Contents
Characteristics and properties of linolenic acid Omega 3
PROPERTIES OF LINOLENIC ACID
What is linolenic acid?
 Photo of walnuts. They are one of the richest foods in omega 3. |
Linolenic acid (C18: 3), is a fatty acid belonging to the group of omega 3 fats, and therefore, it is a polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Linolenic acid (omega-3), along with linoleic acid (omega-6), is one of the essential fatty acids that exist, that is, fats that the organism has to obtain from food, since it is not able to synthesize them by itself.
The structure of this fatty acid is formed by a chain of 18 carbon atoms containing 3 double bonds. It is represented as C18: 3.
The chemical molecular formula of linolenic acid (18: 3) is:
H3C-CH2-CH = CH-CH2-CH = CH-CH2-CH = CH- (CH2) 7-COOH
Through linolenic acid the body can synthesize other polyunsaturated fatty acids of longer chains, such as the following:
Types of Omega 3 Fatty Acids:
– Linolenic acid (C18: 3)
– Alpha-linolenic acid (C18: 3)
– Eicosapentaenoic acid or EPA (C20: 5) (PG3, TX3)
– Docosahexaenoic acid or DHA (C22: 6)
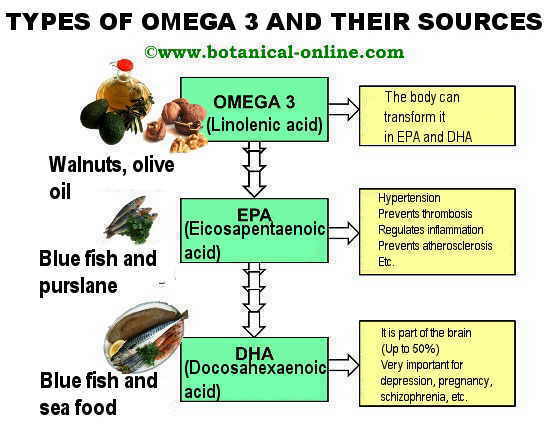
Summary sheet with the different types of omega 3, functions in the body and its sources in the diet. Produced by © Botanical-online |
Properties of linolenic acid
Linolenic acid, specifically the isomer we find as alpha-linolenic acid, is the precursor of the following fatty acids that have longer chains, EPA and DHA
Linolenic acid isomers found in the following structures, either as gamma-linolenic acid (C18: 3) or as dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (C20: 3), are of the omega 6 family and do not belong to the omega 3 family.
Our body is not able to synthesize alpha-linolenic acid, but there are some plants like algae and some plankton types that can synthesize it by themselves. That is why it is classified within the group of essential fatty acids.
Importance of essential fatty acids
 Photo of pearls of linseed oil. Omega 3 supplements are given in beads, because they allow better preservation and dosage |
The body needs these omega 3 fatty acids to work properly. Among its main functions are:
– Functioning of the nervous system: of neurons and chemical transmissions
– The proper functioning of the immune system
– The formation of cell membranes
– To manufacture hormones
– Eye health: For the correct formation of the retina
Foods rich in linoleic acid: Food sources of linoleic acid
Linoleic acid is found in foods of plant origin such as flax seeds and especially flax oil, also called flaxseed oil. Other plants rich in this component are walnuts, chia seeds, soybean, canola oil, evening primrose oil, quinoa, pecans, hemp seeds, etc.
These foods do not contain EPA and DHA.
The only foods that contain sufficient amounts of EPA and DHA are foods of animal origin, and more specifically oily fish such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, herring, etc. Cod liver oil supplements contain EPA and DHA.
Linolenic acid is considered to be less effective than EPA and DHA because it needs to be transformed into the body.
* Related information:
![]() More information on fats.
More information on fats.