Contents
Benefits of collagen for bones, joints and skin
PROPERTIES OF COLLAGEN
What is collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body.
It is part of the skin, the tissues that form the organs, eyes, bone, cartilages and tendons.
It is a molecule in the form of rigid rods which is in charge of providing stiffness or firmness to body tissues.
Collagen is mainly composed of three amino acids: glycine (30%), proline (20%) and lysine (10%).
Properties of collagen in the body
The bones are composed primarily of collagen. Collagen, along with magnesium, phosphorus, vitamin C, protein and calcium, is necessary for the maintenance of bones, joints, tendons and ligaments.
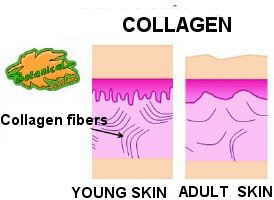
Graphic representation of collagen function in the skin
Being a component that provides firmness, collagen is very important for the health of the skin. The synthesis of collagen in the skin decreases from age 40 and its poverty or deficit is closely related to mature skin sagging.
One theory of aging is that the body makes collagen of poor quality, causing the appearance of more wrinkles, lack of elasticity, heart problems, joint problems, poor healing, weak bones, etc.
Collagen deficit, or its poor quality, causes the appearance of wrinkles, hairloss and brittle nails. The cornea of the eye is comprised of collagen.
Collagen benefits to health

Protein needs increase when muscle injury or suffering broken bones
It may also be advisable to control the intake of collagen from a certain age, in old age, when collagen synthesis decreases, or in the appearance of sagging, wrinkles or bone problems.
Some factors such as vitamin C, magnesium, phosphorus, antioxidants, and a sufficient amount of protein in the diet, prevent the deterioration of these structures and contribute to the formation of collagen.
Due to wear and tear suffered by tissues and joints daily, this protein is very important in our body, especially in cases where there is more wear, as in the case of osteoarthritis, sports, and bone problems (osteoporosis, fractures, etc..).
Collagen may also be suitable for reinforcing the blood vessels and prevent spider veins, which are small expansion of the veins under the skin, sometimes they weaken forming spiders or hematomas.
Foods rich in collagen
In the diet, digestible collagen is provided by gelatinous food rich in animal protein, which are mainly pig’s feet, beef broth or fish with bones (long cooking), and gelatins with isinglass.
Although animal meat contains collagen, is not as rich or not so easy assimilated as other food sources cited above.
* More information: Foods rich in collagen
Hydrolyzed collagen supplements
When not enough of the above food is taken, other forms of collagen can be acquired through hydrolyzed collagen supplements, which is the most absorbable form.
Hydrolyzed collagen supplements increase the activity of osteoblasts, that act on bone formation.
Collagen supplements can be combined with hyaluronic acid or magnesium due to the intervention of these substances in the formation of proteins, as they are components suitable to improve joint health, muscle and skin.
![]() More information on uses and contraindications of collagen supplements
More information on uses and contraindications of collagen supplements








