Contents
- 1 Importance of vitamins B12 and B9 in the metabolism of homocysteine
- 1.1 Why should homocysteine be eliminated?
- 1.2 How is homocysteine eliminated?
- 1.3 Vitamins that decrease homocysteine
- 1.4 How B vitamins eliminate homocysteine
- 1.5 What is the methionine homocysteine cycle?
- 1.6 Outline on the metabolism of homocysteine
- 1.7 .Vitamin B6 in the elimination of homocysteine
- 1.8 What is the use of knowing the cycle or metabolism of homocysteine?
- 1.9 What conclusion do we have of all this?
Importance of vitamins B12 and B9 in the metabolism of homocysteine
Why should homocysteine be eliminated?
Homocysteine is a substance present in the blood that the body produces itself, as a residue of the metabolism of other substances. The problem of homocysteine is that, if it accumulates, it circulates and progressively damages the blood vessels and the heart. High levels of homocysteine in blood are related to the formation of atheromatous plaque that clogs the arteries.
How is homocysteine eliminated?

A healthy diet and lifestyle are necessary to avoid increasing homocysteine and keeping it at adequate levels. For example, it has been observed that people who smoke have very high levels of this toxic, so it would be convenient to quit smoking. It also happens with alcohol consumption, which also increases homocysteine levels.
Vitamins that decrease homocysteine
In addition to avoiding the factors that increase homocysteine, two or three vitamins are recommended that are essential to reduce it:
- Vitamins B12
- Vitamin B9 or folic acid
- Vitamin B6 or pyridoxine also, but since it is found in almost all foods, it is usually not given that much importance.
How B vitamins eliminate homocysteine
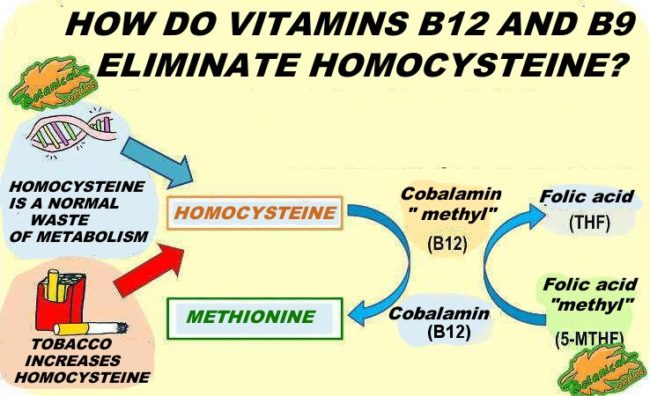
Vitamins are nutrients that in the body have the function of helping to perform chemical reactions of metabolism (due to this function they have, most vitamins are called “coenzymes”). In this issue, vitamins B12 and folic acid are vitamins that act in the metabolism of the elimination of homocysteine, in a process known as the “methionine-homocysteine cycle“.

What is the methionine homocysteine cycle?
The methionine homocysteine cycle is the metabolic process by which the body neutralizes or reduces homocysteine levels, transforming it into another non-toxic amino acid, methionine. In this reaction are involved, as coenzymes or “helpers”, vitamins B12 (present in foods of animal origin) and folic acid or vitamin B9 (present in foods of plant origin).
More technically, what happens is that folic acid passes the methyl group to cobalamin, and this inactivates homocysteine. These are simultaneous reactions of the metabolism of homocysteine, in which all the vitamins are involved at the same time. It could be said that vitamin B12 deactivates homocysteine and converts it into methionine because folic acid “recycles B12”, since it passes its “methyl group”.
Outline on the metabolism of homocysteine
From the outset, the metabolic cycle of homocysteine is a very technical issue that is not necessary to know to learn to eat healthy. But for people interested in going deeper into the subject and knowing how these vitamins act, we have elaborated the following scheme:
.Vitamin B6 in the elimination of homocysteine
Vitamin B6 or pyridoxine acts in the elimination of homocysteine in another step of metabolism, transforming homocysteine into another type of non-toxic amino acid, cysteine.
When talking about foods that decrease homocysteine, not much attention is usually paid to this vitamin as to the other two (vitamin B9 and B12) because the lack of pyridoxine is very rare, as it is found in many foods. For example bananas have a lot of vitamin B6.
What is the use of knowing the cycle or metabolism of homocysteine?
The content of this article has been a bit technical, although very simplified, with the only objective of explaining or implying why vitamins B9 and B12 are so important for people with heart problems.
It is also very interesting to know that high levels of homocysteine have been found as a side effect of Parkinson’s treatment, precisely because of the decrease in B vitamins that occurs as a side effect of the medication.
What conclusion do we have of all this?
In short, we can summarize all of this in the following points:
- Vitamins B6, B9 and B12 improve circulation because they neutralize homocysteine, a toxin that damages the arteries and the heart.
- Good levels of vitamin B6, folic acid (B9) and vitamin B12 are necessary to reduce homocysteine, have a healthy heart and especially to prevent arteriosclerosis or accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries.
- No smoking and a diet with plenty of vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts and foods rich in vitamin B12 like fatty fish, is all that is needed to keep homocysteine at bay.
![]() More information on homocysteine
More information on homocysteine