Contents
ACEROLA AS FOOD
What is acerola?
Acerola or West Indian cherry is a small fruit, 1 – 3cm. in diameter, which comes from a fruit tree called acerolo or acerola (Malpighia emarginata).
Acerola receives interest in the enormous wealth of vitamin C that contains, being one of the richest fruits in this vitamin.
Acerola contains an astounding 1,000 to 4.000mg. vitamin C per 100g. (Depending on maturity). More information: Table of vitamin C from food.
Nutritional value of acerola
Acerola is a fruit rich in pectin fiber, with regulatory properties for the intestinal transit. Its carbohydrate content is low, so it can be consumed by people with diabetes.
Acerola fruit is an antioxidant par excellence. It contains vitamins and phytochemicals with antioxidant functions, acting as potent anti-aging agents or antioxidants.
- High in vitamin C: acerola attains a potentially very interesting result as a dietary supplement of vitamin C, because of the many properties of this vitamin for health.
Food rich in vitamin C, such as acerola, are very convenient to help treat diseases and conditions resulting from body oxidizing. We speak of diseases such as fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, chronic fatigue, arthritis or rheumatism.
Smokers or stressed people can also benefit from the antioxidant effects.
- Tannins: Tannins are responsible for the harsh taste of the fruit when we take it uncooked. Tannins also have antioxidant effects.
Tannins form a protective membrane, helping to protect the gastrointestinal mucosa. For this reason, acerola juice is used for its protective properties to help treat gastritis.
- Natural antioxidants: in addition to vitamins, acerola contains many other components with antioxidant properties for health. These substances help to work and regenerate the body.
Among them, it has carotenoids which are beneficial for the hearta and skin; anthocyanins, that prevent capillary fragility, and flavonols such as quercetin and rutin, benefiting circulation.
* Further information: see medicinal properties of acerola
| Components of Barbados tree per 100 g | |
Nutrient | Content |
| Calories (kcal.) | 32 |
| Carbohydrates (g.) | 6,60 |
| Proteins (g.) | 0,40 |
| Fats (g.) | 0,30 |
| Fiber (g.) | 1,10 |
| Vitamin C (mg.) | 1678 |
| Vitamin B1 or thiamin (mg.) | 0,02 |
| Vitamin B2 or riboflavin (mg.) | 0,06 |
| Vitamin B3 or niacin (mg.) | 0,40 |
| Vitamin E (mg.) | 0,13 |
| Calcium (mg.) | 12 |
| Phosphorus (mg.) | 11 |
| Iron (mg.) | 0,2 |
| Magnesium (mg.) | 18 |
| Sodium (mg.) | 7 |
| Zinc (mg.) | 0,1 |
Acerola production in the world
Currently, the world’s leading producer of acerola is Brazil, which trades it as frozen fruit pulp.

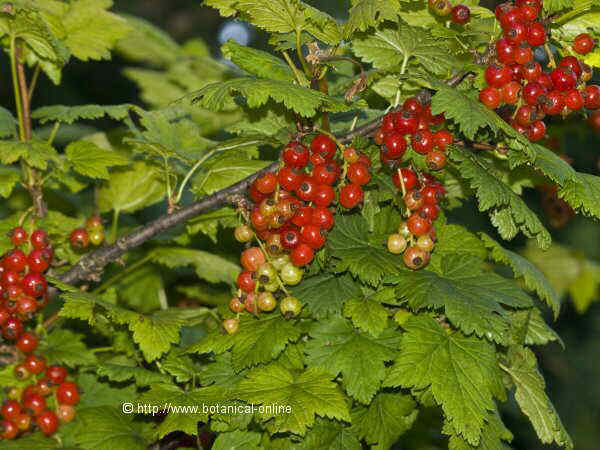
Fruits and branches of acerola
Products from acerola
- Fresh and frozen fruit
- Jams
- Juices
- Concentrated juice
- Capsules
- Tea from its bark
- Dyes and cosmetics
Where to buy fresh acerola?
Fresh acerola is available in local supermarkets in countries where the fruit is grown. Because of its fragility during transportation and because of the time that may elapse from harvest, transportation and storage, it is not available as a fresh fruit outside its country of origin.
You must chose turgid fruits with a healthy appearance. they must be free from odors or spots on the skin, and with the fruit stalk.
Where to buy frozen acerola?
Frozen pulp of acerola can be found in food supplies in some supermarkets, but due to the cost and unpopularity of this fruit, it still very rare.
How to preserve acerola?
Fresh fruits can be kept for 3-5 days after harvest. It is a climacteric fruit that can ripen off the tree. Generally, acerola cherries for export are harvested when immature to be consumed when being just right.
![]() More information on acerola.
More information on acerola.