Contents
- 1 How to grow lettuce
- 1.1 Growing Lettuce: uses and varieties
- 1.2 Characteristics of lettuce (Lactuca sativa)
- 1.3 Growing lettuce: Environment and exposure
- 1.4 Soil type that lettuce requires
- 1.5 Propagation and care of lettuce
- 1.6 SCHEDULE OF LETTUCE GROWING
- 1.7 Watering lettuce crop
- 1.8 Lettuce care and fertilizer
- 1.9 Pests and diseases of lettuce
How to grow lettuce
Growing Lettuce: uses and varieties
Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) is grown for its leaves properties. It should be harvested when the plant presents a consistent manner to the touch without being overly harsh.
It is best planted at different times so as always to have it at hand. Among the many varieties of lettuce that exist, it should be distinguished these three ones:
- Romaine lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. Longifolia)
- Butterhead lettuce or Italian head lettuce (Lactuca sativa var capitata.): In this variety we have Batavia whose cultivation can be done al through the year or other varieties, such as Trocadero, May Queen or Summer Wonder.
- Curly lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. Crispa)
Characteristics of lettuce (Lactuca sativa)

Photo of lettuce in a nursery.
Herbaceous annual plant of the Compositae family. Very short stems. Bright green leaves without spines, entire below, with short petiole. Upper leaves sessile, more rounded and oval. Violet stained yellow flowers in panicles. Fruits with gray, as long as the rest prominent peak.
The origin of the lettuce is in Asia from the species Lactuca serriola. It is widely cultivated throughout the world, featuring many varieties. Sometimes it appears naturalized.
Growing lettuce: Environment and exposure
– Lettuce requires a sunny exposure. The summer varieties have to be planted in partial shade preferably.
– Lettuce likes a cold climate, although there are varieties that are well adapted to warm climates, provided they have moisture.
– It withstands temperatures well until -6. If excessive heat occurs too early, tasseling or leaf burn will appear. Excessive cold leads to colored leaves.
– It does not tolerate drought.
Soil type that lettuce requires
– Soil types: Light, well drained soil. Water must not remain stagnant as it could encourage plant rot or lead to microorganisms development.
– Lettuce prefers sandy loam soils with a pH between 6.5 and 7.5.
Propagation and care of lettuce
- Lettuce is propagated by seed from early spring to midsummer when the weather is cold. In hot climates from autumn to late spring. There are also varieties that can be planted in summer, as Wonder Summer.
- Planting is done in the nursery at a depth twice the diameter of the seed, that is to say, superficially because the seeds are very small (about 1 cm deep,since the deeper you do it, the lower the germination capacity will be)
- Lettuce will germinate at 612 days. After removing the excess of plants, when they have developed about 4 leaves, they should be transplanted to their final location. Keep a distance of 25cm between plants and 30 cm between rows.
- They will be ready for collection in a period ranging from 45 days for the earliest species and 90 for the later.
- It is recommended to plant a few seeds every 23 weeks, from early March to June, so as always to have salad leaves throughout the year.
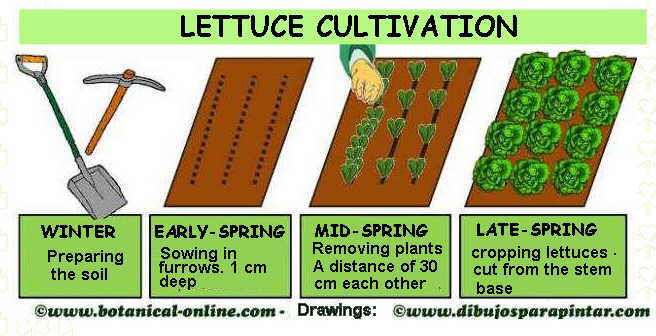
SCHEDULE OF LETTUCE GROWING
Explanatory sheet on growing lettuce
Watering lettuce crop

Lettuce crop
Watering should be regular, not abundant, most common in summer. In any case, it is better not to flood the earth to prevent fungus growth.
Lacking lettuce an extensive root system, soil must not be allowed to dry completely. To this end, lettuce plant should be placed at the top of a ridge to prevent the irrigation water to wet its leaves.
You can water through drip or by means of flood ridges.
The distance between rows should be placed about 50 cm, and the distance between plants should be about 30 cm.
Lettuce is very sensitive to salt water, that greatly reduces production.
Lettuce care and fertilizer
It is convenient to add manure and potassium for plant formation, and magnesium to have a very green appearance.
It is a crop that suffers from an excess of nitrogen that can burn its leaves.
It is advisable to clean the weeds and tie the inner leaves to become more white, making it more attractive to the buyer.
![]()
Pests and diseases of lettuce
The main diseases are:
- Downy mildew, produced by fungi during wetter times, mainly Bremia lactucaei species, causing the leaves to turn yellow. Although it can be treated with a specific product, it is best to choose the species resistant to it, to avoid having to deal with plants that must undergo an early consumption.
- Potato fungus, characterized by rotting in leaf petioles produce by fungus Pellicularia filamentosa.
- Mosaic virus, consisting of leaf spots, caused by viruses that live in the seeds or that are transmitted by aphids. The only solution is to choose the seed free of this disease.
The main pests are:
- Root aphids: They attack specimens planted in spring. It is produced by the aphid species Pemphigus bursarius that suck the sap, causing wilting of the specimen. Lettuce growing in infected places must be avoided until the soil has been disinfected or a cultivar resistant to this pest species has been chosen.
- Other pests: One should also be vigilant for slugs and aphids, which eat the leaves at night. To distinguish them, we must look for silver paths on lettuce leaves.
Similarly, we have to control larvae of moths that live in soil and feed on the roots. When they eat them, they produce an unexpected wilting of leaves.
![]() More information on lettuce.
More information on lettuce.