Contents
Growing cauliflowers
How to grow cauliflowers
Characteristics of cauliflowers
Cauliflowers are characterized mainly by their hearts, consisting of an inflorescence composed of numerous undeveloped flowers that gather around a central axis.
This inflorescence is surrounded by a series of gray-green leaves, wrinkled to the margins, with whitish large nerves.
The leaves protect them and prevent the passage of the sun into the heart. This means that, during this phase of growth, they present whitish hearts caused by the lack of chlorophyll, although we can also find greenish or purple varieties.
If left to mature, the plant produces an inflorescence that acquires a height of 100 cm where the real flowers develop.

Cauliflower. Irrigation and moisture
Cauliflowers need ample moisture, especially after the transplant when the plants are in the growing season. A weekly watering may be sufficient in some areas that retain water well. In warmer climates or in more porous soils watering could be needed every two days.
Cauliflower do not stand waterlogged soils, so they are planted on ridges, in order that when the bottom of the furrow is flooded, the plant is kept moist but not wet at the top. This type of cultivation is essential when planted in clayey soil, very suitable for this crop, provided that we consider the latter advice.
![]()
Cauliflowers. Temperature and exposure
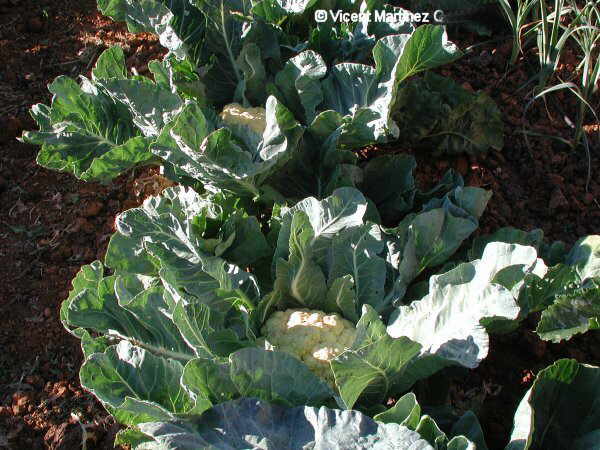

Photo of cauliflower
Cauliflowers can not stand very cold or very hot climates. It is a plant that prefers a temperate climate with temperatures between 15 and 20 ° C.
In climates with frost or strong winds they should be protected not to freeze in cold weather or not to glean when the temperature is very high.
During the growing season, cauliflower inflorescences are affected by direct sunlight in hot weather and frost in cold climates. Similarly, when mature, they should be harvested soon as they can be affected by numerous factors (frost, wind, heat, etc) and rot easily or turn brown, making it impossible to sell them.
![]()
Cauliflowers. Time of planting and cultivation
According to the harvesting period, there are essentially the following types of cauliflower:
- Spring cauliflowers: These are very resistant to frost. They mature in spring. The harvest takes place during the spring or early summer. These varieties require cold weather to produce high quality cauliflowers. Among these there are very well-known varieties, such as, for example, Winter Walcheren, the Giant of Naples or Snowbred.
- Summer and autumn cauliflowers: They are those that are collected during the summer or fall. These include, for example, Catalina or the Presto that may be available on the market from September to November. The planting of this type of cauliflowers is done between the months of May or June. Unlike the earlier variety, they do not require a cold climate, since they are perfectly suited to temperate climates.
- Winter cauliflowers: They are those that are collected during the winter. Within this group we can point out early varieties, such as kangaroo or the turkey on Christmas, that are collected between the months of November and December; midseason varieties, such as Canberra or Primus, that are collected between the months of January and February; and late varieties, such as San Jose, that is collected in March.
- Most popular cauliflowers are those that have a whitish color, which is not to say that they are the most suitable ones. The white color of this type of cauliflower is a response to a lack of chlorophyll which may make them more visually appealing but with a lower content of vitamin C, flavonoids and chlorophyll and therefore with less antioxidant properties.
- Depending on the color of the inflorescence, there are essentially the following types of cauliflower:
- White cauliflowers: They are the best known ones. They are those with white inflorescences, because they are grown covering them with their green leaves so as to keep them out from the sun.
- Green cauliflowers: When they are grown with the inflorescence not covered, because of the action of sunlight, their color becomes green.
- Purple cauliflower: Very rich in some dyes called anthocyanins that give them very interesting properties.
![]()
How to plant, maintain and collect cauliflowers?
Cauliflowers are planted by seed in the nursery. The seeds are drilled to a depth of 1 cm and have to be transplanted after about four weeks when they have a foot or so tall. Enter in the ridge at a distance of two feet between a plant and another, and about 60 cm from the opposite ridge.
The growing season depends on the variety chosen, but it stands for most varieties from May to June. Transplantation generally takes place from July to August. The very early varieties, designed to be collected in summer, have to be sown in winter and transplanted in spring.
The main tasks of maintenance will include a superficial weeding to remove weeds, a much greener and healthier method than using herbicides. Digging provides the necessary oxygen to the ground.
In drier areas the use of dry matter can provide a cushion necessary to prevent moisture loss. When cauliflowers begin to swell, they should be protected from the elements by means of bending two or three leaves above them.
Cauliflowers should be collected when they are well developed and they feel consistent to touch. We should not wait for these to open.
![]()
Cauliflowers. Types of soil and fertilizers
Cauliflowers grow well in slightly acidic or neutral soil, rather than alkaline ones. They require a pH between 6 and 7.5. They prefer well-worked soil, which have been developed soundly till 35 or 40 cm deep. A clay soil requires to be worked prior to planting. In this case, we should add mature manure or compost because it is a type of crop that needs lots of nitrogen. Nitrogen can be added six weeks after transplantation if necessary.
Cauliflower should be planted in areas where no other types of cabbages (Cruciferous) have been planted before. In addition, we will not plant them in the same soil for two or three years. They can be combined with other vegetables such as peas or beans.
![]() More information on cauliflower.
More information on cauliflower.