Contents
FOOD PROPERTIES OF BORAGE
Borage as vegetable
Borage have been consumed for many years as an edible vegetable.
Some written traces on the consumption of this vegetable are found in the book The New Art of Kitchen taken from the School of Economic Experience (published 1767 in Spain), by the monk Juan Altamiras, where it is used in soups, boiled or in recipes to accompany meats.
The nutritional value of this vegetable stands primarily on its high content of fiber, beta carotene and minerals. Borage contains more iron and magnesium than spinach, plus a wealth of vitamin A.
Borage to remove body fluids
Borages are noted for their high water content and because they are low in fat and carbohydrates. (See Table of composition at the bottom of the page)
They contain 93% water. Its carbohydrate content is a little over 3%. This determines that this food is very light and suitable for people with diabetes.
With its large amount of water and its low percentage of calories, they are ideal for diets and for all those who have problems of obesity.

Photo of borage in a Salamanca market, Spain
In addition to these properties, its high amount of water and its richness in potassium (it is one of vegetables containing most) which counteracts the fact that they are quite high in sodium, makes is a very suitable food for fluid retention.
This vegetable will be very convenient for those people who want to remove body fluids, as people with excess weight, problems of retention from heart failure, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, kidney failure, menopause, etc.
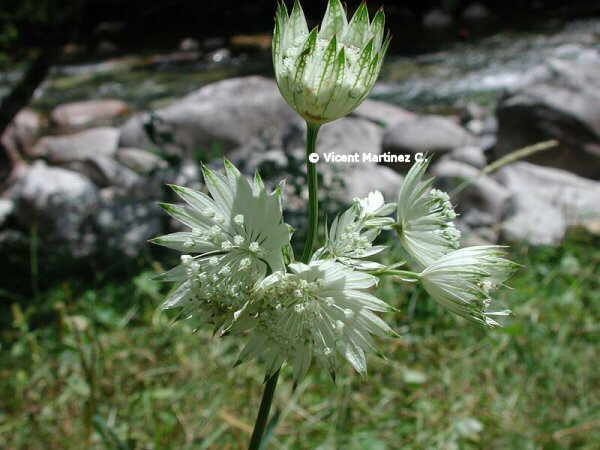
 Borage flowers are edible and can be used to decorate plates
Borage flowers are edible and can be used to decorate plates
Borage contains high amounts of vitamins, especially vitamin C, vitamin A and vitamin B
Vitamin C and vitamin A are two of the best antioxidants, capable of neutralizing the negative effects of free radicals, which can cause many diseases of degenerative nature, including cancer.
It has been demonstrated that food intake of green vegetables can drastically reduce the occurrence of colon cancer.
This property affects both the antioxidant properties of these vitamins as its richness in soluble fiber which increases intestinal transit and promotes a more rapid expulsion of feces in the intestine. This causes less toxins remain deposited in the intestine for less time so they are less likely to act on the cells of the intestinal wall and to develop tumors in them.
Vitamin A in borage appears in the form of carotenes. These are converted to vitamin A in the body. The properties of this vitamin is different. The lack of this element causes night blindness, fatigue, skin or teeth in poor condition, easier to get infections. Vitamin A is necessary to maintain healthy bones and skin, to protect the view, for the formation of red blood cells and to repair accidents suffered by body tissues.
Borage wealth in vitamin A is very large (4200 IU). Among cultivate vegetables, borage has one highest amount, after corn salad (7092 IU) spinach (9900 IU), dandelion (14,000 IU) and carrots (28,000 IU)
Borage, a vegetable with many mucilages
Borage contain soluble fiber in the form of mucilage. Mucilage is what gives the gelatinous and sticky look to borage when cooked.
Mucilage, apart from preventing constipation, is very important to lower the level of cholesterol in the blood and to stabilize sugar levels in the blood. This type of fiber is suitable for patients with diabetes. Also adequate to protect internal mucous, hence its use for the treatment of gastrointestinal irritation (gastritis, heartburn, stomach pain, indigestion, etc)
We must not forget the ability of mucilage to wrap intestinal toxins and to reduce the negative effects of these substances on the cells of the intestinal walls, as well as its capacity to increase bowel movements, to expel these toxins through feces. Therefore, it has been considered that the soluble fiber helps prevent colon cancer and other cancers.
Borage, a vegetable with abundant minerals, especially calcium and iron
Besides containing a lot of magnesium and sodium, as mentioned above, borage contains high amounts of calcium, iron and phosphorus. Calcium and phosphorus are very interesting in bone development and the prevention of bone loss due to osteoporosis.
Iron is essential in the formation of red blood cells and to prevent anemia. Spinach are reputed to be the champions of iron in the plant world (1.5 mg per 100 g of fresh vegetables). However, borage contains more than twice iron than them (3.30 mg).
Borage even outperforms so recognized green leaves foods like amaranth (2. 3 mg). It is slightly surpassed by some cereals such as wheat (3.63 mg), barley (3, 60 mg) and corn (3, 45 mg). On the contrary it is quite widely beaten by oats (4.72 mg), by some legumes such as adzuki beans (4.98 mg) that are far from the amount of wheat germ (6.26 mg) or seeds of amaranth (7.9 mg).
| Edible composition of fresh borage per 100 g | |
| Water | 93 g |
| Fats | 0,70 g |
| Carbohydrates | 3, 06 g |
| Calories | 21 kcal |
| Fiber | 0,9 g |
| Proteins | 1,8 g |
| Potassium | 470 mg |
| Sodium | 80 mg |
| Magnesium | 52 mg |
| Calcium | 93 mg |
| Iron | ../3, 30 mg |
| Copper | 0, 130 mg |
| Zinc | 0, 20 mg |
| Manganese | 0, 349 mg |
| Phosphorus | 53 mg |
| Selenium | 0, 9 mg |
| Vitamin C | 35 mg |
| Vitamin E | – |
| Vitamin A | 4200 IU |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0, 060 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0, 150 mg |
| Folic acid | 13 mcg |
| Niacin | 0, 900 mg |
How is borage cooked?
The young leaves can be eaten as boiled vegetables, either alone or mixed with other vegetables. In this case, it is convenient drinking their broth because it contains all the properties mentioned above. Leaves can be taken raw in salads, fried, sauteed, cheese etc. (It is advisable not to neglet the tender leaves cut for much time because they decompose easily.)
The flowers can be used raw in salads, so they acquire a very exotic touch. (More information about borage recipes)
![]() More information on borage.
More information on borage.