselves, because the amount that can generally be consumed is relatively small, so they would not cover our needs, if consumed alone. But, if we combine it with other protein foods, they can help increase the ingested protein level.
– Spirulina: Spirulina proteins contain all the essential amino acids, from which the body builds its architecture. It is a nutritional supplement, sold in tablets, used as an excellent fortifier and tonic. Their proteins are of better quality than any plant.
VIDEO ON VEGETABLE PROTEINS
* Related information:
– How to combine vegetable proteins
![]() More information on amino acids.
More information on amino acids.