Contents
- 1 Nutritional and medicinal benefits of dry figs
- 1.1 CHARACTERISTICS OF DRY FIGS
- 1.2 What are dried figs?
- 1.3 Why are figs dried?
- 1.4 How are figs dried?
- 1.5 What do dried figs contain? Composition of dry figs
- 1.6 Nutritional composition of dry figs
- 1.7 Minerals in dry figs
- 1.8 Vitamins in dry figs
- 1.9 BENEFITS OF DRY FIGS
- 1.10 Dried figs are very energetic
- 1.11 Dry figs for constipation
- 1.12 Dry figs for anemia prevention
- 1.13 Dry figs, very rich in calcium
- 1.14 Dry figs, against cough and cancer
- 1.15 Dry figs, very important in Man History
Nutritional and medicinal benefits of dry figs
| Fruits of winter 1 | Fruits of winter 2 | Fruits of winter 3 |
CHARACTERISTICS OF DRY FIGS
What are dried figs?

Dry figs are the fruits of the fig tree (Ficus carica) once they have been dried.
Figs have a shape similar to pear, but with a thicker and smoother skin.
The color of the skin indicates its state of maturation, varying from light green to dark black, as the fruit ripens.
If we peel a fig, inside it contains an edible pulp of an intense red color with multiple small white seeds.
The dried figs are dehydrated figs, that is, figs whose water has been removed.
Why are figs dried?
The drying of the figs is done to preserve them throughout the year.
By eliminating water, an environment is established where bacteria have more difficulty developing
This method allows to have a fruit that has very short duration in raw but that can be preserved , when preservation has been is made by hand, throughout the year when it has undergone the drying process.
In an industrial use, the vacuum packaging allows a much longer storage than when it is packaged with homemade methods.
How are figs dried?

Traditionally the drying of the figs has been done manually, placing the figs spread on hurdles placed in the sun.
This process is still being done in rural communities
Most dried figs sold in the market are dried with industrial processes using dehydration ovens .
(See how to dry fruits)
What do dried figs contain? Composition of dry figs
As an energy source, 100 grams of dried figs provide 255 kilocalories.
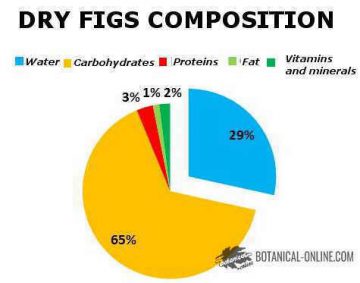
 Nutritional composition of dry figs
Nutritional composition of dry figs
Its proportion of nutrients is divided into:
- More than 28% is water.
- More than 1.17% of fats.
- More than 3% of proteins.
- Close to 64% carbohydrates.
- Almost 10 % fiber.
Minerals in dry figs
It is a fruit very rich in potassium, magnesium, calcium and phosphorus, but it also contains sodium, iron, zinc, selenium, manganese and copper.
Vitamins in dry figs
They are rich in vitamin A, vitamin C and vitamins of group B, especially vitamin B9, but the also contain vitamin E.
BENEFITS OF DRY FIGS
The most important properties of a dry fig are the following:
- It has a good content in water that prevents us from getting dehydrated.
- It gives us a lot of energy to have vitality during the day.
- It is a poor source of fat and protein.
- It has a very high content of carbohydrates, specifically in sugars.
- It has a moderate fiber content.
- It helps us eliminate toxins from our body, because of its potassium content.
- Calcium together with phosphorus, maintains the balance of the formation of strong bones.
- It helps us maintain correct brain functions, due to its content in phosphorus and vitamins of group B.
- For its content in vitamin B9 it helps to grow properly.
- Magnesium helps the muscles relax.
- It protects our skin and helps keep it healthy, due to its vitamin A content.
- It protects us from colds and helps to heal wounds, due to its vitamin C content.
- It protects us from toxic substances and aging, due to its vitamin A, C and E content and the minerals selenium and zinc.
Dried figs are very energetic

Dried figs are extremely energetic – 250 kcal per 100 grams compared with 220 kcal for the same weight of pork chops
Very high in calories, figs are great for energy during the icy winter days. They are very nutritious for children and for athletes, especially the “fig bread” formed by these fruits when dried, mixed with almonds.
An older combination, easy to prepare, has been called “Nougat for the poor”; it consisted in opening a dried fig in half and place a sweet acorn inside. This could be replaced by a peeled almond.
Dry figs for constipation
Dry figs are very rich in fiber so that they regulate intestinal transit.
Dry figs for anemia prevention
Their richness in iron and vitamin C and B makes them very suitable for the manufacture of red blood cells, much needed to prevent anemia.
Similarly, they contain much potassium, a mineral that is essential to regulate body fluids and to control heart rate, nervous system and the production of muscle mass.
Dry figs, very rich in calcium
Dried figs have quite a higher amount of calcium compared with the figs – 144 mg 35 mg, respectively, which are suitable for growth and to prevent osteoporosis.
Dry figs, against cough and cancer
We can prepare a syrup against cough based on 6 dried figs cooked per glass of water, until the liquid becomes thick. We will take four tablespoons per day.
In addition to these traditional uses as nutritious, dried figs, according to recent research, are considered anti-cancer food.
Thus, we should dry the fresh figs, collected in summer and autumn, to take advantage of all its virtues, even increased, when winter comes. For this purpose, extend over canes in the sun. Then place them in cardboard or wood boxes, rather dry.
Dry figs, very important in Man History
Given the nutritional capacity of this fruit and its many healing properties, figs have had a great importance throughout history.
This fruit has a fundamental role in classic mythology.
The fig tree was considered sacred by the Romans, so it was especially dedicated to the god Bacchus.
We must bear in mind that a fig tree was the tree where the wolf that suckled Romulus and Remus lay
In major parties Roman people offered the figs as an offering to those who visited their home and, in many writings of this culture, there are continuous references to this fruit.
| Composition of dry figs compared to raw figs by each 100 gr. | ||
Dry figs | Raw Figs | |
| Water | 30,05gr | 79.11 gr. |
| Calories | 249 kcal | 74 |
| Fat | 0,93 gr. | 0,30 |
| Protein | 3.30 gr. | 0.75 |
| Carbohydrates | 63.87 gr. | 19,18 gr. |
| Fiber | 9.8 gr. | 2,9 |
| Calcium | 162 mg | 35 mg |
| Potassium | 680 mg | 232 mg |
| Iron | 2.03 mg | 0.37 mg |
| Magnesium | 68 mg | 17 mgs |
| Phosphorus | 67 mg | 14 mgs |
| Sodium | 10 mg | 1 mg |
| Vitamin A | 10 IU | 142 UI |
| VitaminB1(Thiamin) | 0.085 mg | 0,060 |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.082 mg | 0, 050 |
| Vitamin C | 1.2 mg | 2 mg |
| Vitamin E | 0,35 mg | |
| Fruits of winter 1 | Fruits of winter 2 | Fruits of winter 3 |
![]() More information on figs.
More information on figs.

 Nutritional composition of dry figs
Nutritional composition of dry figs