How to grow cucumbers
Description of the cucumber plant

Cucumber is a creeping annual herbaceous subtropical plant of the Cucurbitaceae family, relative of pumpkin, zucchini, melons or watermelons.
Its stems are covered with hairs. The stem is very branched. It can grow forming large extensions on the ground or climb up when having a support by means of tendrils
Cucumber leaves are also hairy, simple, alternate, cordiform.
It has shallow roots, that prolong to 25 – 30 cm. of soil depth.
This plant is grown for its fruits, the cucumbers, which are elongated, fleshy, with rough, green skin and numerous seeds inside.
What are cucumber fruits good for?
Nutritionally, the fruits are rich in water and contain very few calories. They have high doses of potassium and vitamin E, which make them very diuretic and suitable for treating skin conditions.
Varieties of cucumbers
There are many varieties, but three types of cucumbers are distinguished:
- French type: They are one of the most consumed varieties in Europe. Elongated fruits of about 20 cm. with dark green skin.
- Spanish type: Cucumbers of more flattened size and thick, of 15 cm. long. Greenish skin with yellow streaks.
- Dutch type: Cucumbers thinner and much longer, 25 cm. Pointy shape.
Cucumber cultivation tips
- Cucumbers are a summer crop, as so, they do not tolerate cold.
- Locate in full sun.
- They need aeration and soil drainage.
- Fertile soils and rich in organic matter.
- Soil reaction: pH between 6.5 and 7.
- High humidity and temperature.
- Preparation of the soil: At least 1 month before planting, weeding the ground (control of weeds) and plowing of 30 – 50 cm. ground.
- Association of crops: Cucumbers can be associated with corn, beans, carrots, peas or beets.
- Rotation of cultivation: It is not recommended to plant cucumber in the same field for more than 2 years.
How to plant cucumbers in a greenhouse
- Get the seeds in a gardening store.
- Sow them at the end of February, when the frosts have ended. To do this, place the seeds on a moist cotton or paper towel for 2-3 days until they germinate. Cover them and move them away from heat and light so moisture does not evaporate.
- When the seeds germinate, they must be transplanted in seedbeds or pots. Protect them from the cold.
- Transplant them to the final place at the end of March, preferably in the greenhouse.
- Maintain a separation between plants of at least 50 cm.

Cucumber care in a green house
Staking with canes or sticks
The plant needs a bamboo cane or a stick to act as support. As the plant develops, the main stem must be tied tied with twine in the cane.
By tying the plant to a support, it improves the aeration of the plant, the use of sunlight and prevents some diseases and avoids field work.
Cucumbers are born from the armpits of the leaves, directly from the stem.
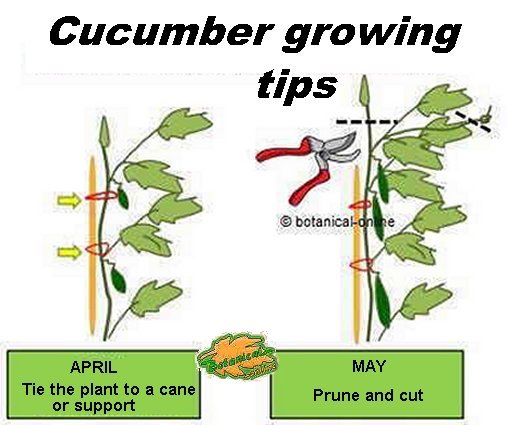
Pruning and removing old parts
- Cut the plant to slow down its development when it is sufficiently high or when it touches the roof of the greenhouse. This will favor the development of the fruits.
- Prune the branches of more than two leaves so that fruits are not born from the secondary branches.
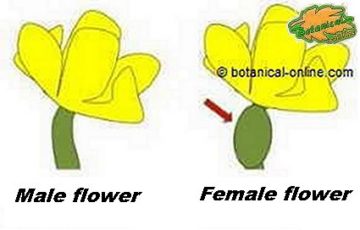
- Remove the male flowers, because when fecundating the female flowers, they can produce cucumbers with a bitter taste.
- Avoid overloading the fruit plant, since, in this case, it will produce cucumbers of smaller size.
- Humidity and temperature conditions must be high. The plant develops quickly in greenhouse.
Cucumbers harvest
Cucumbers are plants that grow quite fast. If they are sown at the end of February, the harvest can be made from May approximately (about 45 days after germination).
Harvest must be done with a clean and sharp knife, being careful not to break the fruits. The fruits must be picked almost mature, because if they are left too long in the plant they become fibrous and bitter.
Diseases and pests of cucumbers
- Cucumber mosaic virus: Causing the speckling of leaves and leading the plant to perish.
- Mildew (common disease) and powdery mildew: Powder coating that covers the leaves and stems.
- Odium usually appears at the end of summer with the temperature drop.
- Aphids
- Monilia fungi: It affects the roots
- Red spider
- White fly
- Snails and slugs
![]() More information on cucumber
More information on cucumber