Contents
How to grow rosemary
Growing rosemary
Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) is an aromatic and medicinal plant widely spread across southern Europe the Mediterranean and Asia Minor and adapted to other regions of temperate climates. It grows wild in the Mediterranean scrub, slopes and hills in the company of other plants such as thyme (Thymus vulgaris), lavender (Lavender spp) and rockrose (Cistus spp).
It grows in sunny and dry places, at altitudes up to 1500m, but thrives best in the basement floor in the mountains.
Description of rosemary
Very aromatic evergreen shrub from Labiatae family up to 3m with erect and branched stems.
Linear leaves to bright green beam and a whitish hairiness the underside.
Lipped flowers pale blue with longer than the petals and stamens with curled upper lip of the corolla. It flowers mainly in the early to mid-spring, although it can bloom all year.

Rosemary climate, exposure, soil
In the wild, rosemary grows in dry and sunny environments, sometimes rocky, with other shrubs and plants like lavender, artemisia, thyme, etc.
It prefers calcareous poor soils. It is recommended a well drained little fertilized soil . The best type of soil is sandy, chalky, light.
It does not like clay soils, compact, wet or dark places, excessive moisture or poorly drained water. It is a typical dry plant.
As for the altitude, rosemary grows best in coastal areas, In the mountains, rosemary produces less essential oil.
Propagation of rosemary
Reproduce by seeds or cuttings in spring:
- Rosemary from cuttings: Reproduction by cuttings is the most common way of spreading rosemary plants because it leads to more development and more vigorous plants. It involves cutting cuttings of about 15 cm long, with 3-4 buds, from an adult and vigorous plant, usually in August, to transplant in September.
The cuttings should have a trunk diameter not exceeding 5 mm. Make a diagonal cut so that there is more surface contact with the ground. You can peel the stem slightly at the base to encourage root growth, using a clean knife well. Basal leaves must be removed (to prevent dehydration), leaving the tip, and the cutting plant in a pot, burying about 5 centimeters on earth.
It will root in about 2 months. Optionally they can be dipped in a preparation to stimulate rooting, before planting, that can be bought at garden stores.
- Rosemary from seeds: This method is slower than the last. Collect the seeds of a vigorous plant in summer, keeping them a tight glass jar, well dry in a dark, cool place. Sow early spring in the nursery.
Planting depth should be pretty superficial, about twice the size of the seed.
Presoaking 24 hours is recommended in water to swell and facilitate germination.
It will germinate in 20 days at 20 ° C.
Although it can be planted directly in the field, you’d better do in the nursery and then transplant it in the final location. To do this, in warm places, we plant the seeds in the fall and early spring will transplant. In cooler places, they should be planted in spring and transplanted in late summer.

Photo of rosemary in a garden
- Reproduction by layering: Reproduction by layering is done in late summer and consists of burying a branch plant to produce roots, which will occur after about 3-6 months. Once rooted, in autumn it is separated from the mother plant and transplanted in the final place.
Irrigation of rosemary
Abundant and rare watering, let the soil dry. Rosemary is a plant that holds the drought well. Planted in dry land, you only need to be watered when the cuttings are planted until they root well.
Yellow leaves are a sign that must be watered. When potted plant, we recommend placing a few stones in the bottom of the pot, to promote drainage and oxygenation of the soil and roots.
Planting of rosemary in the garden: garden chores
Rosemary is an easy plant to grow which requires little care. It does not need to be fertilized since it is an undemanding crop for nutrients. Rosemary prefers loose soil, so, prior to planting, you should plow the soil well to a depth about half a meter.
For good production and plant maintenance it is necessary to keep the weeds out of the plantation. A weeding in early spring, a pair after harvest and another in winter help keep the camp clean.
Cut tender shoots and trim the ends of dry to encourage uniform growth during the first year.
Used to form hedges, and as medicinal and aromatic plant.
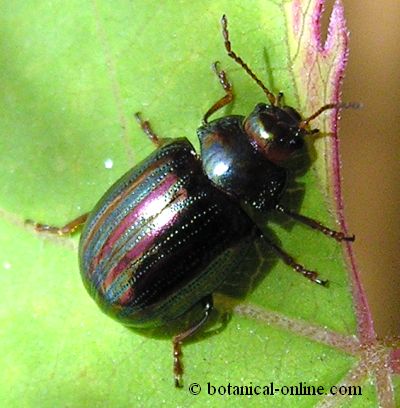

Rosemary beetle
Diseases of rosemary
– Alternaria: disease caused by the fungus Alternaria. It produces leaf spots with dark background and yellow borders. Eventually the death of leaves or leaf necrosis.
– Mildew: A disease caused by fungus (Oidium spp), most often strikes in summer.
Pests of rosemary
– Rosemary beetle: (Chrysolina americana) parasitic beetle that attacks stems and leaves. Often commonly found in rosemary.
– Red Spider
– Root and stem rot: caused by Phytophthora, that kills the plant. They often attack seedlings or young plants, especially in wet conditions or soils with poor drainage.
Harvesting and preservation of rosemary
One should not pick flowers or twigs during the first year. The collection of flowers and flowering tops is made from the second year of bloom between the months of April to June. It should be cut in dry days, never on rainy days or after rain.
Rosemary balsamic period is from April to June, when it has more essential oils. Better harvest in the morning.
Dry in the shade and kept in sealed containers and dry glasses, protected from light
![]() More information about plant cultivation.
More information about plant cultivation.