Contents
How to grow guava Psidium guajava
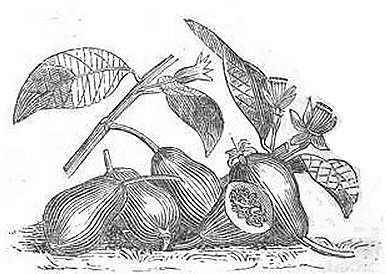
![]() Guava tree description: Guava (Psidium guajava) is an evergreen fruit tree of the Myrtaceae family, native to tropical America and Mesoamerica. In nontropical climates, it is a deciduous tree. The trunk is tilted, rather branched and between 3 and 20m. tall. The leaves are simple, with short petioles, oblong or elliptical, bright green. The oil-bearing leaves have glands that release a pleasant fragrance. The flowers are large, white petals, which give off a pleasant smell.
Guava tree description: Guava (Psidium guajava) is an evergreen fruit tree of the Myrtaceae family, native to tropical America and Mesoamerica. In nontropical climates, it is a deciduous tree. The trunk is tilted, rather branched and between 3 and 20m. tall. The leaves are simple, with short petioles, oblong or elliptical, bright green. The oil-bearing leaves have glands that release a pleasant fragrance. The flowers are large, white petals, which give off a pleasant smell.
The fruit is also called guava. It is a globose berry, sometimes ovoid, which is surely one of the best known within the Myrtaceae fruits. It belongs to the same family than allspice (Pimenta dioica), which is used in food as a type of pepper. Inside the fruit, seeds are numerous.
Climate
- Tropical fruit tree. It can adapt itself to the subtropics, although it prefers dry climates.
- Annual rainfall of 1,000 – 2,000 mm.
- It can grow between 0 and 1,500. altitude. In Ecuador it has come to grow up to 2.300m. Cultivars located below 100m. are more productive.
- The optimum temperature for growth is between 23 and 28 º C, with rain in the time of bud and bloom.
- It does not stand frost.
![]()
Soil
– Well-drained soils rich in organic matter.
– Tree with no special requirement, growing in almost any soil: acid and alkaline soils tolerated.
– Soil texture: sandy clay or silty
– The optimum pH for this culture is between 4.5 and 7 (to 9.4 in calcareous soils).
– It tolerates soil salinity.
Propagation
Sexual spread or seeding
– Recently extracted seeds have to be immersed in fresh water for 24 hours to accelerate germination.
– The seeds usually germinate between 2-3 weeks, but they may take up to 8 weeks.
– Once germinated, seedlings can be transplanted when they are between 5 and 20 cm.
– Transplant them in the definitive field place between the first and second years, with stake.
– If planting more than one copy, keep a minimum distance of 5m. between fruit trees.
Asexual propagation by layering on mound
– For adult trees with developed branches.
Asexual propagation by cuttings
– It is conducted in adult trees of 4-5 years old.
– Cut a new outbreak in a propagator and introduce it until rooted. Learn more.
![]()
Pruning
– Guava requires pruning to develop a strong structure and to increase fruit production.
– It is done after harvest during the three to four years after planting. It consists of blunting the sapling to 80cm from the soil to promote the development of major branches. Once it has developed them, we will prune the shoots of the secondary branches.
– After the fifth year, only prune branches that grow inward, twigs too close together or double twigs, dried or diseased branches.
![]()
Pests and diseases
- Mites: Harvest may be affected by mites. Specifically, in Egypt there are cultivars severely affected by Brevipalpus californicus.
- Caterpillars: Genus Indarbella spp. are particularly dangerous for the cultivation of this tree. They feed on the tree bark. This genus is found in India.
- Guava whitefly (Trialeurodes floridensis) Important pest for Mexican cultivars.
- Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Especially Anthonomus irroratus, a type of beetle that makes holes in the fruit.
- Guava fruit worm (Argyresthia eugeniella): It attacks the fruits when they have not yet matured.
- Fruit lies
![]() More information on guava.
More information on guava.








