Contents
(Panicum miliaceum)
What is millet?

Botanical illustration of millet
Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) is a cereal.
It has long stems ending in spikes where seeds, that are the grains of millet, will appear.
These grains are covered by a brown layer called pericarp.
If we remove this layer, we get the millet grain in its natural form, lighter brown on the outside and beige, almost white, inside.
Millet has a mild and neutral taste.
Multiple elaborations can be performed with this cereal, both sweet and savory, such as soups and stews, as an accompaniment to a dish; substitute for pasta or rice; germinated, in salads either cooked or sprouted buds,
What does millet provide? Composition of millet
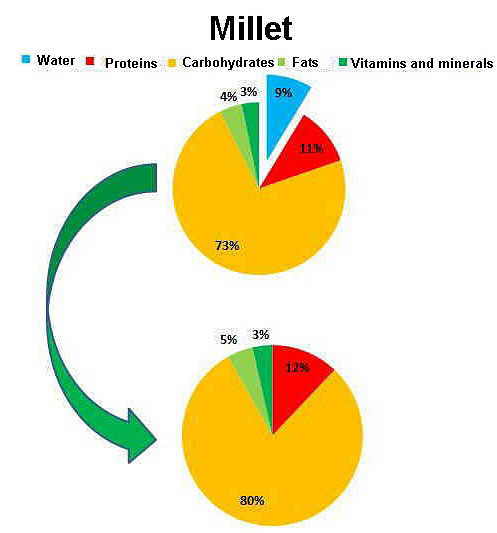
Nutrients of millet
As an energy source, 100 grams of millet give us 378 kilocalories.
Their proportion of nutrients is divided into:
- Nearly 8% is water.
- 4.22%, fat.
- More than 11% protein.
- More than 73% carbohydrates.
- 8.5%, fiber.
Minerals of millet
Millet is a cereal rich in potassium, magnesium, and phosphorus. It also contains calcium, iron, zinc, manganese and selenium, and even small amounts of copper and sodium.
Vitamins of millet
Referring to vitamins, millets is rich in B vitamins, particularly vitamin B3(niacin) and vitamin B9 (folic acid), but it also provides us with vitamin E.
Millet benefits

Photo of millet grain, raw and cooked.
- It has a low water content, being a cereal.
- It gives us a lot of energy in the form of calories, which help us maintain our vitality.
- It contains little quality fat with a lot of health benefits.
- It has a high protein content.
- It is very high in carbohydrates, especially starches.
- It has a very high fiber content.
- It helps to remove toxins from our body, because it contains potassium.
- It helps to maintain our brain function in good health, because of its phosphorus content.
- Being rich in magnesium, it helps the contraction and relaxation of muscles.
- Because of its manganese content, it helps keep our brain and respiratory system in proper condition.
- Being rich in iron, it helps us to prevent anemia.
- As a result of its content in B vitamins, particularly vitamin B3 and vitamin B9, it helps us get energy from fat, protein and carbohydrate from food, to grow properly and maintain our defenses in good condition.
- It protects us from toxins and aging, because it contains vitamin E, selenium and zinc.
How to eat millet
We can prepare, for example, the following recipe:
![]() More information on millet.
More information on millet.








