Contents
Nutritional benefits of frozen vegetables
BENEFITS OF FROZEN VEGETABLES
How to freeze vegetables?
Freezing vegetables is a process of preserving vegetables which is done by very low temperatures (-40 º C) after having been collected and washed properly. Most vegetables can undergo this process. (See different methods of preserving vegetables)
Properties of frozen vegetables

Photo of frozen vegetables
Frozen vegetables do not have the same properties as fresh ones as many of their vitamins and minerals disappear in the process prior to freezing.
In addition to being submitted to washing with water at room temperature to remove impurities strong, vegetables are subjected to a blanching for a few seconds at 98 º C. Thus, enzymatic processes are inactivated, which can damage their appearance and impair their quality.
These processes, along with transportation and storage, decrease these foods richness in vitamin B and vitamin C, which are water soluble and degrade with heat.
It is estimated that the entire frozen vegetables can lose up to 50% of vitamin C before being introduced into our freezer and in the case of vegetables cut and ready to eat, the loss can be up to 75%.
What are best fresh vegetables or frozen vegetables?
Whenever possible, choose fresh vegetables to frozen. Frozen vegetables have lower nutritional value than fresh, but they are more practical, affordable and easier to maintain. (More information)
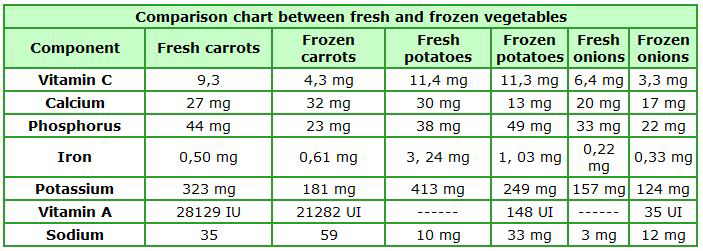
The following table shows the content of some vitamins and minerals from fresh and frozen vegetables.
Frozen foods also need to be stored properly
Remember that, when purchased in the market, as all frozen food, frozen vegetables should be purchased at the end of the purchase and kept in a special bag to keep them frozen.
Later, take them home and introduce them in the freezer as soon as possible. (More information)
![]() More information about vegetables.
More information about vegetables.