Contents
How to grow maca
MACA GROWING TIPS
Common name: Peruvian ginseng, maca, Maka, pepperweed.
Scientific name: Lepidium meyenii Walpers.
Taxonomic Synonyms: Lepidium peruvianum G.Chacón.
Family: Brassicaceae, Cruciferae
Description of Maca
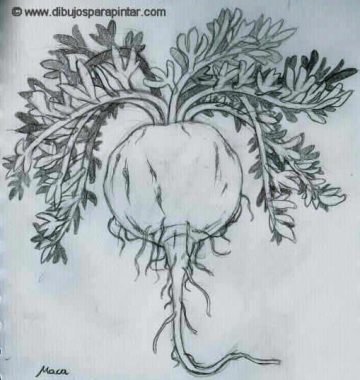
Maca (Lepidium meyenii) is a biennial herbaceous plant, between 10-20 (up 30) inches in height.
During the first year of planting, maca growing season remains for 8-9 months. During this period, it develops its underground part, consisting of a hypocotyl or underground reserve organ and its roots.
The hypocotyl is the edible part of the plant. It has a meaty texture and a rounded, globose, napiform and axonomorf form. It is integrated in the root tissue and ends in a thick central root, with lateral roots having numerous absorbent hairs.
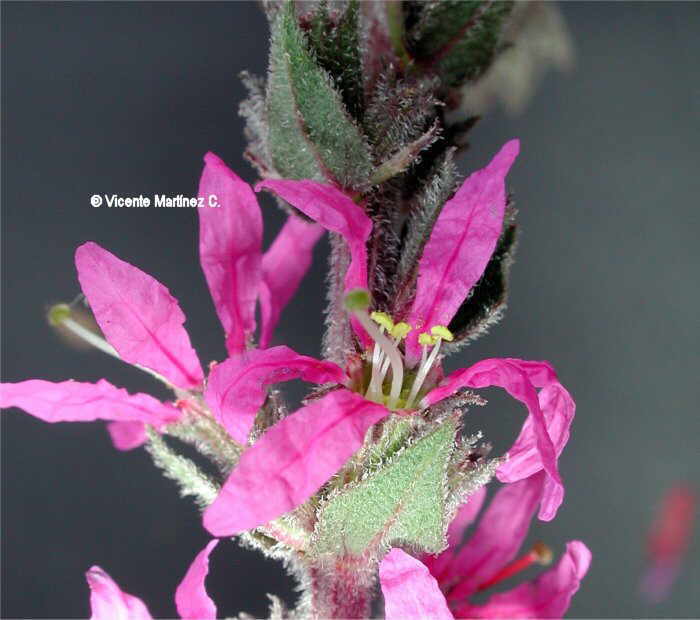
It grows as a rosette, stem short and barely visible due to the dense foliage. Leaves small, compound, with enlarged leaf sheath and composed limb, 6-9 centimeters long. Petiole long with the top flattened. The inflorescence is composed of axillary racemes with tiny flowers, hermaphrodite, actinomorphic and light green. The fruit of maca are two seed pods, separated by a partition that divides the fruit into two equal parts. The seeds are orange, yellow or brown.
Maca irrigation
– During the first months of its vegetative phase, the plant needs watering, so it must be planted in the rainy season.
– However, maca is a rainfed crop, and develops in the summer months when rainfall is lower.
Maca, flowering
Maca is a biennial plant that blooms in the summer of their second year of growth between October and November.
Maca, harvest
– Harvesting of Maca hypocotyls, which are intended both to food production as a dietary supplement, comes at the end of the vegetative stage of the plant, at 6-9 months after harvest. In the southern hemisphere, this happens between the months of May and mid July, before the development of aerial parts of the plant.
– The fruit of the plant has to be harvested in summer, between December and February the second year, when the plant is mature. This is known because no flower appear in the inflorescence and the fruit pods are at the basal part. When most foliage is yellow, it must be harvested. Harvesting should be done manually or with the help of a pickaxe.
Maca is a culture that impoverishes the soil, so that the land needs to rest for 10 years.
Maca, storage
– The seeds should be stored in a dry place until planting, which will be between September and November of the same year. Performance is usually about 0.4 to 0.5 kg. per square meter of crop.
– You should not pile up large amounts of maca hypocotyls because this increased temperature and promotes post-harvest losses.
Maca must be dried for 2-3 days until the leaves are dry, while the dry leaves must be removed to avoid contamination. Then, they have to be kept in plastic baskets or reseed in pools.
A month later, they have to be stored in bags in a cool and dry place with low humidity.
Maca, pests and diseases
Maca is resistant to virtually all types of pests and diseases.
– In its early crop, maca can be attacked by: Premnotrypes sp. Hymeli (Andean weevil), Agrotis sp. Feltia spp. Peronospora (downy mildew), Fusarium and Rhizoctonia.
– During storage or transport, it can be attacked by moths.
Maca, climate
Maca is a plant native to the Andes Mountains, which grows naturally in the ecological zone called Puna or High Andean tundra, located between 3,800 and 4,450 meters above the sea level.
The optimum temperatures for mark range between 4 ºC and 7 º C on average (About -10 º C night temperatures and 22 º C during the day)
Frost hardy to -20 º C. In case the plant can be burnt by ice, you should cover it at night.
Maca, soil
Maca grows in extreme acid soils characteristic of the Andes, with a pH below 5.
– Land sandy loam, without salinity. It can grow in rocky places. It requires fertilized soils with high organic matter, phosphorus and potassium.
– To prepare the ground, the soil should be loose, with plenty of organic matter.
Maca, sowing
– Maca seed is sown in late winter or early spring when frosts end and begin the rainy season. This happens between September and November in the southern hemisphere.
The seeds should be mixed with organic matter and planted at bowling. About 100g. seeds for 15 square meters are required. It takes 20-25 days to germinate.
Over the next 8-9 months, maca remains in a vegetative state until tuberous roots are fully developed. Typically, commercial varieties are collected at the end of the growing season before the plant has develop its aerial parts.
– From the ninth month on, maca starts to develop. At this stage, which can last between 4 and 6 months, the plant begins to produce seeds, which will be used to harvest the following year.
– Maca can also be reproduced by transplanting its tuberous roots once its has developed its aerial parts. It should be transplanted to a minimum distance of 70 cm.
| CALENDAR OF MACA CULTIVATION | |
| Preparing the soil | Acidic soils of pH below 5. Cold weather in winter with sun exposure. |
| Sowing | Maca planting should be done from late winter – early spring, when the rainy season begins. This happens between September and mid November in the southern hemisphere. |
| Vegetative phase of maca | Maca growing season remains underground for 8-9 months. During this period, it develop its hypocotyl and roots. The growing season embraces the months of September to November (planting), up from May to July. |
| Harvesting of hypocotyls | The commercial varieties of hypocotyls are harvested at this stage. This occurs between May and July. To obtain seeds, the plant should be cultivated until the second year. |
| Development of aerial plant parts | Between August and September of the second year, the plant develops its stem and leaves. At the end of this stage, its hypocotyls can be transplanted to reproduce the plant. These are planted in September and will follow the same cycle. |
| Flowering | Maca blooms in spring, October and November the second year. |
| Fructification | The fruit of maca takes place in summer, between December and February the second year. It is harvested in February. |
| Seed storage | Seed must be collected in late summer (February-March) and stored in a dry place until September, when planted again. |
![]() More information on maca.
More information on maca.