Contents [show]
How to grow carrots
 Characteristics of carrots (Daucus carota)
Characteristics of carrots (Daucus carota)
Carrots (Daucus carota) are biennial plants of the Umbelliferae family, the same botanical family to which celery, fennel and cumin belong. These plants are grown for their edible roots.
During the first year of the plant, it develops a thick root with a few leaves in a rosette. The root is a storage organ rich in carbohydrates, which allow the plant to withstand the cold winter temperatures. It presents numerous lateral rootlets that have the function of absorbing nutrients from the soil.
In the second year, plant flowering is induced by low winter temperatures. The carrot develops a short flower stalk, from which arise the inflorescences. The plant inflorescence is umbel-shaped, with very distinctive white flowers. The fruit is an achene.
When are carrots harvested?
Generally carrots are harvested during the first year to get its root. Quite hardy plants, they are sown throughout most of the year, and there are different varieties depending on the size and thickness of the root.
Some carrots produce bunches of leaves used in salads or omelets.
 Carrot climate
Carrot climate

- Ideal climate: Carrots are plants of cold and temperate climates. They resist frost down to – 5 ºC.
- Optimum temperature: 16-18 º C.
- Ideal place: Put them in a sunny spot (do not grow carrots in the shade).
Carrot soil requirements
- Carrots are a nutrient-demanding crop, so that, after its cultivation, it is recommended crop rotation. Carrot planting should NOT be repeated in the same soil sooner than 34 years after planting because they exhaust the soil.
- Soil type: well drained, preferably moist soil, clay-limestone, rich in organic matter.
- Carrots can not develop their roots in rocky or very compact soils because they do not grow properly, they get short-sized, deformed and become woody.
- Good drainage is important since the roots become rot if waterlogged. This happens sometimes when there are many spring rains.
- No carrots should be planted in fields fertilized with manure, at least 2 years. DO NO FERTILIZE WITH MANURE!
- soil pH: between 6.5 and 7.5
Calendar of carrot cultivation
Carrot garden tasks
Carrots: Cultivation tasks
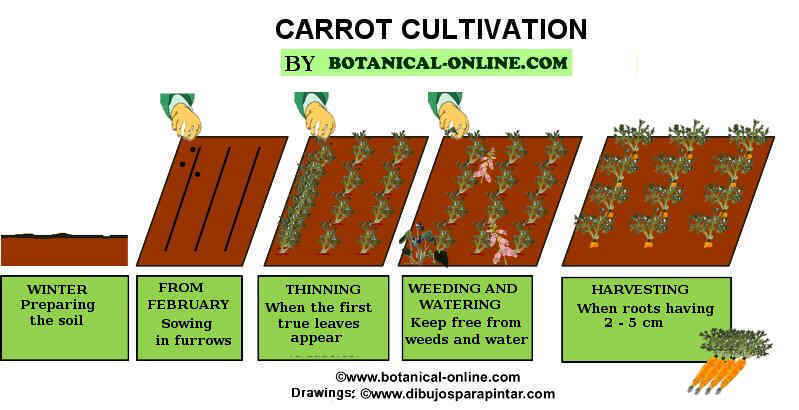
- Prepare the ground one month before planting: deep plowing and fertilizing.
- Plant seeds in furrows 2cm. deep. Cover lightly with soil. Between rows it must be a minimum distance of 15cm.
- Germination takes place in 1015 days.
- Perform a clearing a few weeks after germination, when they start out the first true leaves. You must maintain a separation of 8cm between plants, but this may vary depending on the variety.
- From planting to harvest there is usually a time period of about 90 days, although there is a shorter cycle that only needs 75 days.
- Carrots need little care, mainly weeding: You must conduct a periodic weed control as carrots compete with weeds.
- No special watering needs. You must check that the ground is not dry and water it more often during times of more drought and heat.
- Make sure the roots not to be exposed to the sun or protruding from the ground, as this causes the root to turn green and bitter. Cover with soil.
- Carrots grown with little water become more woody. Avoid little watering and increase the frequency during dry seasons.
- If, on the other hand, soil is watered too much, this will promote leaf growth to the detriment of the root.
Intercropping
Compatible plants growing with carrots are:
– Onion
– Lettuce
– Peas
– Leek
– Radishes
– Chard
– Cabbage
– Potatoes
Plants growing incompatible with carrots
– Celery
– Fennel
– Parsley
– Celeriac
Collecting carrots
Harvesting is done before the carrots are fully developed and become woody, when they have an approximate a root diameter of 2 to 5cm. (depending on the variety). Generally this happens at 3 months after planting.
Manual harvesting is done with a fork stuck deep in the ground, and which serves to withdraw the ground vegetables.
Carrots must be thoroughly washed before eating, and the lateral rootlets remove.
Carrots quality
The quality of the carrot is determined by its firmness, consistency and vivid orange color.
Carrots that are branched or deformed are not bad for health, but they are considered unsuitable for commercial sale. Two of the main reasons for being deformed are shallow or rocky soils.
The presence of green color in the heart of the root indicates that it has been exposed to the sun. carrots roots should not be bitter and sweet taste should prevail.
 Carrots flowering
Carrots flowering
Carrots are in bloom in the second year of cultivation, from June to August.
 Carrots diseases and pests
Carrots diseases and pests
- Carrot fly (Psila rosae) is a type of fly whose larvae cause extensive damage to the tuber, mainly affecting carrots, celery and parsnips. They excavate galleries at the root and tuber branches. The tubers do not grow too much or become fibrous. Outwardly cause staining and discoloration of the leaves.
- Alternaria.
- Cercospora.
- Powdery mildew.
- Botrytis.
![]() More information about carrots.
More information about carrots.

 Carrot climate
Carrot climate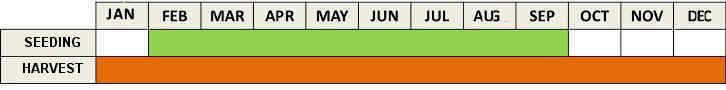
 Carrots flowering
Carrots flowering






