Contents
Types of grapevines
Species of vines
Grapevine (Vitis vinifera) is a plant native from Asia Minor and the Caucasus, naturalized in the Mediterranean region and North Africa.
Among the main grapevine species, different to Vitis vinifera, we distinguish those from America and those from Asia:
| EVALUATION CRITERIA FOR CHOOSING A STRAIN – Quality of the fruits – Resistance to phylloxera. – Adaptation to the type of terrain and climate (dry, chalky soil resistance, etc..) – Ease of multiplication of the strain. – Compatibility with the species to graft (if affinity with V. vinifera grafts). – Resistance to nematodes which may affect crop |
American grapevines

- Vitis riparia: known as River Bank Grape or Frost Grape in English, it is a species native to North America, widely grown in United States It is characterized by luxuriant vegetation and creeping habit. Their roots tend to be shallow and reddish. The leaves are wider and particularly elongated, discrete lobed and dark green.It is resistant to phylloxera, affinity for grafts and easy propagation by cuttings. Fits loamy, loose, deep and shallow limestone. It tolerates drought and compacted soils.From it, derives the variety Gloria from Montpellier (Vitis riparia var. Glory of Montpellier). This variety requires deep, fertile, fresh soils, something loose and non chlorous.
- Vitis rupestris: originally from U.S.A, this is a vigorous vine with thick, deep roots, reddish and quite wide branches with nodes. It has high resistance to phylloxera and ease of grafts, but sometimes it is not very productive. Tolerant to drought and poor soils, the main rootstock is Rupestris Lot, widespread in Spain. Rootstock incompatible with Grenache, Chardonnay and Merlot (produces the shift of the flower).
- Vitis berlandieri: native to North America. Strains creeping, with hairiness in the branches. Leaves almost entire, with little pronounced lobes.It is resistant to phylloxera, but less than the two previous species. Tolerant to calcareous soils and drought. However, it is not goog as rootstock, as their stakes have difficulty taking root. Shortly cultivated in Spain.
Asian grapevines
- Vitis amurensis: species native to China and Russia, very resistant to frost (it tolerates temperatures below -40 º C), and very resistant to drought. Currently not cultivated for production, but mainly as an ornamental.
Main species and varieties of grapevines
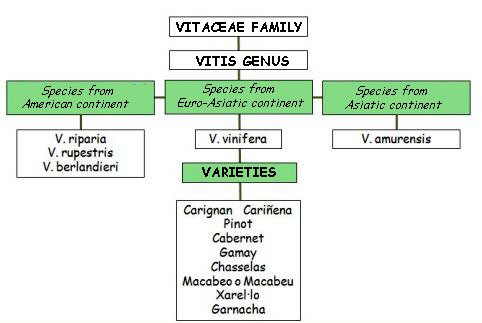
Scheme of the main species and varieties of grapevines
Strains for the production of grapevines
Such strains are the strains used in viticulture. We have to distinguish between white and red varieties, which are used for producing different types of wine
Grapevine white varieties
- Chardonnay: recognized as the finest white grape variety. It is used to produce high quality wine and especially champagne. The variety comes from France, Burgundy.
- Xerel·lo or Xarelo: its name comes from the Italian sciarello, meaning “clear color”. Strain vigorous and long-lived, with good affinity with the rootstock. Rustic variety that tolerates drought and it is very productive. The fruit is sweet and it is used to produce a high quality champagne.
- Parellada: The finest grapes and most difficult to cultivate. It comes from Catalonia. It is basic in developing cavas.
- Macabeo: Used for the production of sparkling wine (“cava”)and white wine from Rioja. It is advisable aging it in oak containers due to its poor oxidation. It is also called Viura.
| Did you know… The grape seems to be a fruit specially designed for the production of wine: it contains a wealth of sugars, abundant juice, and a natural tendency to ferment due to the abundance of yeasts in fruit |
Red and black varieties of grapevines
- Cabernet Sauvignon: traditional strain from Bordeaux (France), recognized as a variety of the highest quality. It produces small clusters, conical, short and slightly lignified stem. The purple skin grapes have are rich in flavonoids. It is the most used for red wines.
- Malbec: grape variety from France, much used for making red wine. Now cultivated worldwide, and mainly found in the great wines of Argentina. It has a high tannin content. The strains are susceptible to frost and fungal diseases that affect grape growing.
- Carignan or Mazuelo: Spanish grape variety, native theoretically from Carignan (Aragon, Spain). In Catalonia (Spain) it is known as samso. It is a traditional wine with Denomination of Origin of Rioja.
- Grenache: Spanish wine variety of attractive purple. This variety is easy to grow. Late, vigorous and productive. There is a variety of red and white grapes that it is one of the most used in mixtures.
- Tempranillo or cencibel: grape variety native to Spain. Its name refers to the fact that it is an early variety, it matures earlier than most grapes. It produces wines with an attractive body and reddish color. In Portugal, it is used to mix with other sines to produce port wine.
![]() More information on grapes and wine.
More information on grapes and wine.