Contents
- 1 Food for intestinal hyperpermeability or too permeable intestine
- 1.1 Diet for too permeable intestine
- 1.2 What is the best food for your intestines?
- 1.3 Recommended foods to get healthy bowel
- 1.4 Vegetables and tubers for the gut
- 1.5 Grains: vegetables, grains and nuts for the gut
- 1.6 Good fruits for the intestines
- 1.7 Which are the best fruit for the intestine?
- 1.8 Healthy probiotics with bacteria and prebiotics
- 1.9 Protein foods for the gut
- 1.10 Spices and herbs for the gut
- 2 Bad foods for the too permeable gut
Food for intestinal hyperpermeability or too permeable intestine
Diet for too permeable intestine
The diet for leaky gut syndrome aims to improve digestive comfort providing foods that help regenerate the gastrointestinal mucosa, regain weakened intestinal flora and seal the intestinal wall.
It is a highly recommended in case of autoimmune diseases, intestinal diseases, die for food allergies or intolerances, and inflammatory diseases such as arthritis.
This diet should be controlled by a nutritionist who has to work together with your doctor.
What is the best food for your intestines?
 Cruciferous vegetables have antioxidant and sulfur components, which help improve intestinal health. Consume boiled, steamed, in soups,…
Cruciferous vegetables have antioxidant and sulfur components, which help improve intestinal health. Consume boiled, steamed, in soups,…
- Chew well all food and eat it in a calm and relaxed atmosphere.
- In case of intolerance, eliminate the causative component: if milk lactose intolerance, or fruit if fructose intolerance. Many experts recommend temporarily suppress the consumption of foods with gluten, such as wheat (bread, flour, pasta and cereals). It is estimated that much of the population has some degree of gluten intolerance (non celiac gluten intolerance), in most cases undiagnosed, which causes inflammation in the intestine. There is no need to remove gluten forever, as this change may be temporary.
- Eliminating or reducing substances that irritate the intestines: alcohol, snuff, spicy, coffee.
- Diet rich in fruits, vegetables and tubers, gently cooked (boiled, steamed, baked, roasted, mashed, foil,…). Fried foods or too abundant meals are not suitable.
- Prevent constipation with a high fiber diet and proper hydration. Laxatives use is not recommended.
- Repair the gut: Diet foods and supplements needed to restore intestinal health. They are explained below
Recommended foods to get healthy bowel
Tubers (potatoes, sweet potatoes,…) are very suitable because they contain starches with demulcent properties, which soothe and calm irritated digestive mucous. They can be introduced into soups, creams, steamed, baked at low temperature, etc.
Vegetables are another essential component in the diet to restore intestinal health. We must not forget that fiber is fermented to give us colon bacteria, and promote proliferation or intestinal healthy microbiota. That is to say, to have a prebiotic effect. Fiber is the main food for the bacteria of our intestines.
Vegetables and tubers for the gut

Carrot cream with turmeric.
The most recommended vegetables to repair the intestines are:
The brightly colored vegetables: such as carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, seaweed, and green leafy vegetables in general. They are rich in beta carotene, a plant components with properties to repair the skin and mucous membranes.
The sulfurrich vegetables: They will help reduce inflammation and counteract the formation of toxic substances in the intestine: onions, garlic, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, radishes, turnips, etc. The cabbage group is also rich in glutamine, an amino acid that helps seal the intestinal walls.
Onions are rich in quercetin, a flavonoid with properties to improve allergies. Along with garlic, both are a powerful natural antibiotic. They are foods that can help eliminate certain infectious bacteria from our intestines.
Those people that find them flatulent may take other softer ones: zucchini, asparagus, green beans, lettuce, tomatoes, potatoes,… They are very nutritious and digestible, the stomach feels good with them and they bring many vitamins and minerals.
Gentle cooking is better to retain their nutrients and to be better digested. Remember that vegetables should be thoroughly washed and peeled, especially if they are not organic, because they may contain harmful pesticide residues for the intestinal flora.
Other vegetables should be eaten less frequently, such as spinach, chard and beets, because they contain oxalates. The inulin rich artichoke can cause gas or bloating in some people.
Grains: vegetables, grains and nuts for the gut
Legumes, cereals or nuts can be eaten, but always presoak at least 12 hours in the case of pulses, and between 1 and 3 hours in the case of cereals and nuts. Soaking serves to clean any dust, pollen, etc., And especially to eliminate antinutrients found in these grains, such as saponins, which are irritating to the intestinal tract.
Among the most recommended are rice, millet or buckwheat. When whole grains are consumed, it is recommended that they are organically grown, because when they do not have traces of pesticides and plant protection products in the husk.
You can also recommend chia seeds, for its high content of fermentable fiber, which acts as a prebiotic (pudding of chia, chia water, etc.), Especially to prevent constipation.
Grains that are recommended to moderate, avoid or reduce are: quinoa and amaranth, because they are high in saponins, even after a long soak. Also, very flatulent legumes, such as soybeans, and dry beans.
Some professionals consider appropriate temporarily eliminate the consumption of legumes, grains with gluten, nuts and seeds. This may be appropriate in certain intestinal diseases or when poor diets should be made into fibers. In these cases, they can be replaced by potatoes, sweet potatoes, bananas or white rice.
Good fruits for the intestines

Photo of applesauce
In general, all fruits are suitable for the gut, because they contains soluble fiber and antioxidant vitamins. One should reduce the consumption of fruit when there is fructose intolerance or when its consumption is very laxative.
Which are the best fruit for the intestine?
The most recommended fruits to the intestine are:
- Apples, pears and quinces: They are the fruits rich in pectin, a type of fiber that regulates bowel habits and promotes the growth of healthy intestinal flora.
- Avocado: It has a very high content of vitamin E, with healing properties. It helps regenerate the intestinal mucosa and seal the barrier. You can eat avocado smoothies, salads, guacamole,, etc.
- Pineapple: Contains the enzyme bromelain, antiinflammatory, digestive and antibacterial. A pineapple cut before meals help us digest better. Ideally suited to people with slow digestion, flatulence and swollen belly.
- Mango: With lot of antioxidants, vitamin C, vitamin E and vitamin A (as beta carotene). Antioxidants are needed to protect the mucosa and prevent the formation of toxic substances in the intestine, such as nitrosamines. The best way to leverage your antioxidants is to eat fresh mango, but you can also freeze it and crush with a little coconut milk if desired, to make a delicious mango sorbet or ice cream.
- Coconut : It is another right fruit for the gut because it is rich in minerals such as selenium and zinc. It is highly recommended for those who, because of intestinal diseases, allergies, etc., do not eat enough nuts and seeds.
Healthy probiotics with bacteria and prebiotics

Photo of yogurt (probiotics) with strawberries (prebiotic).
Probiotics are those that contain healthy bacteria. Bifidus yogurt or miso are examples of probiotic foods. When eating them, we sow our intestines of these microbes.
In intestinal disorders will be very interestaing to take probiotic supplements because this is the way to ensure sufficient intake of these bacteria (Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium). Through food, not enough of these bacteria is eaten.
Attention! Probiotics are contraindicated when taking certain drugs for autoimmune diseases (Consult your doctor)
Protein foods for the gut
People who follow a vegetarian diet should know that their protein intake requirements are higher compared to nonvegetarians. This means that each meal is recommended to introduce some protein food such as eggs or yogurt.
Proteinrich foods are needed to repair the intestine. Eggs are a good source of protein, along with fish and meat. These foods provide glutamine, an amino acid that enhances healing, repairing and maintaining in good condition the intestinal walls.
Glutamine is lost during cooking at high temperatures, so it is recommended not too cooked eggs too much. Medium meat is also desirable or using techniques such as marinated.
The small oily fish is highly recommended for its antiinflammatory properties. If marinated, 48 hours freezing before taking it is necessary to avoid anisakis. Thus it is how best their omega3 fats, which deteriorate the baking are preserved.
We recommend taking omega 3 EPA and DHA in vegetarians or when not enough oily fish is taken.
Spices and herbs for the gut
In the kitchen we can use many spices, seasonings, sauces or herbs that increase the properties and nutritional value of recipes. These include:
- Cumin, fennel, anise, caraway: The fruits of the Umbelliferae are all carminative. They eliminating gases also prevent cramping.
- Turmeric: It is also carminative, but stands out above all as a potent antiinflammatory and antioxidant. It is recommended to combine it with a pinch of black pepper, which improves its absorption. It is added to the end of cooking to retain higher content of active ingredients.
- Ginger: helps to improve digestion by increasing digestive secretions. (In Infusion, powder, ginger squeezed into the dishes).
- Fresh parsley: Rich in vitamin C, it is recommended especially when fructose intolerance and fruit consumption is low.
- Salsa guacamole: Rich in vitamin E, antioxidant and healing properties. The avocado is an excellent food for skin and mucous membranes.
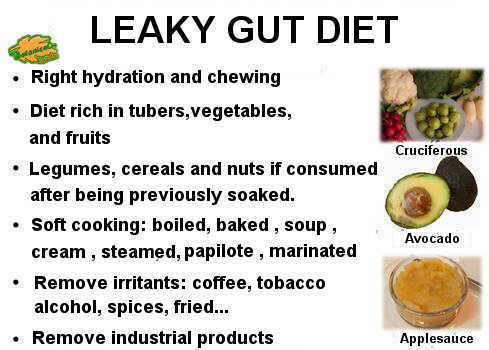
Summary sheet with the basic guidelines and some examples of foods in the diet to bowel syndrome too permeable or leaky gut. © Botanicalonline.com
Bad foods for the too permeable gut

Sausages (ham, sausages, etc.) Should not be routinely consumed.
The worst meat to the intestine and health
It is very harmful for the intestine to eat processed meat, That’s to say, sausages, rashers, and other derivative meat products are part of our daily diet.
People with intestinal problems can quickly notice symptoms of intestinal discomfort when consuming these products. Meats are high in animal fat, plus lots of salt and undesirable additives, such as nitrates and nitrites, preservatives substances of these foods in the colon that become cancerous nitrosamines.
We should not abuse barbecues and grilled at high temperatures, because “roasting” of food leads to the formation of different compounds irritating to the stomach and intestine, called PAHs and heterocyclic amines.
Gluten, or leaky gut and intestinal inflammatory diseases

Bread and wheat flour contain a protein called gluten, which is broken down in the intestine into prolamins and gliadin. It is believed that increasing the separation among enterocytes (intestinal cells). That is, consuming gluten may increase the permeability or “holes” of the intestine. For this reason, some experts always recommend to avoid wheat in case of intestinal diseases, at least temporarily. .
Some cereals such as wheat, barley, rye and their derivatives, contain a protein called gluten, which is broken down in the intestine and prolamins gliadin. There are studies in which there has been an increase in the gap between the enterocytes (intestinal cells) by eating gluten. Gliadin (a component of gluten) may increase the permeability or “holes” of the intestine.
For this reason, some experts recommend avoiding foods with gluten, such as wheat, if and intestinal inflammatory disease exists, at least temporarily.
In a first phase it may be advisable to avoid bread and flour for possible non celiac gluten sensitivity.
To remove gluten is not necessary to consume special glutenfree products but can eat foods that do not naturally contain this component already mentioned: rice and potato, sweet potato, rice cakes, millet, buckwheat, lentils, chickpeas, rice pasta (noodles), cassava, plantain, etc.
Do not chew
Chewing is important because digestion begins in the mouth. Chewing allows digestive juices contact with all food molecules, allowing the enzymes to act on its disintegration, to be transformed into smaller molecules (nutrients) and assimilate them. In the leaky gut it is important that food is chewed well, especially those harder food, such as meats, grains, legumes or nuts.
Lack of chewing or swallowing food involves longer digestion and longer fermentation or putrefaction of food in the digestive tract, more work for the digestive organs, and the production of gases that can irritate or inflame the intestine. There is a saying: Drink solid and chew liquid, especially when digestion problems.
Importance of stress in gut health
Psychological stress affects our digestive system.
Stress affects our emotional state and our intestinal health. This relationship is clear in cases of irritable bowel syndrome, even in healthy people is more difficult to establish relationship, because there is no pain or such exaggerated digestive disorders.
Animal studies have shown that stress alters the composition of the intestinal flora and viceversa, a good digestive health improves emotional state.
Eating too much meat and little vegetables
A diet too rich in animal protein and low in fiber increases the putrefactive bacterial flora, which weakens the intestinal health and increases the formation of carcinogenic substances in the intestine. Therefore it is important to get used to balance the consumption of meat with vegetables, changing the typical “French fries” accompaniment by boiled vegetables, salad or fruit.
The protective microbiota is that one that can ferment vegetable fiber, therefore, you need to eat plenty of vegetables to promote its growth in the colon.
Are milk and milk derivatives suitable for the gut?

Milk and milk derivatives
The consumption of milk and dairy products is also a point discussed in case of intestinal disorders. Some studies have found health has improved when removing dairy in people with celiac disease, autoimmune diseases, lupus, multiple sclerosis and Crohn’s disease.
Therefore, in the above cases, you may advise your dietitian or doctor temporarily remove dairy from your diet and see if there are improvements in your disease.
Sweeteners
The routine use of sweeteners is not recommended. On the one hand, artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, saccharin or sucralose are not recommended because a study showed that could change the intestinal flora and increase the risk of diabetes and obesity.
On the other hand, the consumption of sweeteners (polyols) such as sorbitol, xylitol, mannitol, erythritol, etc., that are found in many gums or other products without sugar, are laxative, so they and are not recommended, either.
Even if there is obesity, it is preferable to use natural sweeteners like raw honey, sugar or brown sugar, all in moderation. The best natural sweetener is cinnamon.
![]() More information on intestinal hyperpermeability.
More information on intestinal hyperpermeability.








