Contents
- 1 Characteristics and properties of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- 1.1 PROPERTIES OF EICOSAPENTAENOIC ACID (EPA)
- 1.2 What is eicosapentaenoic acid?
- 1.3 Properties of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- 1.4 Benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid EPA
- 1.5 Possible indications for eicosapentaenoic acid EPA
- 1.6 Foods rich in eicosapentaenoic acid or EPA
- 1.7 Possible contraindications for eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- 1.8 Balance between omega 6 and omega 3
Characteristics and properties of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
PROPERTIES OF EICOSAPENTAENOIC ACID (EPA)
What is eicosapentaenoic acid?
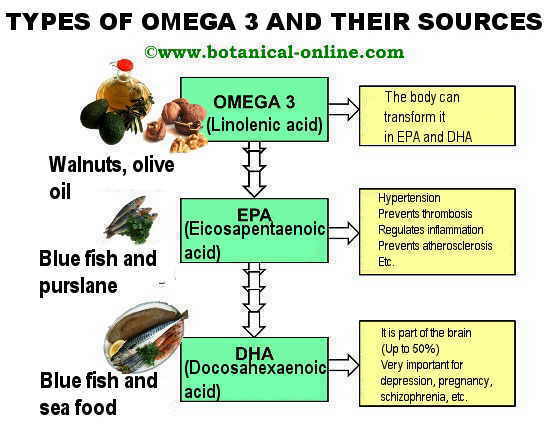
Eicosapentaenoic acid, abbreviated as EPA (C20: 5), is a fatty acid belonging to the group of omega 3 fats, and is a polyunsaturated fatty acid.
It is not one of the essential fatty acids, since the body can synthesize EPA from linolenic acid (omega 3), which is essential.
The structure of this fatty acid is formed by a chain of 20 carbon atoms containing 5 double bonds. It is represented as C20: 5.
From eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), the body can synthesize another polyunsaturated fatty acid with even longer chain called docosahexaenoic acid or DHA (C22: 6).
The chemical molecular formula of eicosapentaenoic acid (20: 5) is:
H3C-CH2-CH = CH-CH 2 -CH = CH-CH 2 -CH = CH-CH 2 -CH = CH-CH 2 -CH = CH- (CH 2) 3 -COOH
Properties of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
 Baked sardines (soft cooking), with parsley. Very rich in proteins and fats EPA and DHA. Parsley brings lots of vitamin C
Baked sardines (soft cooking), with parsley. Very rich in proteins and fats EPA and DHA. Parsley brings lots of vitamin CThe body uses eicosapentaenoic fatty acid (EPA) to synthesize substances called eicosanoids, such as prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes.
All eicosanoids are necessary for proper function of the immune system, interfere with inflammation and blood coagulation systems and cardiovascular health. But not all cause the same effect in our body.
Eicosanoids manufactured from EPA are series 3 and have slightly proinflammatory effects (inflammation regulators). They are vasodilating and antiplatelet agents in the body.
They also boost immunity by keeping cells in the right state such as leukocytes, macrophages and lymphocytes, among others.
Although they have a slightly proinflammatory action, they act as regulators of inflammation and its effect is considered anti-inflammatory. This is because they have a much lower effect than the series 2 eicosanoids, which are produced by the arachidonic acid of the family of omega 6, which are highly inflammatory.
Summary sheet with the different types of omega 3, functions in the body and its sources in the diet, Produced by © Botanical-online |
Benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid EPA
- They reduce the risk of suffering vascular and cardiac pathologies. But, they interfere with other levels than omega 6.
That is, omega 3 fatty acids, specifically EPA and DHA, prevent cardiovascular diseases, thanks to antiinflammatory action.
- An increase in cells responsible for maintaining immunity such as lymphocytes or macrophages, among others.
- Decreased levels of triglycerides, LDL cholesterol and VLDL cholesterol.
- A decrease in tachycardias and hypertension, preventing it from leading to more severe cardiovascular pathologies such as infarction.
Possible indications for eicosapentaenoic acid EPA
 Photo of pearls of cod liver oil. EPA supplements are given in pearls, because they allow better preservation and dosage. Generally these supplements carry EPA + DHA
Photo of pearls of cod liver oil. EPA supplements are given in pearls, because they allow better preservation and dosage. Generally these supplements carry EPA + DHA* For its anti-inflammatory effect, EPA is indicated in:
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable colon, etc.
- Skin diseases such as dermatitis, psoriasis, eczemas, etc.
- Diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
- Diseases that affect the nervous system, such as depression, headache, migraine, attention deficit (with or without associated hyperactivity), Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, etc.
* Because of its hypotriglyceridemic effect, EPA is indicated in:
- In diseases where triglycerides and LDL or VLDL (bad cholesterol) cholesterol are high in the blood, such as overweight, obesity, poor circulation or cholesterol problems.
*Because of its vasodilatory and antiplatelet effect, EPA is indicated in:
- In diseases or when there is a risk of coronary or cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, myocardial infarction, etc.
- It is also considered to have antihypertensive effects, to reduce tachycardia and high blood pressure (hypertension).
Foods rich in eicosapentaenoic acid or EPA
It is possible to make an intake of EPA directly, either with supplementation or through food. EPA is found in oily fish such as salmon, sardines, mackerel, etc.
It should be borne in mind that these fatty acids, when found within the food rich in its content, prove to be more bioavailable than supplements, and therefore better and more easily absorbed and used by our body.
Some foods rich in EPA are:
- Fish oils
- Blue fish, such as salmon, tuna, sardines, etc.
- Functional foods, That is to say, products enriched with omega 3, specifically with EPA and DHA: eggs, dairy, soy drinks, vegetable oils, margarines, biscuits, olives stuffed with anchovies, etc.
Possible contraindications for eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
Due to its antiplatelet effect, it can lead to bleeding.
Balance between omega 6 and omega 3
Fatty acids of the omega 6 family and those of the omega 3 family must remain in balance so that they act beneficially in our organism. The balance between them in the diet should hold a ratio of 3: 1 respectively. If the proportion of omega 6 is higher, will occur the effects cited, contrary to those of omega 3, due to the excess of arachidonic acid that would form.
Since they are polyunsaturated fatty acids and because of their composition, they are more susceptible than other types of fatty acids to become rancid because of oxidation. It is considered advisable to make a contribution of about 200 mg of vitamin E, which thanks to its antioxidant effect, prevents the occurrence of such oxidation reactions prematurely.
It is considered that a correct consumption of fatty acids of the omega 6 family is a good method of prevention against the appearance of pathologies very common in our society, such as cardiovascular ones.
EPA and DHA have a high effectiveness because they do not require metabolic processes to be synthesized, unlike what happens with the intake of linolenic acid.

Summary sheet with some of the properties of oily fish, most of them attributed to its high content in EPA. The most recommended is the small and fresh (not canned) oily fish. © Botanical-online.com
* Related information:
![]() More information on fats.
More information on fats.