Contents
- 1 How to combine food to make complete proteins
- 1.1 FOOD COMBINATIONS WITH INCOMPLETE PROTEINS
- 1.2 Why should we combine plant foods?
- 1.3 How plant proteins should be properly combined?
- 1.4 Legumes and limiting amino acids
- 1.5 Cereals and cereal products, limiting amino acids
- 1.6 Nuts, seeds and limiting amino acids
- 1.7 Vegetables and fruit, limiting amino acids
- 1.8 Meat, fish, eggs and dairy products, limiting amino acids?
- 1.9 How to make a quality protein intake
How to combine food to make complete proteins
FOOD COMBINATIONS WITH INCOMPLETE PROTEINS
Why should we combine plant foods?
Plant foods should be combined to achieve high biological value proteins, that is to say, that the body can get all the essential amino acids required for protein synthesis.
Plant proteins contain essential amino acids. However, some of them are in very limited or insufficient amounts.
An amino acid found in limited amounts is termed limiting amino acid. For this reason, food should be properly combined together for a certain food can supply its amino acid deficit from the other.
How plant proteins should be properly combined?
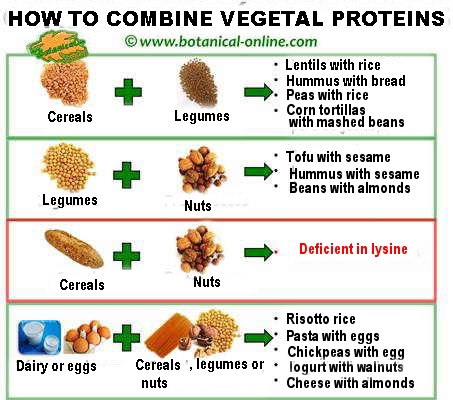
Illustrative table of correct and incorrect combinations of plant proteins according to their content of essential amino acids.
Legumes and limiting amino acids
In general, all legumes are deficient in sulfurous amino acids methionine and cystine. However, they are rich in lysine, phenylalanine, threonine and leucine. In general, foods rich in methionine, and therefore best suited to combine with vegetables, all grains and nuts.
Combine with: Legumes should be combined with foods rich in methionine.
According to the tables of composition of the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) vegetable foods higher in methionine are: spirulina, wheat germ, oats, sesame (sesame paste or tahini), sunflower seeds, rice, rye, wheat, flour, pasta, Brazil nuts, pumpkin seeds, pistachios, etc.
Legume are advisable to combine with animal protein, such as dairy products (cheese, yogurt dessert, etc.) Or egg.
In the case of vegetarian diets, a very suitable combination is hummus, a recipe made with mashed chickpeas and tahini (sesame paste toasted). Sometimes yogurt is added to this recipe, which increases its protein quality. Notably, sesame seed is the richest in methionine, which combines well with vegetable protein.
Cereals and cereal products, limiting amino acids
Overall all cereals are deficient in the essential amino acid lysine, which, among its many functions, is necessary for the formation of collagen (one of the most abundant proteins in the body). Considering its deficit in lysine, cereals with higher biological value proteins or those that contain more lysine are oats, barley and wheat germ.
However, cereals are rich in methionine and cystine, the least abundant amino acids in legumes, reason why they nicely complement proteins.
Combine with: Cereals should be combined with foods rich in lysine, such as legumes or animal protein.
The richest lysine plant foods are undoubtedly soy and its derivatives (tofu, tempeh, soymilk,…). followed by carob, beans, lentils, quinoa, amaranth, lupine, chickpeas, peas, beans, peanuts, peanut butter, etc.
Corn limiting amino acid, in addition to lysine, is tryptophan, whose content is quite poor.
Nuts, seeds and limiting amino acids
Nuts and seeds, cereals like, are deficient in the amino acid lysine, but they contain enough amount of other essential aminoacids, as valine, phenylalanine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, histidine and cysteine.
It is convenient, like cereals, to combine nuts with food such as vegetables or animal proteins that provide this nutrient.
Walnuts and other nuts, plus lysine, are also somewhat deficient in methionine.
Sesame is the richest methionine seed and therefore it is better to combine it with legumes.
Combine with: The same foods as cereals.
Vegetables and fruit, limiting amino acids
This food group has a very low protein content, and although some of these contain essential amino acids, can not be considered an important protein intake.
Among the richest vegetables in essential amino acids are asparagus (very rich in serine, cystine, leucine, histidine), spinach (cystine, isoleucine, histidine), cauliflower (serine, valine), purslane (cystine, leucine), chayote, okra, courgettes (valine).
Combine with: You can not make a protein food intake from vegetables. Vegetables and fruits do not count as protein intake alone, although they are very necessary in food for their nutritional value (mainly because of fiber, vitamins and minerals). They should be combined with protein foods in general.
Meat, fish, eggs and dairy products, limiting amino acids?
Animal proteins contain all the essential amino acids. All animal foods contain protein of high biological value, that is to say, proteins with all essential aminoacids. They have no limiting amino acids.
Combine with: They should be introduced in a balanced diet, along with other food groups, since a diet exclusively with animal protein may have negative health effects. (More information)
How to make a quality protein intake
– If vegan diets, combine vegetable and cereal. Easy ways to combine these foods can be through bread, flour, tofu, hummus, soymilk and veggie burgers.
– Pseudocereal quinoa is a protein of high biological value. We can introduce it as main dish or accompaniment on several weekly meals.
– Introduce in each meal food of animal origin: For example, dairy products or eggs, and, in non-vegetarian diets, fish and meats.
– As important as proteins is vitamin B12, needed to make blood cells. Enrich diet with brewer’s yeast can be a good option for vegetarian and vegan diets.
* Go on reading: Differences between animal proteins and plant proteins, limiting amino acids,
![]() More information on essential fatty acids
More information on essential fatty acids








