Contents
How to grow pepper
Characteristics of Piper nigrum
Common name: pepper, black pepper.
– German: Schwarzer Pfeffer.
– Portuguese and Galician: Pimenta do kingdom.
– French: poivre noir.- Catalan: Pebre, pebre negre.
– Hindi: Gulmirch.
– Chinese: Hu jiao.
– Sanskrit: Maricham.
Scientific name: Piper nigrum L.
Taxonomic synonym: Piper aromaticum Lam.
Family: Piperaceae
Habitat: tropical plant native to India, where it is estimated it was first domesticated. Piper nigrum is a species coming after its congener Piper longum.
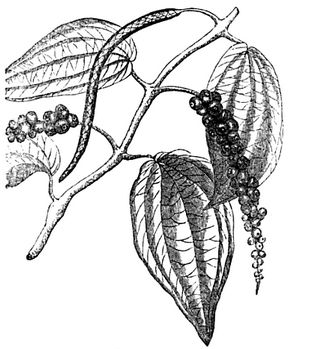
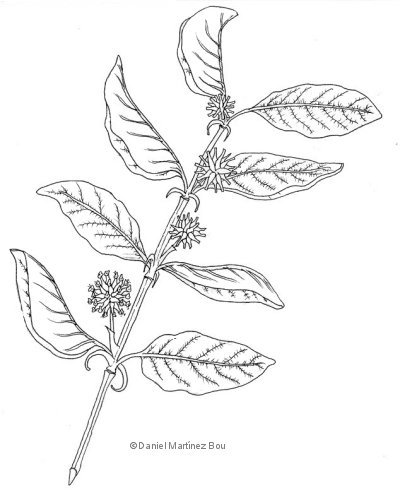
(Piper nigrum).
Black pepper description
Black pepper (Piper nigrum) is a perennial vine from tropical climates. This gnarled vine develops vertical growth stems and adventitious knotted roots. Leaves are petiolate, simple and alternate, leathery, oval, shiny dark green on the upper, and whitish green-on the underside. The inflorescence are flower spikes opposite to the leaves. Each one is composed of more than 70 tiny flowers. Flowers are greenish yellow and arranged in a spiral along the spike. The fruit is a drupe 4 to 6 mm in diameter, green, becoming yellow to red at maturity. The fruits are sessile and do not flow separately from the spike when they mature, but the fall along with fruiting branch.
*More information about black pepper characteristics.
Soil
- Acid soil or slightly acid with pH values between 5.5 and 6.5.
- Alluvial, loose, permeable and well drained.
- Black pepper does not tolerate calcareous, sandy or heavy soils, or those with a low permeability.
Climate
– Black pepper may develop between 0 and 1,000 meters high, being the more productive crops those that are below 500 meters above sea level.
– It requires a tropical, warm and humid climate with a fertile soil.
– Average temperature between 25 and 32 ° C.
– Humidity between 60 and 90%.
Irrigation
The cultivation of black pepper requires precise care, especially in terms of moisture and irrigation. Do not forget that this plant is native to the rain forest, where the relative humidity and rainfall are high.
- Keep the soil always moist and well drained.
- Avoid pooling.
- Water regularly throughout the year.
- Black pepper is not resistant to drought.
- Provide it something to climb
Black pepper is a vine or climbing plant. This means you need a tutor or simply a tree in which in can grasp to develop.
Propagation
Propagation by seed:
– Black pepper can be propagated by seed, though this is the least preferred method if you want to get a seed producer crop.
Propagation by cuttings:
This is the preferred method for obtaining a plant that produces seeds. Cutting consists of taking a cutting of the main branch of a productive pepper plant. Follow these steps:
– Cut the cutting at the base of a knot.
– Ensure that the cutting has not fruiting branches, but only the main stem.
– The cutting should have between 3 and 4 knots. It should be a stem with adventitious roots and a plant that less than five years old.
– Grow the cuttings in the shade or partial shade, in an environment with high humidity and keep the soil always moist, without puddles.
– We carefully recommend to plant it at a distance of 20 to 30 centimeters from the tutor and cover with coconut frond or other vegetation that provides it some shade.
– When the pepper grows between 60 and 80 centimeters, (when it has about 10 knots), we must prune it. Pruning should be done to encourage branching. Cut the top of the vine, leaving only 6-7 knots.
– When the plant regrowth, select the stronger stems and prune the less productive branches.
Propagation by layering
You can get a new plant when one of the main branches in its path with a new tutor.
Collecting the fruits
Pepper yields fruits from the second year and it is more productive in the fourth year.
![]() More information about black pepper and other types of peppers.
More information about black pepper and other types of peppers.