Contents
Health benefits of coconut oil
What is coconut oil?
This oil is obtained from the white colored pulp contained within the seeds of fruit of the coconut
Coconut oil is produced by solvent extraction and in a similar way to other seed oils.
Differences between coconut oil and palm oil
Palm oil is extracted from the fruit of the African oil palm, also called palm oil (Elaeis guineensis). Palm oil is extracted from the layer that is immediately after the crust, that is the mesocarp. It is an inedible fibrous layer.
Coconut oil is extracted from coconut (Cocos nucifera), the inside of the seed of the plant or coconut, and specifically, from the edible white mass (endosperm), which is surrounded by a hardened layer (endocarp).
Coconut oil is more saturated than palm oil since it contains about 90% of saturated fatty acids, whereas palm oil contains up to 50% thereof.
Coconut oil, being the oil having a highest content of saturated fatty acids within the vegetal foods, is the least recommended nutritionally speaking for proper control of cardiovascular health, cholesterol and triglycerides. However, because of its plant origin, it does not rise cholesterol as much as animal fats.
* More information: Coconut oil and cholesterol
What’s in coconut oil?
Its saturated fat composition almost reaches 90 % of its composition. It is formed of medium-chain fatty acids such as lauric (almost 45%), palmitic, stearic and myristic acid.
It also contains small amounts of oleic acid (below 6%), and it practically does not contain linoleic or linolenic acids, that is to say neither omega 3 nor omega 6.
(See composition of coconut oil)
Physical and chemical characteristics of coconut oil
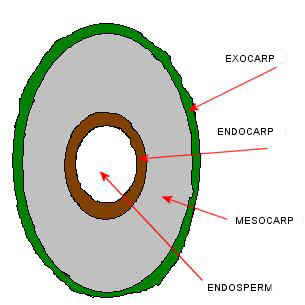
Sectional drawing of a coconut, which shows the different parts of this fruit.
Coconut oil has a slightly yellow color when it is in liquid form, that’s to say, at an ambient temperature of about 25 degrees Celsius.
However, if the temperature is lower, it becomes dense, with white appearance, semisolid or solid if temperature decreases more. Its acidity does not exceed 2 degrees values.
Due to this composition, unlike most vegetable oils, which are liquid at room temperature, this oil is thicker, semi-solid, but not quite as solid as animal fats.
What do you we use coconut oil for?
Among the main uses of coconut oil, there are the following:
- Food uses
It is mostly used in making sauces and margarines, but it is also used in baking, since because its solid characteristic make it ideal to cover some desserts.
- External applications of coconut oil
Being similar to butter, it s an excellent skin moisturizer, not only for its content, but because, being very dense, nutritional effect is more durable and, therefore, more intense.
It is found both in the form of skin creams, face creams, sun lotions, hair preparations, shampoos and even lipsticks.
Obviously, it also used for making soap.
* Related information: Coconut oil for the skin, Coconut oil for your hair, Coconut oil benefits
![]() More information on coconut.
More information on coconut.