Contents
How to grow allspice
Description of Pimenta dioica
Common English name: allspice, Jamaica pepper, pepper, pepper Clover
Scientific name: Pimenta dioica L.
Family: Myrtaceae
Habitat: Allspice is part of the natural vegetation of tropical forest. It has been used since ancient times by the native peoples.
Description of allspice
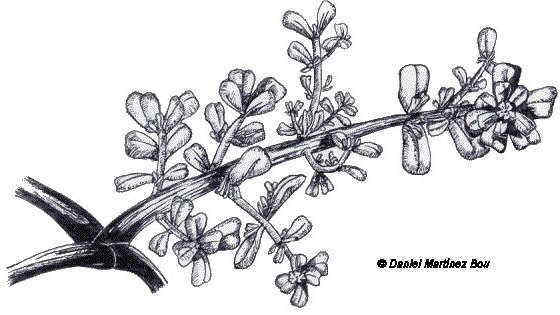
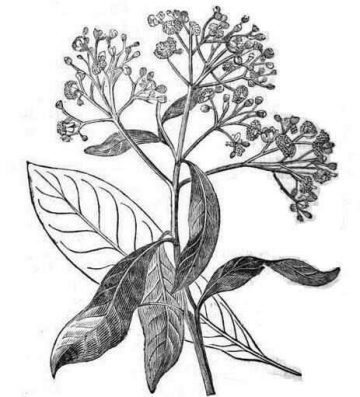
Allspice (Pimenta dioica) is a slow-growing perennial shrub between 6 and 9 (up to 12) meters high. Its stem has a grayish thin bark that easily comes off in long strips. Leaves large, opposite, petiolate, elliptic or oblong, bright green on its surface, pale on the underside, from 5.5 to 17 cm long by 2 to 6.5 cm wide. Inflorescence nin axillary panicles of 5 to 12 centimeters, where the flowers are arranged. Pale pink flowers, dioecious; between 3-4 millimeters in diameter. The fruits are small berries; globose, 7-8 mm in diameter. Inside they contain between 1-2 (up to 3) seeds, 4 millimeters in diameter.
* More information: Allspice characteristics in the listing below.
Climate and culture conditions
- It grows in heights between 500-1300 meters. Below 500 meters may be more susceptible to pests.
- In needs an nnual rainfall of 1000 to 4000mm.
- Its best average temperature is between 18 and 28 º C. Allspice has adapted to tropical climates with a certain level of moisture, so it does not grow well in regions with severe dry season (more than 3 months). It is killed by frost or drought.
- In can grow in calcareous soils, sandy loam, well drained, basic pH. It grows in poorly drained or flooded.
Sun: It can grow in sun, but, during the early years of the plant, it is recommended to grow it in partial shade.
| Allspice cultivation calendar | |
| Sowing | Between early September and November |
| Plant development | The first leaves appear in January. |
| Flowering | The flower panicles occur in March and flowering occurs in late spring, in May. |
| Fruits | After the third or fourth year. The fruits grow in June and are harvested in September and October. |
Propagation of allspice
Allspice is propagated by seeds.
– Extract the seeds of the fruit of the tree. To separate, the fruit should be soaked overnight in water, so the pulp is separated from the seeds. Once removed, dry the seeds in the shade.
– You may also reproduce it by grafting, although the new plants may be less productive.
Sowing allspice
Sow the seed immediately after drying, because, over time, it loses its germination capacity.
In nurseries, observe a minimum of 1 inch between seeds.
Seedling germination occurs approximately in 10 days.
Transplanting allspice
Transplant the plants in pots once true leaves appear. That’s when the plant measures about 5-8 inches tall. If you wait until the plant grow, it may not withstand the transplant.
At 10 months the plant has an approximate height of 25-40 inches and can be transplanted in the field. This is a shrub that can reach heights of 6-9 meters. You should keep distance between trees.
Although Pimenta dioica has bisexual flowers, there are cases when the designation dioica is well applied: there are flowering trees with few stamens and the pollen does not germinate, they are called female trees and they produce fruit.
There are male trees with sterile ovules that bear no fruit. In the cultivation of allspice, it is recommend planting male individuals to increase productivity of female trees.
PIMENTA DIOICA: HOW TO DISTINGUISH MALE AND FEMALE TREES The way to distinguish one kind or another tree is by means of the hypanthium shape of its flowers. The hypanthium is the receptacle of the flower, which is sunk in male trees around the pistil, while in the female trees it is flat. |
Irrigation of allspice: Pimenta dioica does not tolerate periods of drought, so watering should be periodic, avoiding soil to become swamped. It is also very important to plant it in well-drained soils.
Flowering of allspice
The plant blooms in mid-spring in the northern hemisphere.
Fruiting of allspice
- Reproducing by seed, allspice begins to bear fruit at 3-4 years. Best fruit productions happen when the tree is grown, approximately 30 years.
- Reproducing by budding, production begins in the third or fourth year.
Pimenta dioica is a slow-growing tree that can produce fruit but for over 100 years.
Maintenance of allspice
- You must maintain regular weed control.
- Apical pruning is recommended in the third year to encourage branching and fruiting.
- Fertilize every 6 months with nitrogen, organic phosphorus and potassium, to stimulate plant growth. Fertilization in spring and periodic watering will encourage further fruit production.
Pests and diseases
Below 500 meters, allspice is more susceptible to pests and diseases, such as:
– Mealybugs
– Rust
– Termites
![]() More information about allspice and other types of peppers
More information about allspice and other types of peppers