Contents
Characteristics and uses of saturated fatty acids
PROPERTIES OF SATURATED FATTY ACIDS
What are saturated fatty acids or saturated fats?
Saturated fatty acids are a type of fat that is characterized by the absence of double bonds between the carbon chains, which form the fatty acid.
They have chains shorter than the other fatty acids, but also the longer ones, since they can be formed with only 4 carbons, but some waxes can contain 35.
Characteristics of saturated fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids are those that do not contain any double bonds or unsaturation in their carbon chain, so all bonds are simple or saturated.
This feature allows the binding of molecules by Van Der Waals forces, which gives a more stable structure to the molecule.
Physically this stability is manifested by the characteristic that saturated fatty acids are solid or semisolid at room temperature, such as butter.
Foods rich in saturated fatty acids
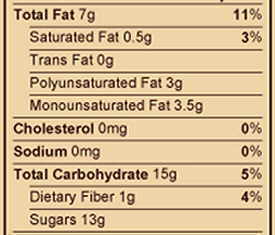
Photo of a detail of some cookies composition. The classification of fats can be distinguished according to whether they are saturated, monounsaturated or polyunsaturated
The most common saturated fatty acids in foods are usually those containing 14, 16 and 18 carbons, which are called myristic acid, palmitic acid and stearic acid, respectively.
They are usually designated by the following nomenclature: C14: 0, C16: 0 and C18: 0.
The number that precedes the quantity of carbons, designates the amount of double bonds or unsaturations, in this case they are saturated and consequently, the value is zero.
Other less common are some waxes, which have a longer chain of 18 carbons.
Types of saturated fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids are classified according to the carbon chain length of the fatty acid. Below, there is a table of the usual saturated fatty acids:
| Saturated fatty acid | Name of fatty acid | Vegetal foods containing it | Animal feed containing it |
| C4:0 | Butyric acid | Milk of cow, cream of milk, butter. | |
| C5:0 | Valeric acid | Valerian root | |
| C6:0 | Caproic acid | Vegetable oils | Goat milk, butter and animal fats |
| C8:0 | Caprylic acid | Palm seed oil and coconut oil | Milk |
| C10:0 | Capric acid | Coconut oil | Milk, Lard |
| C12:0 | Lauric acid | Tropical vegetable oils, coconut oil and palm oil | Breast milk |
| C14:0 | Myristic acid | Nutmeg, coconut, palm kernel, other tropical vegetable oils | Milk of cow, milk cream and derivatives. |
| C16:0 | Palmitic acid | Palm oil, abundant in many oils | Cow milk, meat, eggs, abundant in most fats. |
| C18:0 | Stearic acid | Cocoa butter, abundant in many oils | Meat, eggs, abundant in most fats. |
| C20:0 | Arachidic acid | Peanut oil | Lard |
| C22:0 | Behenic acid | Mustard oil and some waxes | |
| C24:0 | Lignoceric acid | Olive oil and peanut | |
| C26:0 | Ceric acid | Bee wax |
* Related information:
![]() More information on fats.
More information on fats.








