Contents
CHOLESTEROL TYPES
TYPES OF CHOLESTEROL: ” GOOD CHOLESTEROL” AND “BAD CHOLESTEROL”
Importance of cholesterol
Cholesterol is a fatty component essential to life and health found in animals.
In our body, cholesterol has many functions. It is transported by the blood to reach the whole organism.
* More information on the properties of cholesterol.
What does “good and bad” cholesterol means?
It is common knowledge that cholesterol is bad for health. Its excess can cause arteriosclerosis or circulation problems.
But not all types of cholesterol are bad. In our body there are many types of cholesterol. The best known are the “bad cholesterol or LDL cholesterol ” and ” the “good cholesterol” or HDL cholesterol. LDL and HDL are parameters that usually appear in the current blood tests.
In the following article we talk about all types of cholesterol and their relation with health:
 Cholesterol is transported by blood
Cholesterol is transported by bloodWhat types of cholesterol are there?
The dietary cholesterol undergoes many transformations until it becomes used by the body. Each time it passes through the liver, this makes a new type of cholesterol.
In total we talk about five types of cholesterol, and the different types respond to changes experienced by increasing cholesterol molecules passing through the liver:
Chylomicrons
1) Chylomicrons (CM): chylomicrons are the first type of cholesterol that is formed in the body. These are responsible for transporting the fat we eat from the intestine to the liver, to be exploited. They are found in the blood for 6-8 hours after eating.
The chylomicrons are formed in about 90% triglycerides. Triglycerides are molecules that transport fat in the body, they are in fact larger packages of fat circulating in the blood.
| Composition of chylomicrons | |
| Proteins and phospholipids | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 8% |
| Triglycerides | 90% |
Normally, chylomicrons did not show up in analytics as only remain in the blood up to eight hours after eating.
People with elevated chylomicrons are usually very hungry people and with a high digestive capacity, so, they generally eat large amounts of food. These people also tend to have high triglycerides.
In this type of alteration genetic factors are normally involved. However, chylomicrons are poor in cholesterol (8%), so that, they do not present risk of arteriosclerosis.
* More information: Diet for high chylomicron, High triglycerides diet
Cholesterol VLDL
2) Cholesterol VLDL: VLDL stands from the Very Low Density Lipoprotein in English, and means “very low density lipoproteins.” Lipoproteins are the scientific name of fats circulating in the blood.
VLDL cholesterol is formed from excessive fats and carbohydrate or high-sugar diet. People with low tolerance to glucose, as in diabetes, may have high levels of VLDL cholesterol. In the same way, these levels can also be high in people with elevated uric acid and atherosclerosis.
VLDL cholesterol is considered a type of bad cholesterol because it helps cholesterol to accumulate in the walls of arteries. The Normal VLDL cholesterol level is between 5 and 40 mg / dL.
| VLDL cholesterol Composition | |
| Protein | 10% |
| Phospholipids | 15% |
| Cholesterol | 15% |
| Triglycerides | 60% |
People with high VLDL cholesterol, also tend to have high LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. This disorder usually occurs at menopause, and it is controlled by reducing the intake of sugars and carbohydrates (muffins, excess of fruit, pasta, refined cereals, jams, juices, fructose, etc..) And consuming healthy fats.
These people need to follow a diet to reduce LDL cholesterol and control the sugar ingested in the diet (honey, sugar, soda, milk – substitute part of the milk by non-fat yogurt-, excess fruit, sugar jams, etc.)
Cholesterol IDL
3) Cholesterol IDL: It is intermediate between VLDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. Generally, it is not detected in the analytical, but it is reflected in the levels of VLDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. People with high IDL cholesterol values also tend to have high triglycerides (over 200mg./dl.). A diet for high triglycerides is recommended.
| IDL cholesterol Composition | |
| Protein | 10% |
| Phospholipids | 20% |
| Cholesterol | 30% |
| Triglycerides | 40% |
LDL or “bad cholesterol”
4) LDL or “bad cholesterol”: LDL stands from the Low Density Lipoprotein in English, and means “low density lipoprotein”. Lipoproteins are the scientific name of fats circulating in the blood.
LDL cholesterol is the most important means of transport of cholesterol in the body. Of all the types, it possesses the highest percentage is cholesterol (50%). (More information)
| LDL cholesterol composition or “bad cholesterol” | |
| Protein | 25% |
| Phospholipids | 18% |
| Cholesterol | 50% |
| Triglycerides | 7% |
LDL cholesterol is responsible for 65% of total cholesterol in analytics. Generally, when a person has high total cholesterol, means he/she has high levels of LDL cholesterol. This component of the blood circulates through the body, and during its course, it releases cholesterol that builds up in the arteries forming arteriosclerosis.
High levels of bad cholesterol are what is known as “high cholesterol” or hypercholesterolemia. Cholesterol is a silent disease that appears in lean, young, adult or overweight, with no apparent symptoms.
The recommended levels of LDL cholesterol are between 70 – 130mg/dl. (low levels are healthier). (More information)
People who have high bad cholesterol, may also have high VLDL cholesterol. Usually these people’s diet is rich in cholesterol, such as sausages, cooked meats or fats. Smoking increases the risk of high LDL cholesterol.
Thin people may take supplements of brewer’s yeast to prevent weight loss, and always keep the intake of olive oil in the diet.
If they are people who are used to taking large portions of food or too much sugar, high triglycerides may occur along with cholesterol.
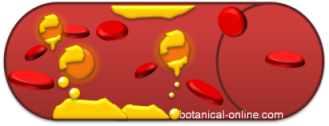 Scheme representing LDL molecules (orange).
Scheme representing LDL molecules (orange).
For its richness in cholesterol, LDL cholesterol is released in the artery walls during its transport by blood.
| RELATED INFORMATION: |
Cholesterol HDL or “good cholesterol”
– Cholesterol HDL or “good cholesterol”: The letters HDL mean “high density lipoprotein”. Lipoprotein is the scientific name of fats circulating in the blood.
This type of cholesterol has a high percentage of protein (50%) and phospholipids (25%). Phospholipids or lecithins are a class of molecules that attract cholesterol. While circulating in the blood, the good cholesterol “catches” the “bad cholesterol” accumulated in the arteries, preventing arteriosclerosis.
| HDL cholesterol composition or “good cholesterol” | |
| Protein | 50% |
| Phospholipids | 25% |
| Cholesterol | 20% |
| Triglycerides | 5% |
HDL cholesterol protects the body from cardiovascular diseases. People with good cholesterol high levels usually have it because of genetics or because they lead a healthy diet and a very healthy lifestyle. Having this type of cholesterol high poses no health risk, but, on the contrary, it is a protective factor for the cardiovascular system.
Levels of HDL cholesterol are recommended between 40 – 60mg/dl. (high levels are healthier). (More information)
Factors that increase the good cholesterol are, for example, the intake of lecithin (from legumes and nuts mainly), fruits and vegetables, regular exercise, not smoking and drinking little alcohol.
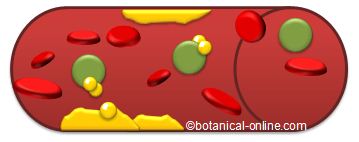 Drawing representing the role of good cholesterol.
Drawing representing the role of good cholesterol.
Good cholesterol (represented by green balls) being transported by blood drags bad cholesterol (represented in yellow) deposited in the arteries, reducing the plaque.
| RELATED INFORMATION: |
![]() More information about cholesterol.
More information about cholesterol.








