Contents
- 1 Definition, characteristics and benefits of omega 3 fats
- 1.1 What is omega 3?
- 1.2 OMEGA 3 CHARACTERISTICS
- 1.3 What are omega-3 fatty acids?
- 1.4 Types of omega-3
- 1.5 What are the properties of omega-3?
- 1.6 Omega 3 for the nervous system and eyesight
- 1.7 Anti-inflammatory properties of omega 3
- 1.8 Properties of omega 3 for health
- 1.9 Types of omega 3 that we can find in food
- 1.10 Omega 3 metabolism
- 1.11 How can we obtain omega 3?
- 1.12 Consumption needs of omega 3
- 1.13 Omega 3 supplements
- 1.14 Can supplements replace foods rich in omega 3?
- 1.15 Balance between omega 3 and omega 6 of the diet
- 1.16 Safety of omega 3
Definition, characteristics and benefits of omega 3 fats
What is omega 3?
Omega 3 is a type of fat that is found in large quantities in nuts and oil seeds, especially in hemp seeds, in flaxseed meal, in ground chia seeds, in walnuts and in fatty fish.
Hemp seeds are very rich in omega3
Peeled hemp seeds are the richest food in omega 3, they are also very rich in magnesium (one tablespoon provides the same amount as a magnesium supplement), and they are the richest food in phosphorus that exists.
OMEGA 3 CHARACTERISTICS
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
It is classified within the essential fatty acids (AGE). Essential means that the organism can not manufacture omega 3, and therefore, this component has to be supplied through the diet.
Chemically, omega 3 is a polyunsaturated fatty acid. It is called polyunsaturated because it contains more than one unsaturation (1 double bond) in its molecule.
Types of omega-3
There are three omega-3 fatty acids:
- Alphalinolenic acid (ALA): Found primarily in the oil plant seeds. Among them, the most important are the seeds of flax and especially linseed oil, also called linseed oil. Other plants rich in this component are the seeds of soybean canola, walnuts, hemp, etc.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): Found mainly in oily fish oils and milk. There are traces of it in the purslane.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): Found mainly in oily fish oils and some microscopic algae.

Summary of the main properties of omega 3. The foods richest in omega 3 are fatty fish and nuts, followed by flaxseed meal and chia seeds
What are the properties of omega-3?
What are omega-3 for? The body needs omega-3 fatty acid to work properly. The main functions of linolenic acid are the following:
- to manufacture hormones and anti-inflammatory components. Without omega 3 these substances could not be produced.
- Operation of the nervous system: omega 3 is part of neurons and chemical transmissions of the brain and eyesight.
- The formation of cell membranes, all cells contain omega 3.
- Eye health: For the correct formation of the retina, along with vitamin A containing carrots.
- The correct functioning of the immune system.
Omega 3 for the nervous system and eyesight

Photo of omega 3 fatty acids food sources: Avocado, vegetable oils, nuts and seafood.
Omega 3 fats are found in high concentration in the brain and nervous system, specifically in the retina of the eye and the cerebral cortex.
A diet rich in omega 3 fats is necessary to keep this system in good condition. It is recommended to people with insomnia, hyperactivity, stress or anxiety.
It has been shown that omega 3 improves some psychological alterations such as hyperactivity in children. Supplements with omega 3 essential fatty acids are recommended as natural antidepressants, for mood swings, seasonal depression, etc.
Summary with the main properties of omega 3. The foods richest in omega 3 are fatty fish and nuts, followed by flaxseed meal and chia seeds.
Anti-inflammatory properties of omega 3
The body is able to make its own anti-inflammatories from omega 3 fats. In addition, omega 3 fats are anti-inflammatory, antithrombotic and antiarrhythmic, important in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, its consumption is very suitable in cases of menstrual pain, arthritis, gastritis, dermatitis, asthma, psoriasis, etc. The following article explains why omega 3 helps reduce pain in arthritis.
Properties of omega 3 for health
In addition to the basic functions discussed in the previous sections, it has been proven that the ingestion of omega-3 fatty acids represents a series of benefits for the organism.
Types of omega 3 that we can find in food
Omega 3 fatty acids are a family of fats. It is a rather extensive and complex subject that is usually treated at the level of specialized nutrition. There are three main omega 3 fatty acids:
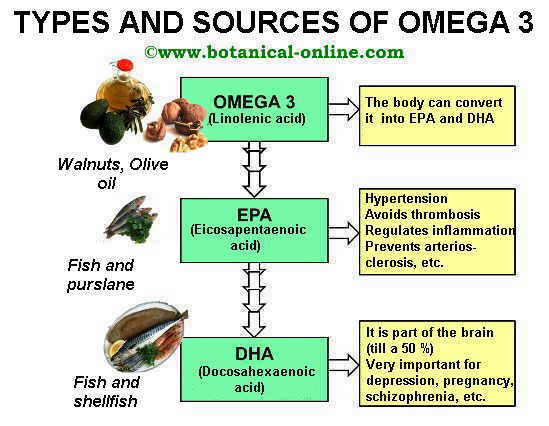
Foods that provide different types of omega 3 and 6 fatty acids
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): Found primarily in the oil of vegetable seeds. It is the type of omega 3 with softer effects, since the body must transform it to be active and have its benefits. It is found in plant sources, such as flax seeds and especially flaxseed oil, also called flaxseed oil.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): It is a more active form of omega 3 than ALA, has the properties already discussed, anti-inflammatory, antiarthritic, antithrombotic and vasodilator. It is found mainly in the oils of blue fish and breast milk. Cod liver oil supplements are rich in this component. There are traces of it in purslane.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): It is part of the tissue of the nervous system, and can be found in it in concentrations as high as 50%. The deficit of this type of fat has been linked to postpartum depression. DHA is found primarily in fatty fish oils and some microscopic algae. Cod liver oil supplements are rich in this component. It is the most important type of omega 3 in terms of its properties for the central nervous system, so it is very suitable for students, problems of memory loss, or people with depression, headaches, migraines, schizophrenia, dementia, Parkinson or Alzheimer .
* More information on: Types of omega 3
Omega 3 metabolism
Omega-3 acid, called alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), is abundant in vegetables. This type of acid must be transformed by the body to be active and have anti-inflammatory effects. In this transformation the organism is slow, so the effects are not as remarkable as in fish oil, which is considered a more direct and better source for the ingestion of this principle.
How can we obtain omega 3?
These essential fatty acids can be obtained from the following sources:
- Oily fish: Contains two types of omega-3 fatty acids: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) – sometimes referred to him as EPA acronyms come from English ” Eicosapentaenoic Acid” – and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) – also called DHA by the English form of “Docosa-Hexaenoic Acid”. Fish oil is the richest in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Hemp seeds: they have a large amount of omega 3, in addition, they are the foods richest in phosphorus that exist and also constitute a natural supplement of magnesium. (1-2 tablespoons of peeled hemp seeds a day)
- Linseed and chia: in that order, are foods rich in omega 3, when they are ground or chewed. If they are consumed whole, they can not assimilate their fats, which are found inside the seeds.
- Walnuts: Walnuts are the vegetable foods richest in omega 3. It is recommended to eat 7-8 nuts daily to get enough omega 3.
- Other vegetable and animal food:T hey contain lower amounts of omega 3 than those previously described: other seeds and vegetable oils, flaxseed, tahini, sesame oil, quinoa, soy, pecan nuts, almonds, purslane and spinach.
Fish oil is considered a direct and better source for the ingestion of this principle. Most vegetable food containing these principles are vegetable oils.
The one containing the highest proportion is flaxseed oil (533 mg per 100 g), followed by canola oil (111mg) or walnut oil (104 mg). Other vegetable oils that contain oil are soya, wheat germ oil or hazelnut oil.
Consumption needs of omega 3
Omega is an essential nutrient and as such should be consumed regularly in the diet. However, the daily amounts depend on the diet. Certain amounts of this type of fat can be stored in adipose tissue, such as in a warehouse.
If one day a very powerful source of this nutrient is consumed , such as a fatty fish ration, there is no problem if the next day you consume less omega 3.
* More information: Amount of recommended fat
Omega 3 supplements
Supplements are a way to ingest omega 3 fatty acids for those who do not take it from plant sources, who need higher requirements, or who do not eat enough fish.

Omega 3 supplements are given in pearls format, because they allow better preservation and dosage.
They are taken in the form of capsules containing fish oils, but there are also vegetarian options:
- Fish oils: These supplements contain EPA and DHA.
- Krill Oil: Very rich in fatty acids EPA and DHA.
- Vegetarian DHA supplements
Can supplements replace foods rich in omega 3?
It should be noted that, observing the tables of food composition, no supplement contains as much omega 3, EPA and DHA as a serving of fatty fish or nuts, so a diet rich in omega 3 is recommended before taking supplements:
Recommended supplements of omega 3
Balance between omega 3 and omega 6 of the diet
The proper relationship between omega-3 and omega-6 must be established in the diet because the excess of omega-6 is inflammatory and must be balanced with the intake of omega-3.
Currently there is a high intake of omega-6 (corn, precooked meals, sunflower oil, etc.) and little omega 3.
The omega 6: omega 3 ratio of the desirable diet would be 4: 1, ie four parts of omega-6 per 1 part of omega-3. This ratio currently ranges between 10: 1 or 20: 1. The enormous superiority (imbalance) of omega-6 can sometimes be responsible for some diseases, such as heart disease, certain depressions, diabetes. etc.
- You should increase foods containing more omega-3 or take supplements of this component, and decrease the intake of those foods rich in omega-6.
Safety of omega 3
Eating natural foods rich in omega 3 does not present any danger, because these foods are highly satiating and can hardly be consumed in high quantities … Taking supplements present some contraindications
![]() More information on omega 3.
More information on omega 3.