Contents
- 1 LENTILS CHARACTERISTICS
- 1.1 What are lentils?
- 1.2 Description of lentils
- 1.3 Origin and history of lentils
- 1.4 When were lentils cultivated for the first time?
- 1.5 Lentils in the ancient times
- 1.6 Lentils nowadays
- 1.7 Species of lentils
- 1.8 Varieties of lentils
- 1.9 Small, rounded lentils
- 1.10 Large lentils
- 1.11 Production of lentils in the world
LENTILS CHARACTERISTICS
What are lentils?
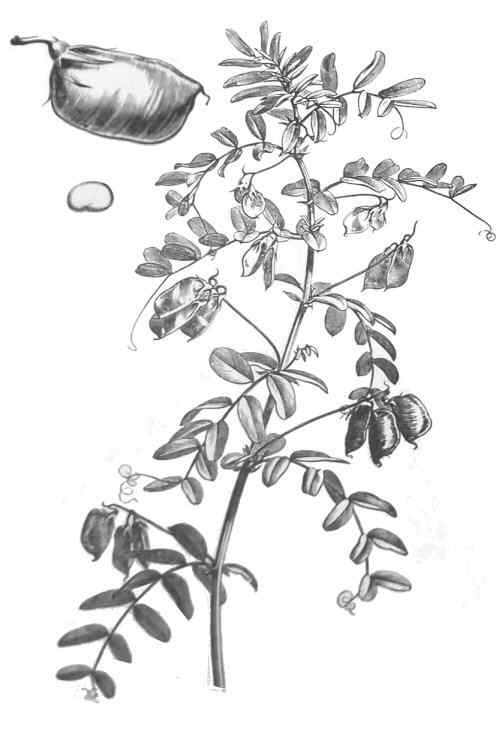
Drawing of this plant. In the superior part, on the left, a detail of a fruit and a seed.
A lentil (Lens culinaris Med = Lens esculenta Moench) is a plant of the Papilionaceae family, the same family where there are trees as well known as carob tree or grasses such as clover.
Beans, or peas are also plants of the same family used by the food value of the seeds enclosed in their fruit pods.
Description of lentils
A lentil plant is an annual herb up to 75 cm tall.
Stems angular, thin, bearing a great hairiness.
Leaves compound, alternate, provided up to 7 pairs of oval leaflets without petiole.
Flowers of different colors (white, pink, purple, etc.) gathered in groups up to 4 on long stems.
The fruits are pods from 1.5 to 2 cm in length within which there are two flattened seeds about half a cm wide also called lentils, that are edible.
It is a plant that is cultivated in many parts of the world, although is can also be found in the wild because it has become feral
Origin and history of lentils
It is unclear the real origin of lentils though some historians put it at the Far East, southwestern Turkey or northern Syria where they seem to be collected along with other wild plants such as oats. Apparently in these areas even today you can find the species in the wild (Lens culinaris subsp. orientalis).
No one knows exactly when they started to be grown. The first remains of lentils have been found in excavations in Syria for more than 11000. In this case, they consist on collected seeds from wild plants.
When were lentils cultivated for the first time?
Found in archaeological Turkish remains (excavations Halicar), lentil seeds were cultivated about 5500 BC, but the oldest remains of cultivation dating from 6600 BC and were found in Israel which makes them one of the most ancient food cultivated by man almost 9000 years ago.
They were widely used by the Egyptians who considered them a staple food, along with beans or wheat. In Egypt, its richness in proteins greatly helped the slaves who built the pyramids. It is known that Egypt lentils were dark red and small. Geshem, later known as Facusa, was an Egyptian city that was called the “city of lentils.”
Lentils in the ancient times
Later, they were used by the Greeks and Romans. Romans dried and kept them in their pantry for the famous Roman lentil soups available along all year.
Lentils were eaten by people throughout the Middle Ages.
Lentils nowadays
However, as we move toward our days, lentils were losing their reputation in favour of peas, and were relegated to a commonly used type of food for the poor or during times of scarcity. Often this legume has been used to feed livestock, especially pigs.
Today, they are mainly grown in the Far East, North Africa and Europe. On Europe, they can be found in all countries bordering the Mediterranean. Along the Atlantic coast, lentils cultivation expands from southern countries till Germany.
Species of lentils
Among the wild species of lentils we must consider the following:
- Lens culinaris: Species from which derives the cultivated lentil (Lens culinaris Med). It is divided into four subspecies:
- Lens culinaris ssp. culinaris.
- Lens culinaris ssp. orientalis.
- Lens culinaris ssp. tomentosus
- Lens culinaris ssp. odemensis
- Lens nigricans
- Lens lamottei
- Lens ervoides
The cultivated species (Lens culinaris Med) has two groups:
- The Microesperma group or green lentils group: normally occur in southern Europe, North Africa and America. They are higher plants with more elongated pods and with larger seeds. These are flattened and generally containing yellow cotyledons,
- The Macroesperma group consists of red lentils. They are smaller plants that have smaller and rounder seeds . The cotyledons may vary from yellow to black. This group of lentils is found in Asia, Ethiopia and Afghanistan.
Varieties of lentils
There are many varieties of lentils grown. Among them we could mention the following according to their size and aspect:
Small, rounded lentils
- Beluga Lentil: It’s a very small shiny black lentil that takes its name from the resemblance it has with caviar. Mainly used for salads and soups, it has a cooking time of about 20 minutes over low heat. Among the lentils, it has a higher proportion of protein.
- Pardina lentil: It is called brown lentil. It’s a small lentil that melts when cooked. It is rich in carbohydrates. It is earthy brown or reddishbrown with yellow interior. Especially suitable to combine with pasta and salad or a Mediterranean dish. It must be cooked on a low heat, having a cooking time of about 30 minutes.
- Puy lentil: Also called “green Puy”, comes from the French region of Puy. It is said to be the preferred lentil by great chefs both for its taste and for its ability not to disaggregate when being cooked. It is preferred in Europe and served in the best restaurants, widely used in soups with herbs, in soups and salads. It is bluish green and a little smaller than Verdina lentil. You need simmering them for about 30 minutes.
- Verdina Lentil: Small and green, verdina lentil is most used in South America where it appears frequently in baked dishes and stews sauce combined with chilli. You need about 35 minutes over low heat to cook it well.
- Urad Dal Lentil: A lentil from India. It has a size about half a cm and an ivory white color. Its protein content is very high, so it was harvested in this country to replace meat.
Large lentils
- Queen lentil: One of the largest lentils. It is yellow and flattened.
- Armuña lentil: Also called Armuña Blonde by its yellow color and the growing area that gives it the appellation of origin (region of Monterrubio of Armuña, located north of the province of Salamanca in Spain). Armuña lentil is a very large one, being considered one of the tastiest in the world.
- Peeled lentils:
- Crimson Lentil: Native from Turkey, it is a very suitable lentil for pureeing. Its cooking time is about 10 minutes.
- Red chief Lentil: Also known as Egyptian lentil. You can eat it peeled. In India they are known as Masoor dal. They are consumed in abundance in Pakistan.
Production of lentils in the world
The main producers of lentils in the world are, in order of production, India, Canada, Turkey, Syria and Australia.
Although India is the country that produces more lentils, all the production is for domestic consumption and still needs to import more lentils from abroad to meet their needs.
Canada is the largest exporter in the world. Other exporting countries are Turkey, United States, Syria and Australia.
![]() More information on lentils.
More information on lentils.