Contents
How to grow greater celandine

 Greater celandine description
Greater celandine description
Celandine (Chelidonium majus) is a plant of the family of poppies (Papaveraceae), the same family than poppy. In English, it is called greater celandine or swallowwort.
Greater celandine is an herbaceous perennial or biennial plant, measuring between 30 and 100cm. tall.
Stem erect, branched and knotted, hairy at the base, growing from a thickened rhizome..
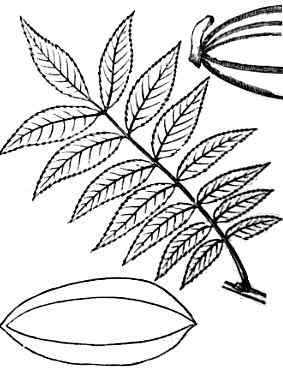
Alternate compound leaves, deeply divided, green above, glaucous on the underside. Toothed margins. The upper leaves are sessile, basal ones petioled.
Actinomorphic flowers, pedicellated, with two deciduous sepals and four petals arranged in a cross, yellow, 1.2 to 1.8 cm. in diameter. It blooms from May to October.
The fruit is a capsule in silique, thin, cylindrical, 3-4cm. length, dehiscent (which opens at maturity). Inside the the fruit we can see the numerous tiny seeds.
 Suitable climate for celandine
Suitable climate for celandine
- This plant is accustomed to cold and wet climates, native from Central and Northern Europe and the Caucasus region.
- It is frost resistant (tolerant to 15 ºC).
- It prefers cool, shady sites. Plant in shade or partial shade.
- It can also grow in dry and sunny places.
- When the weather is favorable, it is usually a fast growing plant.
- It can leave from 0 to 1.600msm.
 Suitable soil for celandine
Suitable soil for celandine
- Moderately wet or dry.
- Good drainage to prevent waterlogging.
- Calcareous soil. It tolerates a pH from 4.5 to 7.5. Better soil: Nitrophilous soils, rich in organic matter.
- Due to its rhizomatous growth, this plant can become invasive.
 Suitable irrigation for celandine
Suitable irrigation for celandine
- Maintain soil moist. It needs regular watering.
- It does not tolerate drought.
 How to propagate celandine
How to propagate celandine
Celandine can be reproduced by seed or by division of clumps.
Reproduction by seed
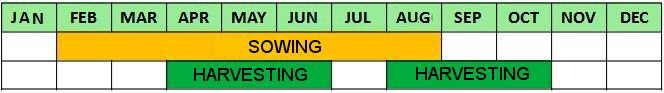
- Sow it in the nursery, in a warm bed, in February-March.
- Transplantation can be performed in April.
Reproduction by division of clumps
- This method of reproduction involves transplanting a piece of the plant, a mature plant (three years or more) from its rhizome.
- In autumn or mid February, divide a clump of a plant from its rhizome. For this we can unearth the adult plant, and divide it into as many rhizomes as it has developed.
- From each adult plant, we can separate 57 rhizomes, which become new plants after transplanting them.
 Use of greater celandine
Use of greater celandine
- Aerial parts: the harvest is done during flowering, when it has better medicinal components.
The leaves harvested in the morning have more alkaloids than those set out in the late afternoon.
- Leaves: We can use the flower, the leaves or stem. From the flower, we can make a cream for calluses. The leaves and stems decoction is used to treat different ailments: herpes, gingivitis, warts, etc.
Attention!!: Used Internally, it is a very toxic plant.
– Cream of celandine for corns.
![]() More information on greater celandine.
More information on greater celandine.

 Suitable irrigation for celandine
Suitable irrigation for celandine