Contents
What are the limiting amino acids?
LIMITING AMINO ACIDS IN FOOD
What is a limiting amino acid?
A limiting amino acid is one that is not found in food. If a food has all amino acids, it is said to have its complete protein.
Animal proteins are complete because they have all amino acids. In other words, foods of animal origin have no limiting amino acids.
Virtually all plant proteins are incomplete proteins because they have limiting amino acids (are deficient in some essential amino acid).
Quinoa, amaranth and buckwheat have full vegetable proteins.
For this reason, these grains, which are pseudocereals, have a great importance on strict vegetarian diets.
Definition of limiting amino acid
A limiting amino acid is one that is in insufficient amounts in a food.
A food can have many proteins, but these may not contain a specific amino acid. For example, wheat gluten is a concentration of wheat protein, but it is deficient in lysine as wheat.
Limiting amino acids in plant foods
Functions of essential amino acids

Some vegetables should be combined to get complete proteins
Essential amino acids are important because the body can not manufacture them, so they must be supplied by the diet, because without them the body can not synthesize the needed protein.
Instead, nonessential amino acids can be obtained by the body from other amino acids or substances.
Incomplete protein is said to lack some essential amino acid in its composition.
When a food presents some essential amino acid deficit, or contains very low amounts, it is told to have incomplete proteins, because it lacks any amino acid (limiting amino acid or amino acid deficit).
Given that amino acid deficiency, the body does not have all the necessary ingredients to make proteins. For example, grains and nuts are deficient in lysine, which is the limiting amino acid.
Foods with limiting amino acids must be combined to achieve complete proteins.
Limiting amino acids in nuts
The protein of nuts is incomplete because it has little lysine, which is an essential amino acid.
Thus, lysine is the limiting amino acid of nuts.
Limiting amino acid in cereals and legumes
Cereals, although they have a certain amount of lysine, this is not sufficient to form a protein. Thus, it is said that lysine is the limiting amino acid of all cereals.
In addition, maize is the only cereal deficient in the amino acid tryptophan.
The presence of all amino acids in the right proportions, makes a food proteins to be better exploited. That is, the body not missing any ingredients to make their proteins.
For example, to make collagen lysine is necessary. Grains contain lysine, but in very low amounts.
So, especially people with extra protein needs or collagen (burns, broken bones, ligaments, athletes, etc.) should combine cereals with lysine-rich foods (vegetables, eggs, dairy, fish or meat) to get a complete protein.
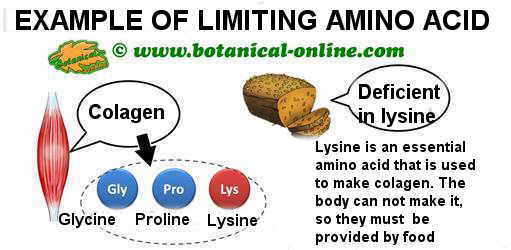
Schematic example to illustrate what means a limiting amino acid. Lysine is an amino acid that must be provided by food, since it is necessary to make important proteins such as collagen, which develops vital functions. Especially those with high protein needs, must combine cereal with proteins of high biological value each meal. Produced by © Botanical-online
Table of limiting amino acid in cereals and legumes
The following table shows amino acid deficits of different plant proteins are summarized below:
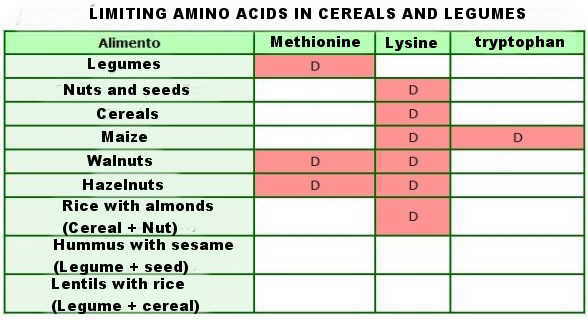
*Caption: D = Deficient (limiting) Amino Acid
The table shows the essential amino acids of the food groups in general and how, by the combination of plant foods, high biological value proteins are achieved.
Proteins of high biological value
Proteins that have no limiting amino acids
The proteins of high biological value or complete proteins are those that have no limiting amino acids. Food of animal origin are an example because they contain all essential amino acids.
It is therefore desirable to combine foods with limiting amino acids with other foods containing that amino acid, to obtain proteins of high biological value.
Cereals are often combined with pulses (lentils and rice) to offset the deficits of both amino acids and get high quality protein because grains are rich in methionine, which is deficient in legumes.
* More information: Proteins of high biological value
Composition table of content in essential amino acids of food
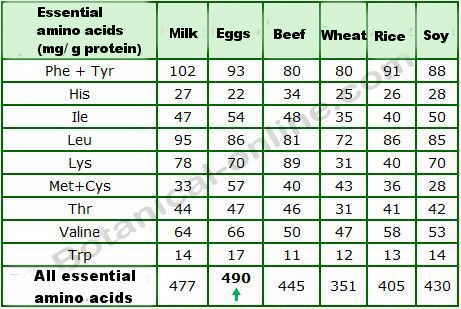
Table or box with the count of amino acids from different foods. Egg is the food that provides the greatest amount of essential amino acids and in better proportion, for this reason it is considered the best source of protein (protein biological value 1, the highest)
![]() More information on essential fatty acids.
More information on essential fatty acids.








