Contents
- 1 How to grow fenugreek?
- 1.1 Characteristics of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
- 1.2 Fenugreek climate requirements
- 1.3 Fenugreek soil
- 1.4 Fenugreek irrigation
- 1.5 Fenugreek propagation
- 1.6 Fenugreek flowering
- 1.7 Fenugreek harvest
- 1.8 Fenugreek fertilizer
- 1.9 Fenugreek diseases and pests
- 1.10 Fenugreek use
- 1.11 Medicinal properties and applications of fenugreek
How to grow fenugreek?
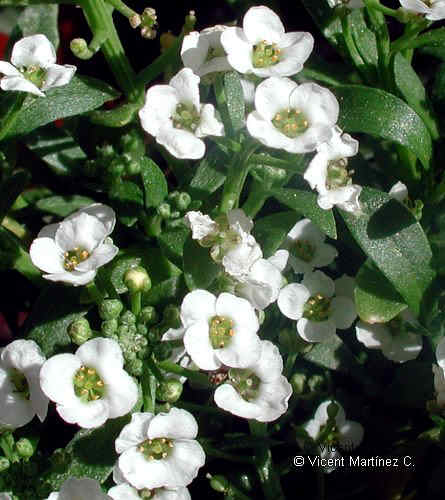
 Characteristics of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
Characteristics of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
Fenugreek, Greek hay, bird’s foot o Greek-clover (Trigonella foenum – graecum L.) is a leguminous plant, belonging to the Papilionaceae family, which grows in the Mediterranean region, the Middle East, India, China, Africa North and the United States.
The word fenugreek derives from foenum- graecum, which means ” Greek hay “. It was given this name because of the strong smell of this plant, reminiscent of hay, since it is intensively cultivated in the Mediterranean region.
Botanically, fenugreek is an annual herbaceous plant between 20 and 50cm high. (sometimes up to 100cm.). Its stem is erect, branched, grooved and with little pubescence.
The leaves are compound, petiolate, oblong leaflets formed by three kills reminding those of alfalfa. White or yellow flowers, isolated or arranged in pairs.
Fenugreek fruits are narrow and elongated pods. They contain 10 to 20 seeds, tiny yellow, quadrangular, with a groove in the central part.

 Fenugreek climate requirements
Fenugreek climate requirements
- Plant adapted to rainy climates or those provided with irrigation. It is favorable to temperate climates such as those found in the Mediterranean region, or in the tropics.
- It requires a warm climate with mild temperatures for a good seed production (between 8 and 27 º C)
- It grows well in full sun.
- Sow it in places sheltered from the wind.
- Resistant to frost and temperatures down to -5 º C. However, low temperatures during planting causes not all seeds to germinate.
| Characteristics of fenugreek cultivation | |
| Type of crop | Annual |
| Crop cycle | 90-100 days |
| Height of adult plant | 20-50 ccm. |
| Germination time | 4-6 days |
| Percentage of seed germination | 90-95 % |
| Flowering | 40-60 days |
| Pods per plant | 10-15 pods |
| Number of seeds per pod | 10-13 seeds |
| Seeds in 1 gram | 50-54 seeds |
 Fenugreek soil
Fenugreek soil
– Soil with medium consistency, clayey-calcareous, well drained.
– Neutral pH, slightly acidic or alkaline, between 5.3 and 8.2
– This leguminous plant has a symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria. This type of bacteria are characterized by forming nodules on the roots of fenugreek and fix atmospheric nitrogen.
– This nitrogen is used by the plant to grow, but it can also be used by other plants growing around increasing the growth of other crops and improving soil quality.
– For this reason, it is recommended not to remove the roots of fenugreek at harvest, but only remove the aerial parts of the plant, leaving the roots in the soil to release nitrogen. This is one of the principles of crop rotation.
– It does not tolerate clayey soils, neither too wet.
 Fenugreek irrigation
Fenugreek irrigation
- Fenugreek cultivation requires a lot of water and well-drained soils.
- Keep the soil moist without stagnation.
- It is recommended slow drip irrigation instead of surface irrigation. Water in drip irrigation penetrates deeper in the soil that in the surface irrigation method.
 Fenugreek propagation
Fenugreek propagation
– Fenugreek is propagated by seeds.
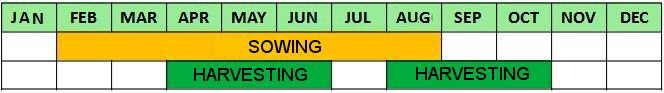
– The seeds can germinate in early spring, from April to May; or in autumn, from September to October.
– To make seeds germinate better, soak them in warm water for 6-12 hours, low light and average temperature of 20 º C.
– Plant them preferably in spring, in situ. Keep the soil moist for the plant to germinate. Do not let water to become stagnant.
– Prepare the breeding soil: plow the soil at least 1 month before planting adding fertilizer.
– Fenugreek is a very fast growing plant, its fruits are collected at 5 months after planting. It allows two crops a year.
– keep the soil free of weeds.
– In crops for animals, you should keep in mind that fall plantings produce less forage.
– Crops for seed should be provided with a generous dose of phosphates.
 Fenugreek flowering
Fenugreek flowering
Fenugreek flowering in optimal conditions occurs approximately 40 days after planting.
 Fenugreek harvest
Fenugreek harvest
– This crop is harvested when the plant is in bloom.
– The fruit is harvested when the pods have reached maturity, and many of them have acquired a curved shape resembling a sickle.
– Drying of seeds is done in full sun and in a well ventilated area.
 Fenugreek fertilizer
Fenugreek fertilizer
– Fertilize the soil with fermented manure.
– Being a legume, it does not require nitrogen fertilizers because it grows with atmospheric nitrogen fixing bacteria.
– Phosphates accelerate flowering and benefit grain production. Scientific studies suggest that this fertilizer reduces crop height.
 Fenugreek diseases and pests
Fenugreek diseases and pests
– The most serious disease of this crop is produced by the fungus Sclerotinia trifoliorum, which causes rotting of leguminous plants.
It is manifested by spots on the leaves, which in the warmer months are spread throughout the plant, destroying the leaves and even resulting in roots rot. It can be treated with antibiotics, although, if the disease is far advanced, this plant should be removed.
– When the disease has devastated this crop, legumes should not be planted in the same place for over the next 5 years. This fungus is persistent, so it can lie dormant in the soil for years and could affect subsequent legume crops.
 Fenugreek use
Fenugreek use
– Human consumption fenugreek: Fenugreek is a plant widely used in human nutrition and a herbal medicine.
– It is a very widespread in India, China, Thailand and North Africa (Morocco) (see Recipes with Fenugreek in the listing below)
– It is a highly valued aromatic condiment in the East, taking part, for example, in the popular curry mixture (see Fenugreek in the kitchen).
– Due to the amount of mucilaginous fiber, fenugreek is used as a thickener in sauces and stews.
– It has a yellow pigment used as a colorant in some rice and soup preparations.
– From its essential oil. aromatic components are extracted to flavor different foods and drinks, such as cheese, pickles, syrups and liqueurs.
– Fenugreek intended for animal fodder:
– It has a strong odor that makes it not very palatable to animals.
– It should be consumed in small quantities because it can pass an unpleasant taste to meat and milk.
– It can help increase cattle weight.
 Medicinal properties and applications of fenugreek
Medicinal properties and applications of fenugreek
Fenugreek is a plant widely used for its medicinal properties. The following table summarizes the applications of this grain in phytotherapy (see all Fenugreek Medicinal Properties):
| Properties of Fenugreek | Medicinal uses of Fenugreek |
| – Aromatic – Stomachic – Cardioprotective – Laxative – Steroidal – Rich in choline – Anti-inflammatory – Vasodilator | – Appetite – Restorative – Increase weight – Anorexia – Lack of appetite – Anemia – Tonic – Digestive ulcers – Menopause – Dysmenorrhea or menstrual pain – Erectile dysfunction – Diabetes – Increase of milk production (galactogogue) – Alzheimer’s disease – Arthritis (topical) – Osteoarthritis (topical) – Gout (topical) – Alopecia (topical) – Hemorrhoids (topical) |
*Related information:
Fenugreek uses and preparations
![]() More information on fenugreek.
More information on fenugreek.