Contents
HOW TO GROW MUSTARD PLANTS
How to cultivate mustard
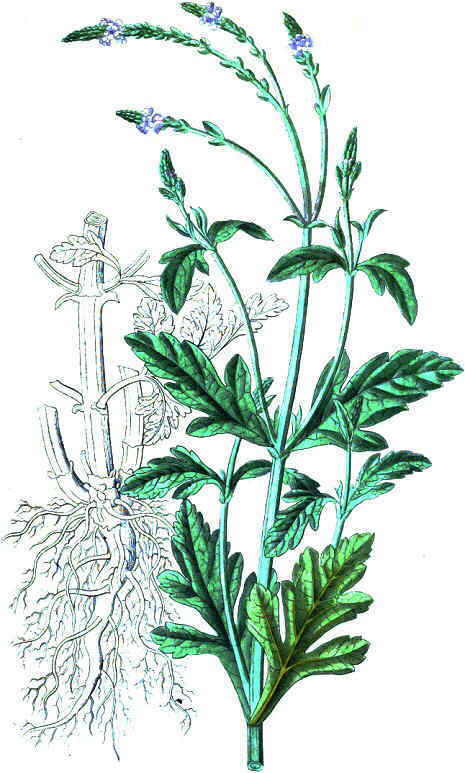
Different species of mustard (Sinapis alba, Brassica nigra, Brassica juncea) are a type of farming that are associated with horticultural crops and vines. Its cultivation in orchards and vineyards fields improves the physical conditions of the terrain, providing nitrogenous fertilizer to earth when used as “green manure”.
Mustard crop benefits
The main benefits of mustard are:
- Green manure consists on burying the plants before flowering takes place in order to fertilize the horticultural soil. This is possible in this type of plants because they have a very fast growth. This mass of green plants decomposes in a very short time (less than one year), and provides important minerals for future plants.
- Weed control: It is also used because these plants help to control weeds thanks to its sulfur content in its essential oils having fungicidal properties, which inhibits the germination of other seeds (unwanted herbs in productive crops). Other cruciferous plants also possess these properties.
- Fruit trees production and development: It has been shown that, covering the soil where crops of apple trees grow with mustard, increases the productivity and development of these fruit trees.

Illustration of two types of medicinal mustard: common mustard (Brassica nigra) (left), and white mustard (Sinapis alba) (right). The white mustard is distinguished by the villi in its stem and leaves
Mustard weather requirements
White mustard prefer cold weather, although it is able to adapt to all kinds of temperatures. It grows in full sun or semishade. low humidity and cool environment in summer. In irrigated fields, warm temperatures are favorable.
Resistant to frost: Height between 0 and 2,300 meters.
Mustard required soil
- Moist soil with a dry environment. Well-drained soil.
- It has a well developed branched root system that allow it to make good use of all soil nutrients.
- It prefers sandy calcareous soils, land of medium consistency, loamy or one that can retain moisture.
- Neutral and basic floor, with pH above 6.
- This plant adapts to almost all types of soil, although less than 5.4 pH adversely affects its development.
Propagation of white mustard
White mustard is mainly spread by seeds.
- When the cultivation is intended to obtain seeds, mustard should be sown in spring, between March and April to favorable weather during the months of seed development.
- When the crop is destined for animal fodder: planting can be done between February and September in cold areas . The southern regions can plant all year round, when conditions are favorable. If sown in mid August, mustard can provide fodder in late December.
Weed the ground to remove all weeds and remove dirt. You can sow broadcast, if it is intended to forage; or in furrows for grain crops. After planting, you should tamp the soil lightly. The seeds can take 8 to 10 days to germinate without light, at 20 ºC.
Mustard irrigation
When the plant has produced its first 4 leaves we carry out irrigation. Repeat watering if it has not rained the next 2 weeks. Water regularly without flooding the ground. Loose soil texture will provide the necessary moisture for plant development, dry and low humidity environments are favorable.
Flowering and fruiting
Flowering takes place in 6-8 weeks after planting. These flowers give off a pleasant scent and honey. Fruiting occurs about a month later.
Fertilizer and care
- Manure or compost: You can also use the press cake after having extracted the oil.
- Fertilizer: Fertilize directly with organic fertilizers P, K, N. For the growth of white mustard P and K (phosphorus and potassium, respectively) are important nutrients, and to a lesser extent, N (nitrogen). Mustard contains sulfur in its essential oils, so that this nutrient must be also provided
- If the crop goes to seed production, we can provide phosphates for a greater production. In the same case, weeding is necessary when the plants draw the first 4 leaves and, after two months, make another final weeding and thinning of the crop. Thus more seed production is obtained. In case of domestic cultivation, it does not need such a care.
- When the field is grown for fodder, it should be mowed before flowering. The leaves of the plant are considered toxic when they have developed flowers. Animals should not consume mustard in bloom or its fruit because flower and fruits contain toxic substances for cattle, called glucosinolates.
![]() More information on mustard.
More information on mustard.